At its core, an autoclave is a high-pressure chamber used to sterilize equipment and supplies. By subjecting items to high-pressure saturated steam at temperatures well above boiling, it effectively kills all microorganisms, including bacteria, viruses, fungi, and resilient spores, which simple washing or boiling cannot.
An autoclave’s purpose extends beyond simple cleaning; it provides a method for achieving total sterility. It is the gold standard for decontamination in any field where the complete absence of microbial life is critical for safety and accuracy.

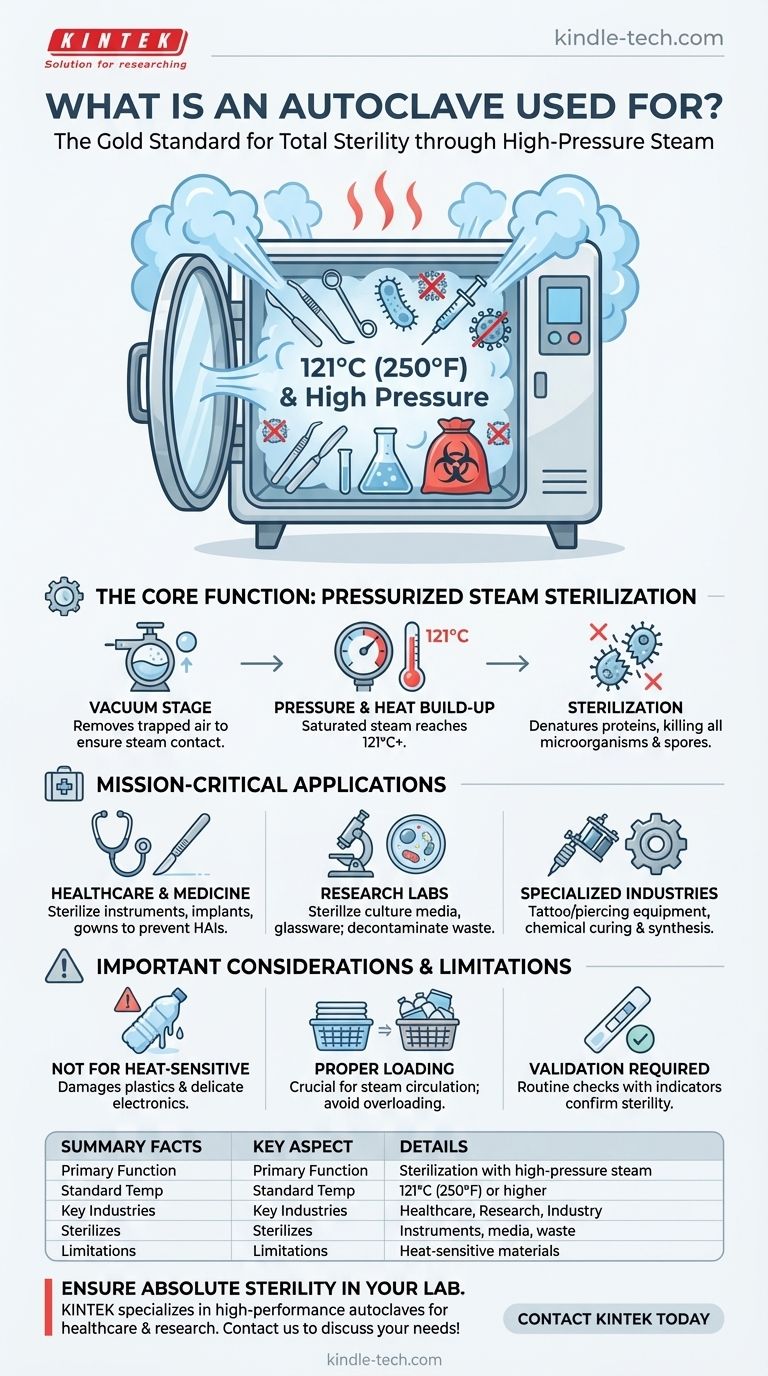
The Core Function: Pressurized Steam Sterilization
The effectiveness of an autoclave comes from its ability to harness the combined power of heat, pressure, and moisture. This process is far more effective than dry heat or chemical disinfectants for many applications.
How Steam Achieves Sterility
Under normal atmospheric pressure, water boils at 100°C (212°F). While this kills many microbes, it is not sufficient to eliminate highly resistant bacterial spores.
An autoclave is a sealed chamber that increases the internal pressure. This rise in pressure allows water vapor (steam) to reach much higher temperatures—typically 121°C (250°F) or higher—before it becomes steam.
This superheated, moist steam rapidly penetrates materials and denatures the essential proteins and enzymes within microorganisms, causing them to die.
The Role of a Vacuum System
Many modern autoclaves begin their cycle by creating a vacuum, removing all air from the chamber.
This step is critical because trapped air can create "cold spots" where the temperature does not reach the required level, leading to incomplete sterilization. By removing air, the system ensures that high-temperature steam makes contact with every surface of the items being sterilized.
Where Autoclaves are Mission-Critical
Because of their unmatched effectiveness, autoclaves are indispensable tools across several professional fields where sterility is a non-negotiable requirement.
In Healthcare and Medicine
In hospitals, dental offices, and surgical centers, autoclaves are used to sterilize surgical instruments, implantable medical devices, and reusable supplies like gowns and dressings. This process is fundamental to preventing healthcare-associated infections (HAIs).
In Scientific and Research Laboratories
Microbiologists and biotechnologists use autoclaves to sterilize culture media, glassware, and other lab equipment. This prevents unwanted microbial contamination that would invalidate experimental results. They are also used to decontaminate biohazardous waste before disposal.
In Specialized Industries
Beyond medicine and science, autoclaves are used in tattoo and piercing parlors to sterilize needles and equipment, preventing the transmission of bloodborne pathogens. In some chemical industries, industrial autoclaves are used under high pressure and temperature to cure coatings, vulcanize rubber, and synthesize crystals.
Understanding the Trade-offs and Limitations
While highly effective, an autoclave is not a universal solution. Understanding its limitations is key to using it safely and correctly.
Not for Heat-Sensitive Materials
The primary limitation is heat. Any material that cannot withstand high temperatures and moisture will be damaged or destroyed. This includes many plastics, heat-labile chemicals, and delicate electronic instruments.
The Importance of Proper Loading
Items must be loaded correctly to allow for steam circulation. Overloading the chamber or using improper containers can prevent steam from penetrating the load, resulting in a failed sterilization cycle.
Process Validation is Required
Simply running a cycle does not guarantee sterility. Autoclaves require routine maintenance and validation using biological or chemical indicators to confirm they are reaching the necessary time, temperature, and pressure parameters for every run.
Key Applications by Goal
Your specific use case will determine how you rely on the autoclave's function.
- If your primary focus is patient safety in a clinical setting: Use the autoclave for all reusable surgical and dental instruments to eliminate the risk of infection.
- If your primary focus is maintaining experimental integrity in a laboratory: Sterilize all culture media, solutions, and lab equipment to ensure your results are not compromised by outside contaminants.
- If your primary focus is safe waste management: Use the autoclave to decontaminate all biohazardous waste, rendering it inert and safe for standard disposal.
Ultimately, the autoclave provides a reliable and verifiable method for achieving absolute sterility, a foundational requirement for modern science and medicine.
Summary Table:
| Key Aspect | Details |
|---|---|
| Primary Function | Sterilization using high-pressure saturated steam |
| Standard Temperature | 121°C (250°F) or higher |
| Key Industries | Healthcare, Research Laboratories, Tattoo/ Piercing, Industry |
| Sterilizes | Surgical instruments, lab media, glassware, biohazardous waste |
| Limitations | Not suitable for heat-sensitive materials (e.g., some plastics) |
Ensure absolute sterility and safety in your lab. KINTEK specializes in high-performance lab equipment, including reliable autoclaves designed to meet the rigorous demands of healthcare and research. Our experts can help you select the perfect sterilization solution to protect your work and your patients. Contact KINTALK today to discuss your laboratory needs!
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Laboratory High Pressure Steam Sterilizer Vertical Autoclave for Lab Department
- Laboratory Sterilizer Lab Autoclave Herbal Powder Sterilization Machine for Plant
- Desktop Fast Laboratory Autoclave Sterilizer 35L 50L 90L for Lab Use
- Desktop Fast Laboratory Autoclave Sterilizer 20L 24L for Lab Use
- Portable Digital Display Automatic Laboratory Sterilizer Lab Autoclave for Sterilization Pressure
People Also Ask
- What is the normal temperature of an autoclave? Achieve Sterile Confidence with Precise Control
- What is the necessity of using an autoclave for pre-treating culture media? Ensure Accurate Ag2O/TiO2 Testing
- What types of items and materials can be processed in a laboratory autoclave? Essential Guide for Lab Safety
- What role does an autoclave play in the acid treatment for microalgae disruption? Unlock High-Yield Cell Pretreatment
- What are the advantages of using an autoclave equipped with a stirring device for molten salt testing? Dynamic Accuracy



















