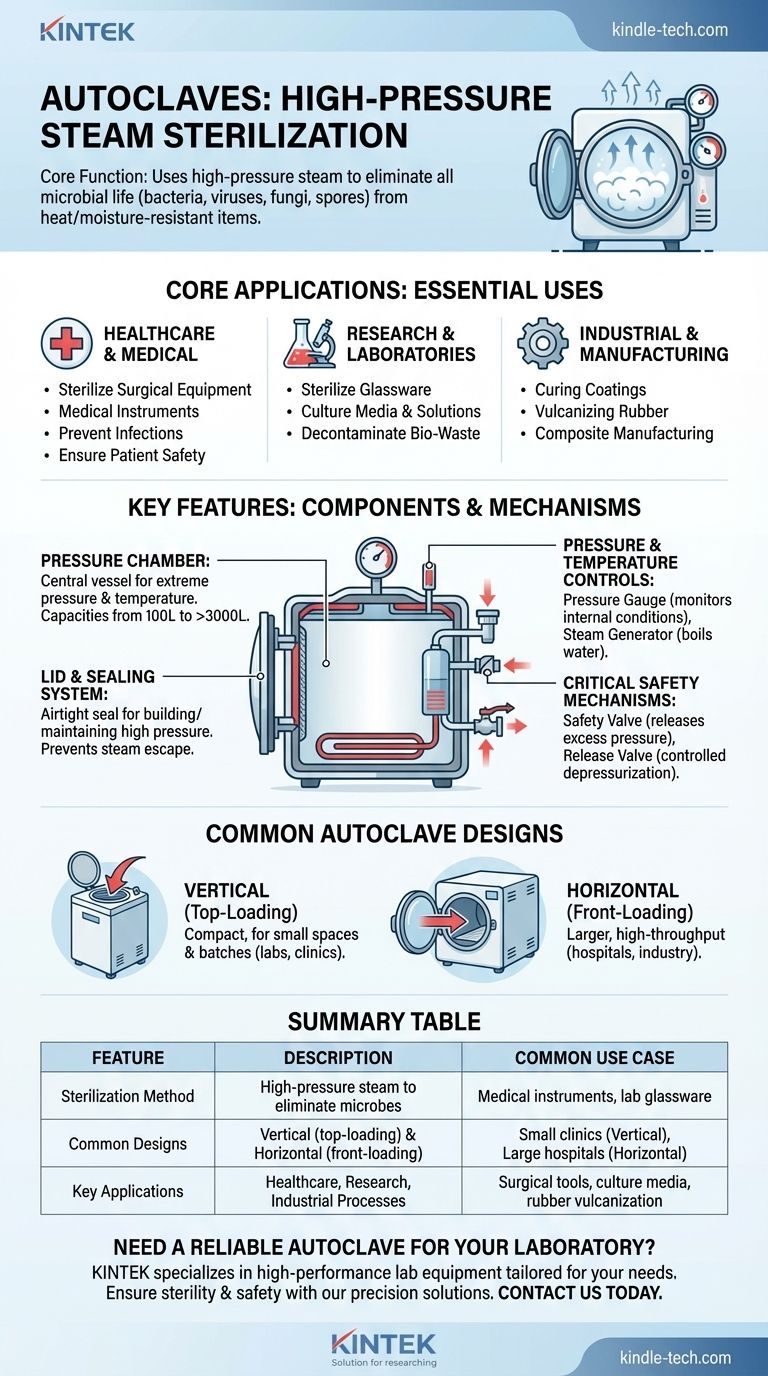
At its core, an autoclave is a specialized machine that uses high-pressure steam to sterilize equipment and supplies. Its primary function is to eliminate all forms of microbial life, including bacteria, viruses, fungi, and spores, from items that are heat and moisture-resistant. This makes it an indispensable tool in any environment where absolute sterility is required.
The critical function of an autoclave is not just heating, but using pressurized steam to achieve temperatures far above the boiling point of water, ensuring the complete and rapid destruction of all microorganisms.

Core Applications: Where Autoclaves are Essential
An autoclave's ability to ensure complete sterility makes it a cornerstone of safety and quality control across numerous fields.
Healthcare and Medical Fields
In settings like hospitals, dental clinics, and veterinary offices, autoclaves are used to sterilize surgical equipment, medical instruments, and other reusable items. This process is fundamental to preventing infections and ensuring patient safety.
Research and Laboratories
Microbiology and life science labs rely on autoclaves to sterilize laboratory glassware, culture media, solutions, and other equipment. They are also used for the critical step of decontaminating biological waste before disposal.
Industrial and Manufacturing Processes
Beyond medicine and research, autoclaves have specialized industrial uses. They are employed in the chemical industry for curing coatings, vulcanizing rubber, and in the manufacturing of complex composites where high pressure and temperature are required.
Key Features: Understanding the Components
An autoclave is a precision instrument where several key components work in unison to create the conditions necessary for sterilization.
The Pressure Chamber
This is the central vessel, typically built with inner and outer walls, designed to withstand extreme pressure and temperature. Its capacity can range from small tabletop units of 100 liters to large industrial models exceeding 3000 liters.
The Lid and Sealing System
The lid or door creates an airtight seal, which is crucial for building and maintaining the high pressure inside the chamber. This seal ensures that steam cannot escape, allowing the temperature to rise effectively.
Pressure and Temperature Controls
A pressure gauge allows operators to monitor the internal conditions, while a steam generator (often an electric heater) boils water to create the necessary steam. These systems work together to reach the target sterilization temperature.
Critical Safety Mechanisms
Every autoclave is equipped with essential safety features. A safety valve is designed to automatically release pressure if it exceeds a safe limit, while a release valve allows for controlled depressurization at the end of a cycle.
Common Autoclave Designs
While the core principle remains the same, autoclaves are commonly available in two primary configurations that suit different workflows and space constraints.
Vertical Autoclaves
These units are loaded from the top, much like a chest freezer. They are typically smaller in size and well-suited for laboratories or clinics with limited space and smaller batches of items to sterilize.
Horizontal Autoclaves
Also known as front-loading autoclaves, these have a door that opens outward. They are generally larger and are designed for high-throughput environments like large hospitals or industrial facilities that require processing significant volumes.
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
Selecting the appropriate autoclave depends entirely on the specific demands of your application, from scale and throughput to the types of materials being sterilized.
- If your primary focus is a research lab or small clinic: A compact, top-loading vertical autoclave is often sufficient for sterilizing media, glassware, and small instruments.
- If your primary focus is a high-volume hospital or medical facility: A large, front-loading horizontal autoclave is necessary to handle the throughput of surgical kits, linens, and diverse medical equipment.
- If your primary focus is an industrial manufacturing process: Your choice will be dictated by the specific requirements of the material, such as vulcanization or composite curing, often requiring custom-sized horizontal units.
Ultimately, understanding the principles of pressurized steam sterilization allows you to leverage the autoclave as a powerful tool for ensuring safety, integrity, and reliability in any critical application.
Summary Table:
| Feature | Description | Common Use Case |
|---|---|---|
| Sterilization Method | High-pressure steam to eliminate all microbial life. | Medical instruments, lab glassware. |
| Common Designs | Vertical (top-loading) and Horizontal (front-loading). | Small clinics (Vertical), Large hospitals (Horizontal). |
| Key Applications | Healthcare, Research Laboratories, Industrial Processes. | Surgical tools, culture media, vulcanizing rubber. |
Need a reliable autoclave for your laboratory? KINTEK specializes in high-performance lab equipment, including autoclaves tailored for healthcare, research, and industrial needs. Ensure sterility and safety with our precision solutions—contact us today to find the perfect fit for your requirements!
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Laboratory High Pressure Steam Sterilizer Vertical Autoclave for Lab Department
- Laboratory Sterilizer Lab Autoclave Herbal Powder Sterilization Machine for Plant
- Desktop Fast Laboratory Autoclave Sterilizer 35L 50L 90L for Lab Use
- Desktop Fast Laboratory Autoclave Sterilizer 20L 24L for Lab Use
- Portable High Pressure Laboratory Autoclave Steam Sterilizer for Lab Use
People Also Ask
- What are the standard operating parameters for an autoclave? Master Temperature, Pressure, and Time for Sterilization
- What is the normal temperature of an autoclave? Achieve Sterile Confidence with Precise Control
- What are the advantages of using an autoclave equipped with a stirring device for molten salt testing? Dynamic Accuracy
- What is the necessity of using an autoclave for pre-treating culture media? Ensure Accurate Ag2O/TiO2 Testing
- What role does an autoclave play in the acid treatment for microalgae disruption? Unlock High-Yield Cell Pretreatment



















