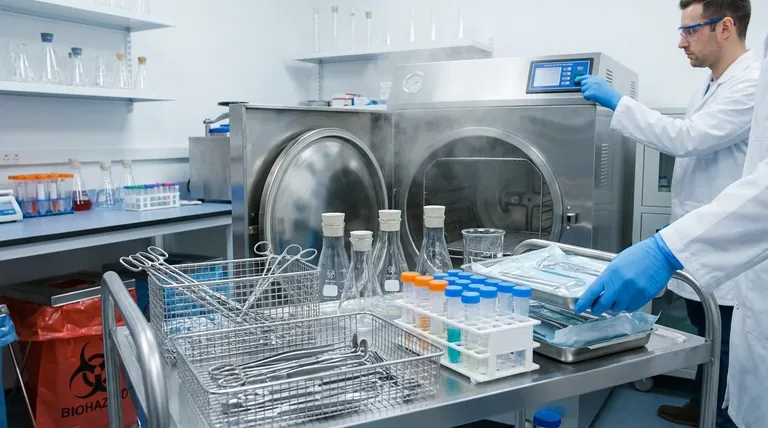
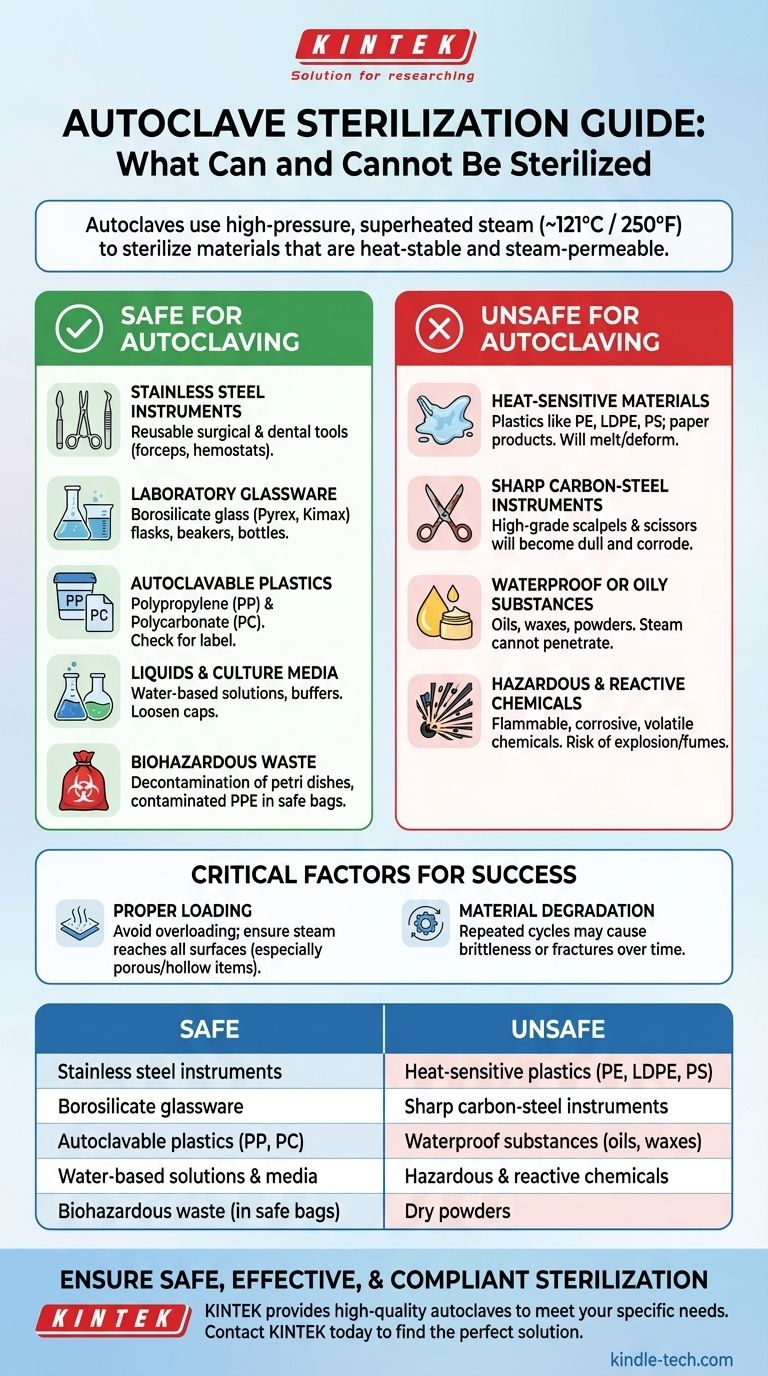
An autoclave is the gold standard for sterilizing a specific range of materials that can withstand high-pressure, superheated steam. It is exceptionally effective for sterilizing surgical instruments, laboratory glassware, specific types of plastics, water-based solutions, and biohazardous waste. The key determinant is a material's ability to tolerate temperatures around 121°C (250°F) and allow for complete steam penetration.
The core principle of autoclaving is not about the item itself, but its material composition. For sterilization to be successful, an object must be both heat-stable and permeable to steam, as moisture is the critical agent for destroying microorganisms.
How Autoclave Sterilization Works
An autoclave does not sterilize with dry heat. Instead, it creates an environment of high-pressure steam that is significantly hotter than boiling water.
This pressurized steam forces out cooler air and makes direct contact with all surfaces of the items inside. The combination of intense heat and moisture rapidly and irreversibly denatures the essential proteins and enzymes within microorganisms, rendering them sterile.
What Can Be Safely Autoclaved?
The following materials are generally considered safe for autoclave sterilization, assuming proper loading procedures are followed.
Stainless Steel Surgical and Dental Instruments
Most reusable metal instruments, such as forceps, hemostats, and retractors, are made of stainless steel and are designed specifically for autoclave sterilization.
Laboratory Glassware
Borosilicate glassware, such as products branded Pyrex or Kimax, is highly resistant to thermal shock and is routinely sterilized in an autoclave. This includes flasks, beakers, and bottles.
Autoclavable Plastics
Only specific types of plastics can survive autoclaving. Look for materials like polypropylene (PP) and polycarbonate (PC). Always check for a manufacturer's label or symbol indicating the item is "autoclavable."
Liquids and Culture Media
Aqueous (water-based) solutions, buffers, and microbiological culture media are primary candidates for autoclaving. The caps on containers must be loosened to prevent pressure from building up and causing an explosion.
Biohazardous Waste
The autoclave is a critical tool for decontaminating waste such as used petri dishes, culture tubes, and contaminated personal protective equipment (PPE) before disposal. This must be done in designated autoclave-safe biohazard bags.
What Must NEVER Be Autoclaved?
Attempting to sterilize the wrong materials can destroy the item, damage the autoclave, or create a significant safety hazard.
Heat-Sensitive Materials
Any item that melts or deforms at high temperatures cannot be autoclaved. This includes most common plastics like polyethylene (PE), low-density polyethylene (LDPE), and polystyrene (PS). Paper products will also degrade.
Sharp Carbon-Steel Instruments
While stainless steel is safe, high-grade carbon steel scalpels and scissors will become dull and corrode under the high heat and moisture of an autoclave.
Waterproof or Oily Substances
Steam cannot penetrate oils, waxes (paraffin), or powders. Autoclaving these materials will not result in sterilization because the sterilizing agent (moisture) cannot make contact.
Hazardous and Reactive Chemicals
Never autoclave flammable, corrosive, or volatile chemicals such as solvents, bleach, or radioactive materials. The high heat and pressure can cause dangerous reactions, release toxic fumes, or lead to an explosion.
Understanding the Trade-offs and Critical Factors
Achieving true sterility requires more than just placing an approved item in the chamber.
The Risk of Incomplete Sterilization
If an autoclave is overloaded or items are packed too tightly, "air pockets" can form that prevent steam from reaching every surface. This is particularly true for porous items like textiles or hollow instruments unless you are using a specialized Class B autoclave with a vacuum cycle.
The Degradation of Materials
Even approved materials have a lifespan. Repeated autoclaving can eventually cause plastics to become brittle or glassware to develop stress fractures. Furthermore, some heat-sensitive compounds within a solution, like certain proteins or antibiotics, may degrade and lose their effectiveness.
The Importance of Proper Protocol
Effective sterilization depends on achieving the correct temperature for the required duration. This requires regular calibration of the autoclave and the use of sterilization indicators (like autoclave tape or biological indicators) to verify that conditions for sterility were met within each load.
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
Use the material's properties and your sterilization goal to guide your decision.
- If your primary focus is robust tools and glassware: The autoclave is your most reliable and efficient method for items like stainless steel instruments and borosilicate glass.
- If your primary focus is heat-sensitive materials: You must explore alternatives like ethylene oxide (EtO) gas, chemical sterilization, or gamma irradiation for non-autoclavable plastics and delicate electronics.
- If your primary focus is sharp-edged instruments: Consider dry heat sterilization or disposable options for carbon-steel blades to preserve their cutting edge.
- If your primary focus is liquids or biohazard waste: The autoclave is the gold standard, provided the liquids are water-based and all safety protocols for containment are strictly followed.
Understanding the principles of steam sterilization empowers you to use the autoclave safely and effectively, ensuring both material integrity and absolute sterility.

Summary Table:
| Safe for Autoclaving | Unsafe for Autoclaving |
|---|---|
| Stainless steel instruments | Heat-sensitive plastics (PE, LDPE, PS) |
| Borosilicate glassware | Sharp carbon-steel instruments |
| Autoclavable plastics (PP, PC) | Waterproof substances (oils, waxes) |
| Water-based solutions & media | Hazardous & reactive chemicals |
| Biohazardous waste (in safe bags) | Dry powders |
Ensure your laboratory's sterilization process is safe, effective, and compliant. KINTEK specializes in providing high-quality autoclaves and reliable lab equipment to meet your specific sterilization needs. Our experts can help you select the right equipment to protect your instruments, ensure complete sterility, and streamline your workflow. Contact KINTEK today to find the perfect autoclave solution for your lab.
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Laboratory High Pressure Steam Sterilizer Vertical Autoclave for Lab Department
- Portable Digital Display Automatic Laboratory Sterilizer Lab Autoclave for Sterilization Pressure
- Portable High Pressure Laboratory Autoclave Steam Sterilizer for Lab Use
- Desktop Fast Laboratory Autoclave Sterilizer 20L 24L for Lab Use
- Laboratory Sterilizer Lab Autoclave Herbal Powder Sterilization Machine for Plant
People Also Ask
- What types of items and materials can be processed in a laboratory autoclave? Essential Guide for Lab Safety
- Why is the standard autoclave temperature set to 121? The Science of Effective Sterilization
- What is the life expectancy of an autoclave machine? Maximize Your Investment with Proper Care
- What critical environmental conditions does a laboratory autoclave provide for evaluating wear resistance? - KINTEK
- What is the normal temperature of an autoclave? Achieve Sterile Confidence with Precise Control



















