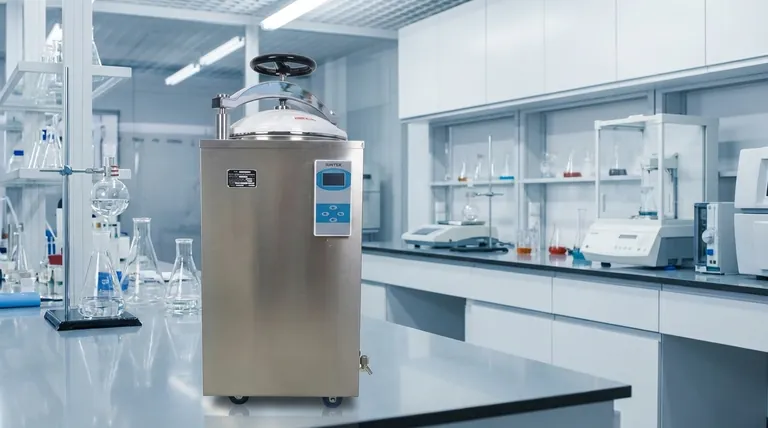
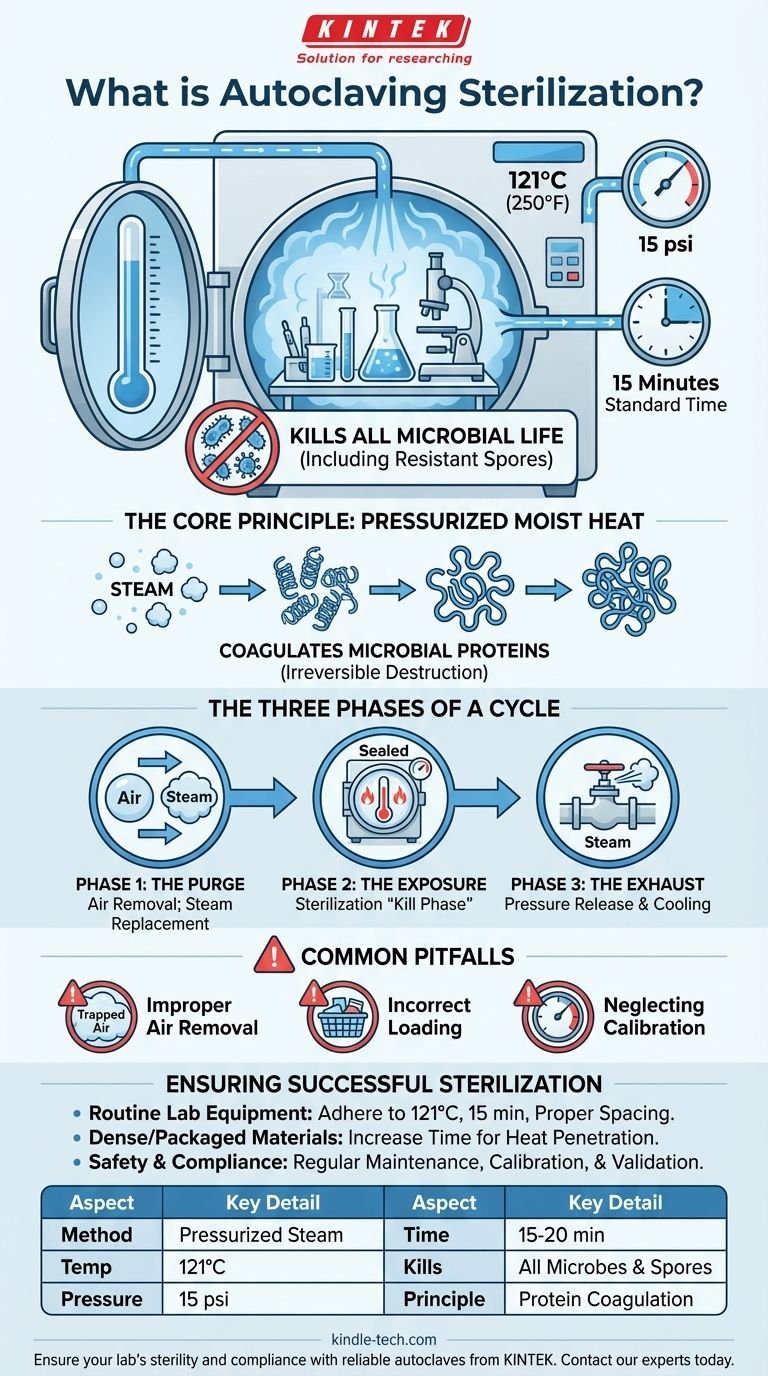
In essence, autoclaving is a sterilization method that uses high-pressure steam to kill all forms of microbial life, including bacteria, viruses, fungi, and even highly resistant bacterial spores. It achieves this by heating materials to a standard temperature of 121°C (250°F) under pressure for a specified duration, typically 15 minutes, ensuring the complete eradication of microorganisms.
The core principle of autoclaving is not just heat, but pressurized moist heat. The pressure allows water to reach temperatures far above its normal boiling point, and the resulting steam effectively transfers this lethal heat to denature and coagulate the essential proteins of microorganisms.

The Core Principle: How Pressurized Steam Works
An autoclave operates on a fundamental principle of physics. By increasing the pressure within a sealed chamber, it can dramatically increase the boiling point of water. This superheated, moisture-laden steam is the key to its effectiveness.
Why Pressure is Essential
At normal atmospheric pressure, water boils at 100°C (212°F). This temperature is not sufficient to reliably kill all microbial life, especially tough endospores.
By increasing the pressure inside the autoclave to approximately 15 pounds per square inch (psi) above atmospheric pressure, the boiling point of water is raised to 121°C. This higher temperature is lethal to all known microorganisms.
How Moisture Kills
The moisture in the steam is the true agent of destruction. It causes the coagulation of microbial proteins, an irreversible process that is functionally equivalent to cooking an egg.
This process of "moist heat" sterilization is significantly faster and more effective than "dry heat," as the moisture helps to rapidly penetrate materials and transfer thermal energy.
The Three Phases of a Sterilization Cycle
A typical autoclave cycle is a precisely controlled process consisting of three distinct phases to ensure complete and safe sterilization.
Phase 1: The Purge
The cycle begins by purging all air from the sterilization chamber and replacing it with steam. This step is critical because air pockets can act as insulators, preventing the hot steam from making direct contact with the surfaces of the items being sterilized.
Phase 2: The Exposure (Sterilization)
Once all air is removed, the chamber is sealed and the steam pressure and temperature are maintained at the target level (e.g., 121°C at 15 psi). This is the "kill phase," which is held for a set duration, typically 15 minutes, to ensure complete heat penetration.
Phase 3: The Exhaust
After the exposure time is complete, an exhaust valve opens to release the steam and pressure from the chamber. The internal environment slowly returns to ambient pressure, and the sterilized items can begin to cool.
Common Pitfalls and Protocol Failures
While highly effective, the success of autoclaving depends entirely on adhering to proper protocol. Failure at any stage can compromise sterility.
Improper Air Removal
If the initial purge phase is incomplete, trapped air can prevent items from reaching the required sterilization temperature. This is one of the most common causes of sterilization failure.
Incorrect Loading
Overloading the autoclave or packing items too densely prevents steam from circulating freely. This creates cool spots within the load, leaving some items unsterilized even if the cycle completes successfully.
Neglecting Calibration
The temperature and pressure gauges on an autoclave must be accurate. Regular calibration is essential to verify that the conditions inside the chamber are actually reaching the setpoints required for effective sterilization.
Ensuring Successful Sterilization
To apply this knowledge effectively, focus on the specific goal of your sterilization task.
- If your primary focus is routine lab equipment: Adhere strictly to the standard cycle of 121°C for 15 minutes and ensure items are loaded with adequate space for steam circulation.
- If your primary focus is dense or packaged materials: Increase the sterilization time to account for the "heat lag"—the extra time it takes for heat to penetrate to the center of the items.
- If your primary focus is safety and compliance: Implement a regular schedule for maintenance, calibration, and validation using biological indicators to prove the autoclave is performing correctly.
Understanding these core principles transforms the autoclave from a simple machine into a reliable tool for guaranteed sterility.
Summary Table:
| Aspect | Key Detail |
|---|---|
| Method | Sterilization using pressurized steam |
| Standard Temperature | 121°C (250°F) |
| Standard Pressure | 15 psi above atmospheric pressure |
| Standard Time | 15-20 minutes (varies with load) |
| Kills | Bacteria, viruses, fungi, and bacterial spores |
| Core Principle | Coagulation of microbial proteins by moist heat |
Ensure your lab's sterility and compliance with reliable autoclaves from KINTEK.
Whether you are sterilizing routine lab equipment, dense materials, or require validated cycles for compliance, KINTEK's range of autoclaves delivers the precise temperature control, effective steam penetration, and reliable performance you need. Our equipment is designed to eliminate common pitfalls like improper air removal and uneven heating.
Contact our sterilization experts today to find the perfect autoclave solution for your laboratory's specific requirements and achieve guaranteed sterility.
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Laboratory Sterilizer Lab Autoclave Vertical Pressure Steam Sterilizer for Liquid Crystal Display Automatic Type
- Laboratory Sterilizer Lab Autoclave Pulse Vacuum Lifting Sterilizer
- Laboratory Test Sieves and Sieving Machines
- Benchtop Laboratory Freeze Dryer for Lab Use
- Benchtop Laboratory Vacuum Freeze Dryer
People Also Ask
- What is the primary purpose of mini-autoclaves in supercritical water corrosion? Ensure Data Integrity with KINTEK
- What does autoclaving do to bacteria? It Destroys Them with High-Temperature Steam and Pressure
- What function does a PTFE-lined autoclave serve for ZnS nanopowder? Achieve Pure, High-Performance Synthesis
- What is the primary application of a laboratory autoclave in the rice husk biorefining process? Ensure Process Purity
- How do you maintain an autoclave in a lab? A Complete Guide to Safety and Reliability
- What is the purpose and principle of autoclave? Achieve Absolute Sterilization with High-Pressure Steam
- What role does an autoclave play in simulating PWR conditions? Advanced Material Validation for Nuclear Safety
- How are high-pressure autoclaves or high-temperature laboratory furnaces used to test green flame retardant stability?



















