In microbiology, an autoclave is an essential device that sterilizes equipment and supplies using high-pressure saturated steam. It is the most reliable method for eliminating all forms of microbial life, including bacteria, viruses, fungi, and highly resistant bacterial spores. This process is non-negotiable for ensuring the validity of experimental results and maintaining a safe laboratory environment.
The autoclave is not merely a piece of cleaning equipment; it is the cornerstone of microbiological integrity. Its function is to create a completely sterile environment, which is the absolute prerequisite for studying microorganisms without contamination and for safely neutralizing biohazardous materials.
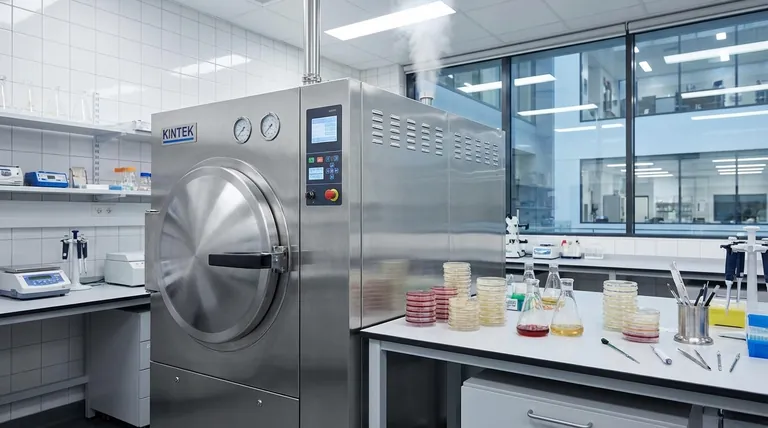

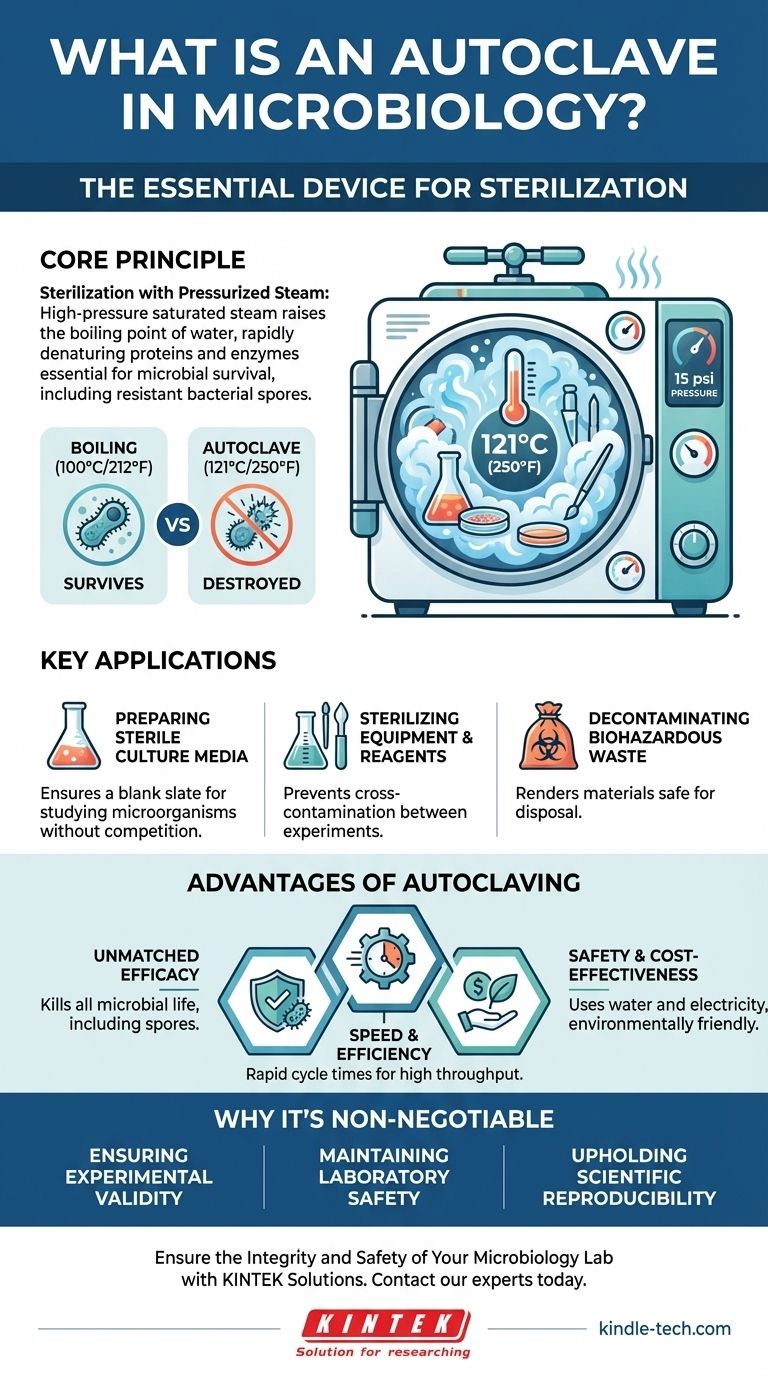
The Core Principle: Sterilization with Pressurized Steam
To understand the autoclave's importance, we must first understand why simpler methods are insufficient. The core challenge in sterilization is not just killing active bacteria, but eliminating their dormant, highly resilient forms.
Why Simple Boiling Isn't Enough
Many bacteria can form endospores, which are tough, non-reproductive structures that can survive extreme conditions, including boiling water at standard atmospheric pressure (100°C or 212°F). These spores can later reactivate and contaminate an experiment.
How an Autoclave Achieves Sterility
An autoclave functions like a sophisticated pressure cooker. By creating a sealed chamber, it increases the internal pressure, which in turn raises the boiling point of water. Typically, an autoclave operates at 121°C (250°F) and 15 psi of pressure.
This combination of high temperature and moisture is lethal to all microorganisms. The hot, pressurized steam rapidly denatures the essential proteins and enzymes that microbes, including spores, need to survive.
Key Applications in a Microbiology Lab
The autoclave is a workhorse in any microbiology setting, used daily for several critical tasks that ensure both the quality of research and the safety of personnel.
Preparing Sterile Culture Media
Before a specific microorganism can be grown, its food source—the culture medium—must be a blank slate. Autoclaving liquid, semi-solid, and solid media ensures no other microbes are present to compete with or contaminate the organism being studied.
Sterilizing Equipment and Reagents
Glassware, surgical instruments, pipette tips, and various other lab supplies must be sterile to prevent cross-contamination between experiments. The autoclave provides a fast and effective way to prepare these items for use.
Decontaminating Biohazardous Waste
After an experiment is complete, all materials that have come into contact with microorganisms are considered biohazardous waste. Autoclaving is the primary method used to kill all organisms on these materials, rendering them safe for disposal.
The Advantages of Autoclaving
While other sterilization methods exist, autoclaving remains the gold standard in microbiology due to its unmatched combination of efficacy, efficiency, and safety.
Unmatched Efficacy
The use of pressurized steam ensures the complete destruction of all microbial life, including the most heat-resistant bacterial spores. This provides a level of certainty that is difficult to achieve with chemical disinfectants or dry heat.
Speed and Efficiency
A typical autoclave cycle can sterilize a load in minutes, a significantly shorter time than required for methods like dry heat sterilization. This allows for a high throughput of materials in a busy lab environment.
Safety and Cost-Effectiveness
Autoclaving uses only water and electricity, eliminating the need for harsh or toxic chemicals. It is a highly cost-effective and environmentally friendly method for both preparing materials and decontaminating waste.
Why Autoclaving is Non-Negotiable
Failing to properly sterilize materials has profound consequences that undermine the very foundation of scientific work and laboratory safety.
Ensuring Experimental Validity
Contamination from an outside microbe can completely invalidate an experiment. The autoclave ensures that any observed results are due to the organism being studied and not an unknown variable, making the data trustworthy.
Maintaining Laboratory Safety
Perhaps most importantly, the autoclave is a critical tool for infection control. By thoroughly decontaminating waste and equipment, it protects researchers and the surrounding community from exposure to potentially pathogenic microorganisms.
Upholding Scientific Reproducibility
For science to advance, experiments must be reproducible. Standardized autoclaving protocols ensure that labs around the world can start with the same sterile baseline, which is essential for comparing and validating results.
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
The autoclave's role is central to every aspect of the microbiological workflow, from preparation to disposal.
- If your primary focus is research and experimentation: Use the autoclave to guarantee your culture media and equipment are sterile, protecting the integrity and validity of your results.
- If your primary focus is clinical diagnostics: Rely on the autoclave for absolute sterilization of instruments to prevent patient infection and ensure accurate test outcomes.
- If your primary focus is laboratory safety and compliance: Implement strict autoclaving protocols for decontaminating all biohazardous waste before it leaves the lab.
Ultimately, mastering the principles and application of the autoclave is fundamental to conducting safe, valid, and reproducible microbiological science.
Summary Table:
| Aspect | Key Function |
|---|---|
| Primary Use | Sterilization using high-pressure saturated steam (typically 121°C at 15 psi) |
| Key Applications | Preparing sterile culture media, sterilizing lab equipment, decontaminating biohazardous waste |
| Key Advantages | Unmatched efficacy (kills all microbes/spores), speed, cost-effectiveness, and safety |
| Core Importance | Ensures experimental validity, laboratory safety, and scientific reproducibility |
Ensure the Integrity and Safety of Your Microbiology Lab
Choosing the right sterilization equipment is fundamental to achieving reliable results and protecting your team. KINTEK specializes in high-performance lab equipment and consumables, providing autoclaves designed for the rigorous demands of microbiology.
Let us help you select the perfect autoclave to meet your specific research, diagnostic, or safety compliance goals. Contact our experts today to discuss your laboratory's needs and discover how KINTEK can support your mission for sterile, safe, and valid science.
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Laboratory Sterilizer Lab Autoclave Herbal Powder Sterilization Machine for Plant
- Desktop Fast Laboratory Autoclave Sterilizer 35L 50L 90L for Lab Use
- Portable High Pressure Laboratory Autoclave Steam Sterilizer for Lab Use
- Portable Digital Display Automatic Laboratory Sterilizer Lab Autoclave for Sterilization Pressure
- Laboratory High Pressure Steam Sterilizer Vertical Autoclave for Lab Department
People Also Ask
- What is the necessity of using a steam autoclave for dental alloys? Ensure Pure Bacterial Adhesion Data
- What experimental conditions do stainless steel autoclaves provide for PCT-A leaching? Optimize Phosphate Glass Testing
- How should solid materials in bags be prepared for decontamination? Master Steam Penetration for Safe Sterilization
- What is the primary purpose of an autoclave in the preparation of media for the biological leaching of uranium?
- Why is the prevention of air entrapment critical for the autoclave sterilization process? Ensure 100% Sterility Today



















