At its core, a batch reactor is valued for its operational simplicity and versatility but is fundamentally limited by its inefficiency for large-scale production. It operates like a kitchen pot with a lid: you add ingredients, run the process (like cooking), and then empty the finished product before starting over, making it ideal for specific applications but impractical for others.
The central trade-off of a batch reactor is its flexibility versus its efficiency. While its design offers excellent control and the ability to produce multiple products in the same vessel, the necessary downtime between batches makes it economically unsuitable for high-volume, continuous manufacturing.

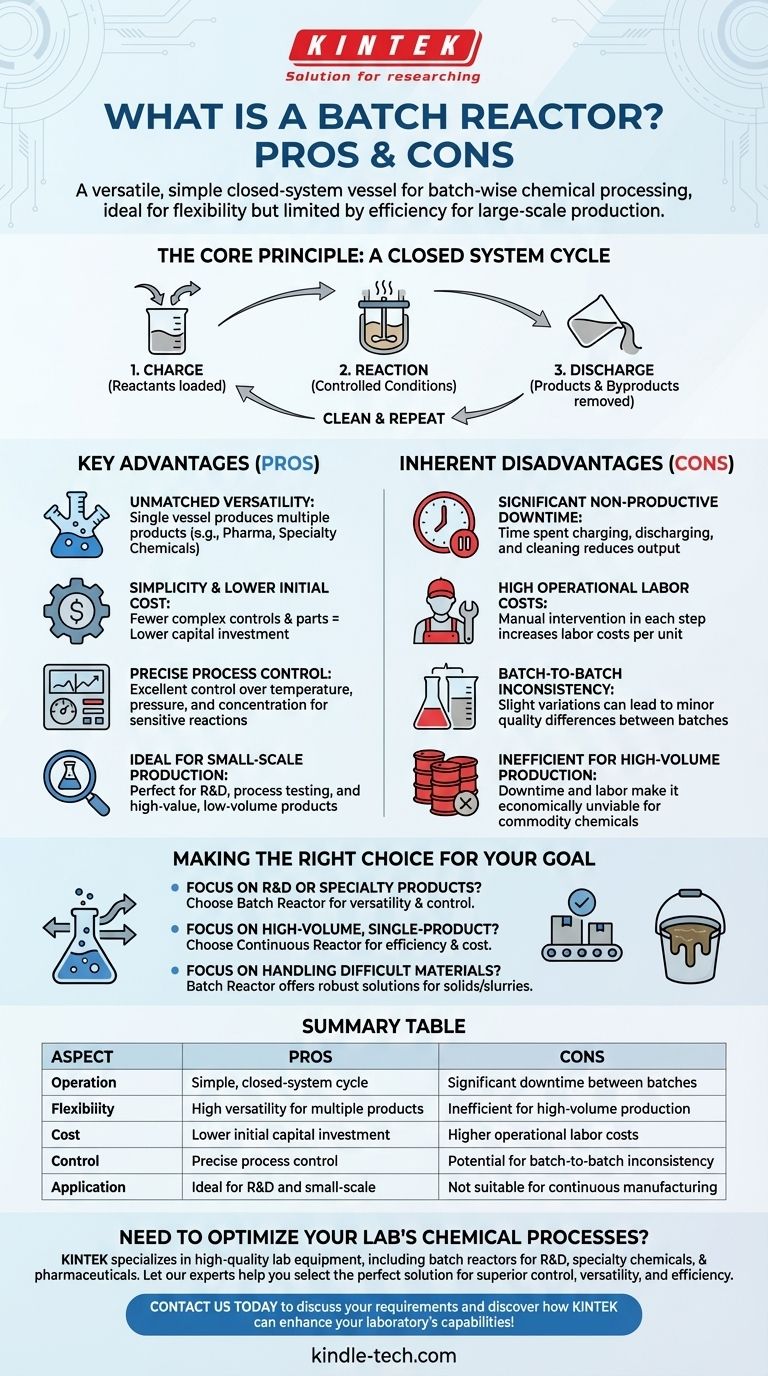
The Core Principle: A Closed System Cycle
A batch reactor is defined by its discontinuous operation. Understanding this cycle is key to grasping its inherent strengths and weaknesses.
How It Works
The process follows a distinct, sequential cycle. First, reactants are loaded or charged into the sealed vessel.
Next, the chemical reaction is carried out under controlled conditions, such as specific temperatures and pressures. This is the reaction phase.
Finally, once the reaction is complete, the process is stopped, and the products and byproducts are discharged. The reactor is often cleaned before the next cycle can begin.
Key Advantages of the Batch Approach
The discontinuous nature of a batch reactor creates several distinct advantages, particularly for smaller, more specialized operations.
Unmatched Versatility
Because each batch is a discrete event, the same reactor can be used to produce many different products. This makes it a cornerstone of industries that require flexibility, such as pharmaceuticals, specialty chemicals, and food production.
Simplicity and Lower Initial Cost
A batch reactor is, in essence, a simple, sealed vessel, often with a mixer and heating/cooling jacket. This design involves fewer complex controls and moving parts compared to continuous systems, resulting in a lower initial capital investment.
Precise Process Control
The closed-system nature allows for excellent control over the reaction environment. Temperature, pressure, and reactant concentration can be managed precisely throughout the batch's duration, ensuring the reaction proceeds as intended. This is critical for sensitive or complex chemical syntheses.
Ideal for Small-Scale Production
For research and development (R&D), process testing, or the manufacturing of high-value, low-volume products, batch reactors are perfect. The cost and complexity of a continuous system cannot be justified for small quantities.
Understanding the Trade-offs: Inherent Disadvantages
The very cycle that provides flexibility also introduces significant operational inefficiencies that limit the reactor's application.
Significant Non-Productive Downtime
The time spent charging reactants, discharging products, and cleaning the vessel between cycles is non-productive time. This inherent downtime is the single largest drawback, as it directly impacts overall output and asset utilization.
High Operational Labor Costs
Each step of the batch cycle—loading, monitoring, unloading, and cleaning—often requires manual intervention. This results in higher labor costs per unit of product compared to a highly automated continuous process.
Batch-to-Batch Inconsistency
While conditions within a single batch are well-controlled, slight variations in raw materials, operator actions, or cleaning effectiveness can lead to minor differences between batches. For products demanding absolute uniformity, this can be a significant quality control challenge.
Inefficient for High-Volume Production
The combination of downtime and high labor costs makes batch reactors economically unviable for producing large-volume commodity chemicals. The cost per kilogram of product is simply too high to compete with efficient, continuous alternatives.
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
Selecting a batch reactor is a strategic decision based on your specific production volume, product variety, and economic priorities.
- If your primary focus is R&D or producing multiple specialty products: The versatility, control, and lower initial cost of a batch reactor are perfectly aligned with your needs.
- If your primary focus is high-volume, single-product manufacturing: The superior efficiency, lower operational cost, and consistency of a continuous reactor are the clear choice.
- If your primary focus is handling difficult materials (like solids or viscous slurries): A batch reactor often provides a more robust and straightforward solution than complex continuous systems.
Ultimately, understanding the fundamental conflict between flexibility and continuous efficiency is the key to selecting the right tool for your chemical process.
Summary Table:
| Aspect | Pros (Advantages) | Cons (Disadvantages) |
|---|---|---|
| Operation | Simple, closed-system cycle | Significant downtime between batches |
| Flexibility | High versatility for multiple products | Inefficient for high-volume production |
| Cost | Lower initial capital investment | Higher operational labor costs |
| Control | Precise process control for sensitive reactions | Potential for batch-to-batch inconsistency |
| Application | Ideal for R&D and small-scale production | Not suitable for continuous manufacturing |
Need to optimize your lab's chemical processes?
Choosing the right reactor is critical for your productivity and budget. At KINTEK, we specialize in providing high-quality lab equipment, including batch reactors, to meet your specific needs—whether for R&D, specialty chemicals, or pharmaceuticals.
Let our experts help you select the perfect solution for superior control, versatility, and efficiency. Contact us today to discuss your requirements and discover how KINTEK can enhance your laboratory's capabilities!
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Mini SS High Pressure Autoclave Reactor for Laboratory Use
- High Pressure Laboratory Autoclave Reactor for Hydrothermal Synthesis
- Customizable High Pressure Reactors for Advanced Scientific and Industrial Applications
- Stainless High Pressure Autoclave Reactor Laboratory Pressure Reactor
- Cylindrical Resonator MPCVD Machine System Reactor for Microwave Plasma Chemical Vapor Deposition and Lab Diamond Growth
People Also Ask
- Why is a High-temperature and High-pressure Autoclave necessary for zirconium alloy testing? Ensure Nuclear Safety.
- Which critical experimental conditions does a high-pressure autoclave provide? Optimize Mixed Sulfide Leaching
- What is the function of a high-pressure static autoclave in biomass HTL? Optimize Your Biomass Conversion Research
- What is the function of high-pressure reactors in semiconductor catalyst preparation? Optimize Your Heterojunctions
- What is the role of a high-pressure reactor in h-BN magnetic nanocomposite synthesis? Master Precision Deposition



















