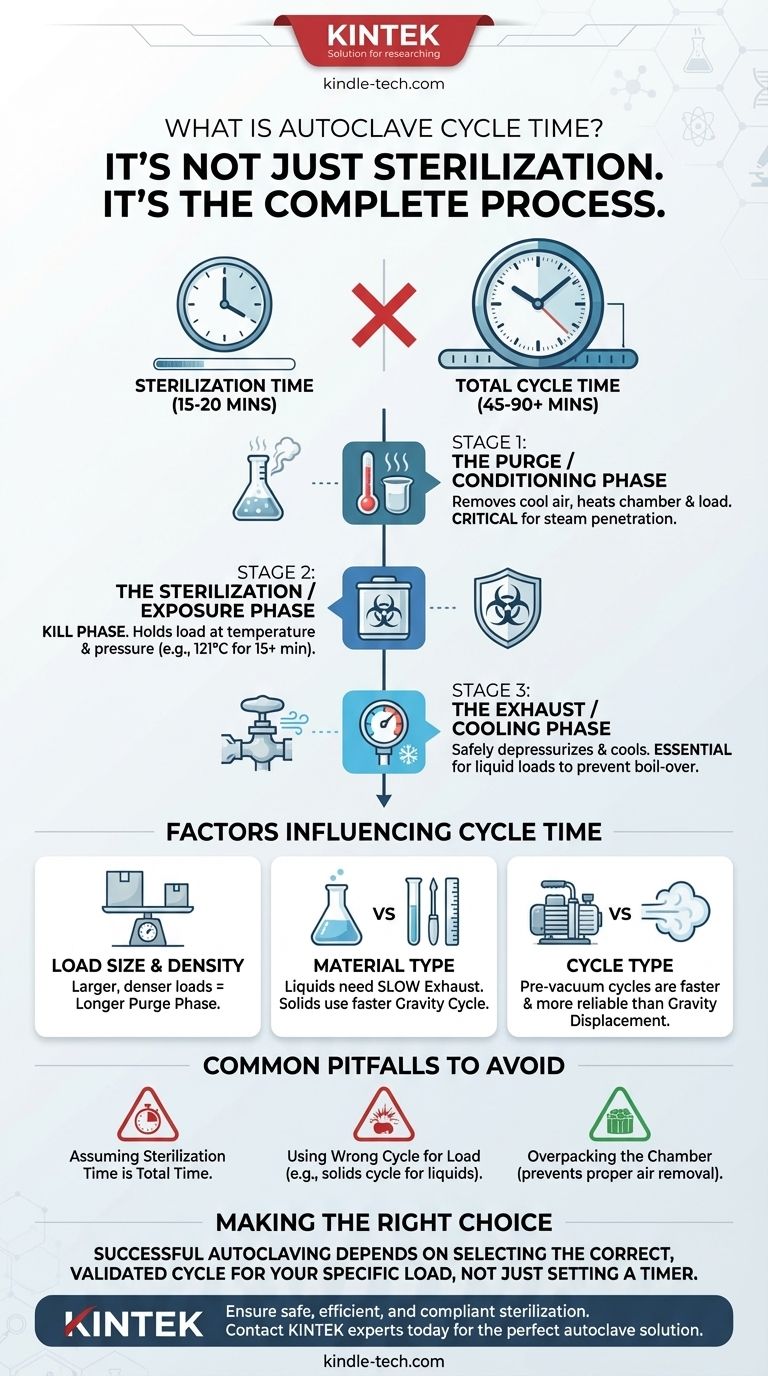
In autoclaving, cycle time is not just the sterilization period. It is the total duration the machine runs from the moment you press "start" to the moment the door can be safely opened. This complete process includes critical heating, air removal, and cooling phases, making the total cycle time significantly longer than the core sterilization time.
The most common mistake is confusing the sterilization time (the 15-20 minutes when microbes are actively killed) with the total cycle time (the 45-90+ minute end-to-end process). Understanding this distinction is fundamental to achieving effective and safe sterilization.

The Phases of a Complete Autoclave Cycle
An autoclave doesn't instantly reach sterilizing temperatures. The total cycle time is a programmed sequence of distinct phases, each with a specific purpose. A typical cycle includes three main stages.
Phase 1: The Purge (or Conditioning) Phase
Before sterilization can begin, all cool air must be removed from the chamber and the load. Trapped air acts as an insulator, preventing steam from making direct contact with surfaces and causing sterilization to fail.
This phase heats the chamber and load while purging the air, ensuring the environment is saturated with pure steam.
Phase 2: The Sterilization (or Exposure) Phase
This is the "kill" phase and what most people think of as autoclaving. The autoclave holds the load at a specific temperature and pressure for a set duration to destroy all microorganisms.
A common standard for this phase is 121°C (250°F) at 15 psi for at least 15 minutes. However, this time can vary based on the load.
Phase 3: The Exhaust (or Cooling) Phase
After the sterilization phase is complete, the chamber must be safely depressurized and cooled. Steam is vented from the chamber, and the pressure is slowly returned to ambient levels.
This phase is critical, especially for liquid loads. Releasing pressure too quickly will cause liquids to boil over violently, creating a mess and a safety hazard. This phase alone can take a significant amount of time.
Factors That Influence Cycle Time
A "one-size-fits-all" cycle does not exist. The total time required is highly dependent on what you are sterilizing.
Load Size and Density
A large, dense load takes much longer to heat than a small, sparse one. The purge phase must be long enough to ensure steam penetrates to the very center of the densest item in the load.
Type of Material
Liquids require a much slower exhaust phase than solid goods like glassware or surgical instruments. Therefore, a liquid cycle will always be longer than a gravity (solids) cycle, even if the sterilization time is the same.
Chosen Cycle Type
Different autoclaves offer different cycles. For example, a pre-vacuum cycle actively pumps air out of the chamber, leading to a faster and more reliable purge phase compared to a standard gravity displacement cycle where steam pushes the heavier, cooler air out.
Common Pitfalls to Avoid
Misunderstanding cycle time can lead to failed sterilization or damaged equipment.
Assuming Sterilization Time is Total Time
Setting an autoclave timer for only 15 minutes is incorrect. This only accounts for the exposure phase, completely ignoring the necessary time for purging and exhausting. You must always select a pre-validated, complete cycle.
Using the Wrong Cycle for the Load
Running liquids on a fast "solids" cycle is a common and dangerous mistake. The rapid pressure release will cause the superheated liquid to boil over, resulting in loss of media, a contaminated autoclave, and a potential safety risk.
Overpacking the Chamber
Tightly packing items into an autoclave chamber prevents proper air removal and steam circulation. This creates cool air pockets where microorganisms can survive, invalidating the entire run.
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
Always refer to your autoclave's manual to select the appropriate pre-programmed cycle for your specific application.
- If your primary focus is sterilizing solid instruments or glassware: Use a gravity or pre-vacuum cycle designed for dry goods, ensuring items are spaced to allow steam penetration.
- If your primary focus is sterilizing liquids or media: You must use a dedicated liquid cycle that features a slow, controlled exhaust to prevent boil-over.
- If your primary focus is decontaminating biohazardous waste: Select a robust waste cycle, which often includes extended sterilization times to handle dense, challenging loads.
Ultimately, successful autoclaving depends on selecting the correct, validated cycle for your specific load, not just setting a timer.
Summary Table:
| Phase | Purpose | Key Detail |
|---|---|---|
| Purge/Conditioning | Remove air, heat load | Ensures steam penetration |
| Sterilization/Exposure | Destroy microorganisms | Typically 121°C for 15+ minutes |
| Exhaust/Cooling | Depressurize safely | Critical for liquids to prevent boil-over |
Ensure your lab's sterilization process is safe, efficient, and compliant. Misunderstanding autoclave cycle times can lead to failed sterilization, damaged equipment, and safety risks. KINTEK specializes in providing reliable lab autoclaves and expert support to help you select the right equipment and cycles for your specific needs—whether you're sterilizing liquids, glassware, or biohazardous waste.
Contact our experts today to find the perfect autoclave solution for your laboratory.
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Desktop Fast Laboratory Autoclave Sterilizer 35L 50L 90L for Lab Use
- Laboratory High Pressure Steam Sterilizer Vertical Autoclave for Lab Department
- Laboratory Sterilizer Lab Autoclave Herbal Powder Sterilization Machine for Plant
- Portable High Pressure Laboratory Autoclave Steam Sterilizer for Lab Use
- Desktop Fast High Pressure Laboratory Autoclave Sterilizer 16L 24L for Lab Use
People Also Ask
- What conditions do stainless steel autoclaves provide for reactor simulation? Expert Material Testing Solutions
- What is the safety wall in an autoclave? The Jacketed Chamber Explained for Secure Sterilization
- How is an autoclave checked and maintained? A Guide to Guaranteed Sterilization
- What are the 3 most common machines used in sterilization? Choose the Right Method for Your Materials
- What can't be sterilized in an autoclave? Avoid Damaging Heat-Sensitive Materials
- Why is zirconium preferred as a lining material for HPAL autoclaves? Ensure Unmatched Corrosion Resistance
- Why is a high-pressure autoclave essential for TiO2 synthesis? Master Hydrothermal Nanomaterial Engineering
- How often should an autoclave be serviced? A Risk-Based Guide to Sterilization Compliance



















