High vacuum is used for advanced scientific and industrial processes where the presence of air or other gas molecules would interfere with the operation. Its primary applications are found in laboratory instruments like electron microscopes, mass spectrometers, and particle accelerators, where particles must travel long distances without collision.
The purpose of a high vacuum is not the vacuum itself, but the creation of an ultra-clean environment. By removing virtually all gas molecules, we ensure that particles like electrons or ions can travel from a source to a target without being deflected or absorbed.
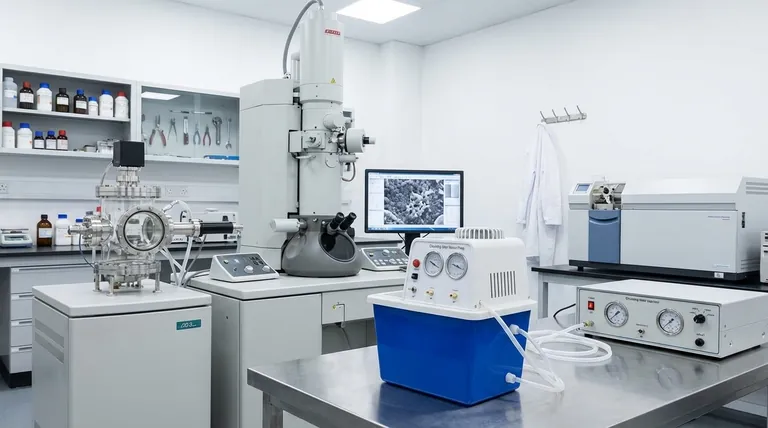

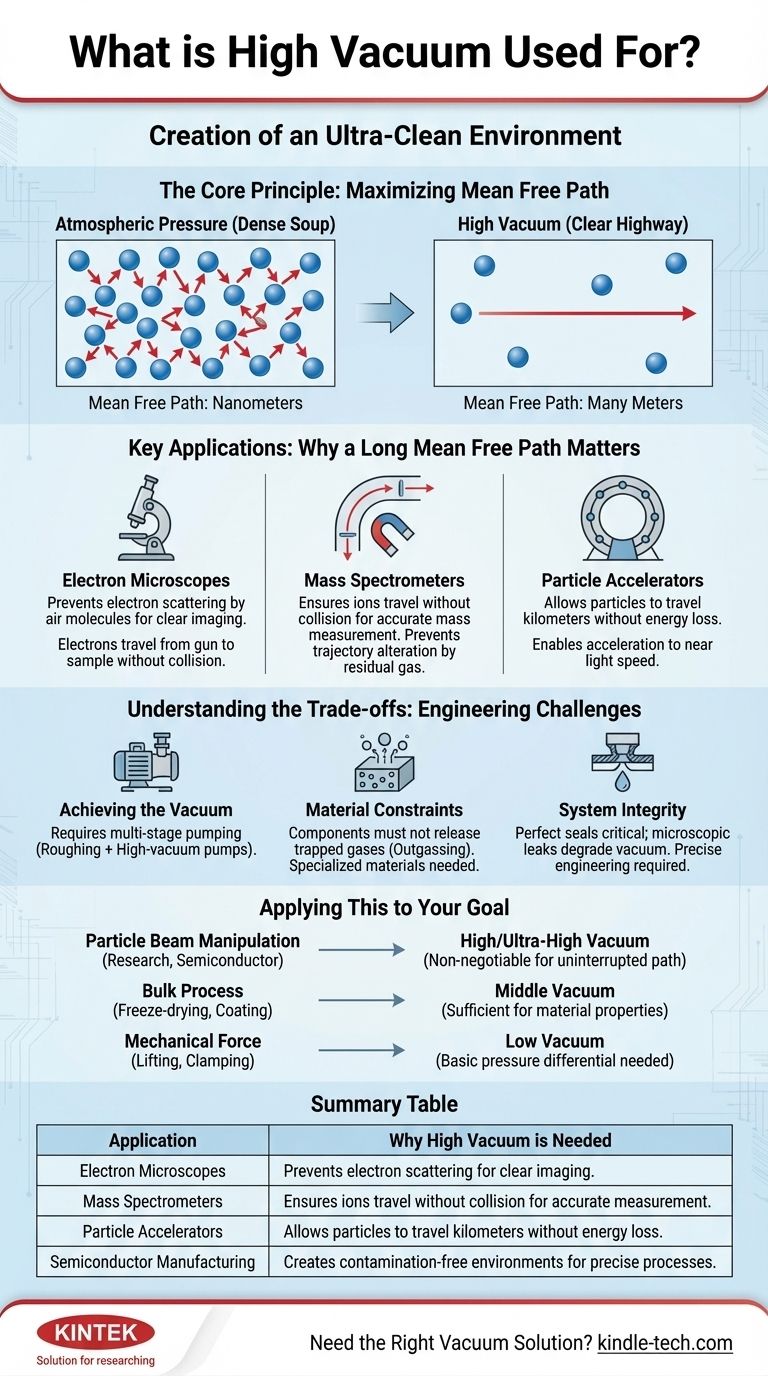
The Core Principle: Maximizing "Mean Free Path"
To understand why high vacuum is necessary, you must understand the concept of mean free path. This is the fundamental principle governing its use.
What is Mean Free Path?
Mean free path is the average distance a particle (like an electron, ion, or gas molecule) can travel before it collides with another particle.
At normal atmospheric pressure, this distance is incredibly short—measured in nanometers. The air around us is a dense soup of molecules in constant collision.
Why This Matters
Creating a vacuum involves removing these molecules from a sealed chamber. As more molecules are removed, the average distance between the remaining ones increases dramatically.
A high vacuum extends the mean free path from nanometers to many meters, creating a clear, uninterrupted highway for particles to travel along.
Key Applications Explained
The need for a long mean free path drives the use of high vacuum in several key technologies.
Electron Microscopes
An electron microscope generates a beam of electrons to create a highly magnified image of a sample.
High vacuum is essential to ensure these electrons travel from the electron gun to the sample and then to the detector without colliding with air molecules, which would scatter the beam and destroy the image.
Mass Spectrometers
A mass spectrometer measures the mass-to-charge ratio of ions. It does this by turning molecules into ions and sending them on a curved flight path toward a detector.
Collisions with residual gas molecules would alter the ions' trajectory, making it impossible to accurately measure their mass.
Particle Accelerators
These massive instruments accelerate subatomic particles to nearly the speed of light over distances that can span kilometers.
The particle beam pipe must be held at an extremely high (ultra-high) vacuum. Even a single collision with a gas molecule would rob an accelerated particle of its energy and disrupt the entire experiment.
Understanding the Trade-offs
While powerful, achieving and working with high vacuum presents significant engineering challenges.
Achieving the Vacuum
Creating a high vacuum is not a simple one-step process. It requires a multi-stage pumping system, often starting with a roughing pump to remove the bulk of the air, followed by a high-vacuum pump (like a turbomolecular or diffusion pump) to remove the remaining molecules.
Material Constraints
The chamber and all components inside it must be made of specialized materials that do not release trapped gases, a phenomenon known as outgassing. Common plastics and porous metals are unsuitable.
System Integrity
The entire system must be perfectly sealed. Even a microscopic leak can quickly degrade the vacuum level, rendering the instrument useless. This demands precise engineering and specialized seals.
Applying This to Your Goal
The required level of vacuum is dictated entirely by the process you need to perform.
- If your primary focus is particle beam manipulation (e.g., in research or semiconductor manufacturing): High or ultra-high vacuum is non-negotiable to guarantee an uninterrupted path for electrons or ions.
- If your primary focus is a bulk process (e.g., freeze-drying, degassing, or coating): A less demanding and more cost-effective middle vacuum is typically sufficient to achieve the desired material properties.
- If your primary focus is mechanical force (e.g., vacuum lifting or clamping): A simple low vacuum is all that is needed, as you only need to create a basic pressure differential.
Ultimately, choosing the right vacuum level is about defining how much molecular interference your process can tolerate.
Summary Table:
| Application | Why High Vacuum is Needed |
|---|---|
| Electron Microscopes | Prevents electron scattering by air molecules for clear imaging. |
| Mass Spectrometers | Ensures ions travel without collision for accurate mass measurement. |
| Particle Accelerators | Allows particles to travel kilometers without energy loss. |
| Semiconductor Manufacturing | Creates contamination-free environments for precise processes. |
Need the Right Vacuum Solution for Your Lab?
KINTEK specializes in high-vacuum lab equipment and consumables for research, analysis, and industrial applications. Whether you're working with electron microscopy, mass spectrometry, or advanced material processing, our expertise ensures optimal performance and reliability.
Contact us today to discuss your specific vacuum requirements and enhance your laboratory's capabilities!
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Circulating Water Vacuum Pump for Laboratory and Industrial Use
- Laboratory Vertical Water Circulating Vacuum Pump for Lab Use
- Laboratory Benchtop Water Circulating Vacuum Pump for Lab Use
- Oil Free Diaphragm Vacuum Pump for Laboratory and Industrial Use
- Laboratory Rotary Vane Vacuum Pump for Lab Use
People Also Ask
- What is the purpose of the compression chamber in a vacuum pump? The Heart of Vacuum Generation
- What types of gases can a water circulating vacuum pump handle? Safely Manage Flammable, Condensable & Dirty Gases
- What are the advantages of a water circulating vacuum pump? Superior Durability for Demanding Lab Environments
- Why is a water circulating vacuum pump suitable for handling flammable or explosive gases? Inherent Safety Through Isothermal Compression
- What is the importance of a vacuum pump for Schottky hybrid interfaces? Achieve Atomic-Level Purity and Bonding



















