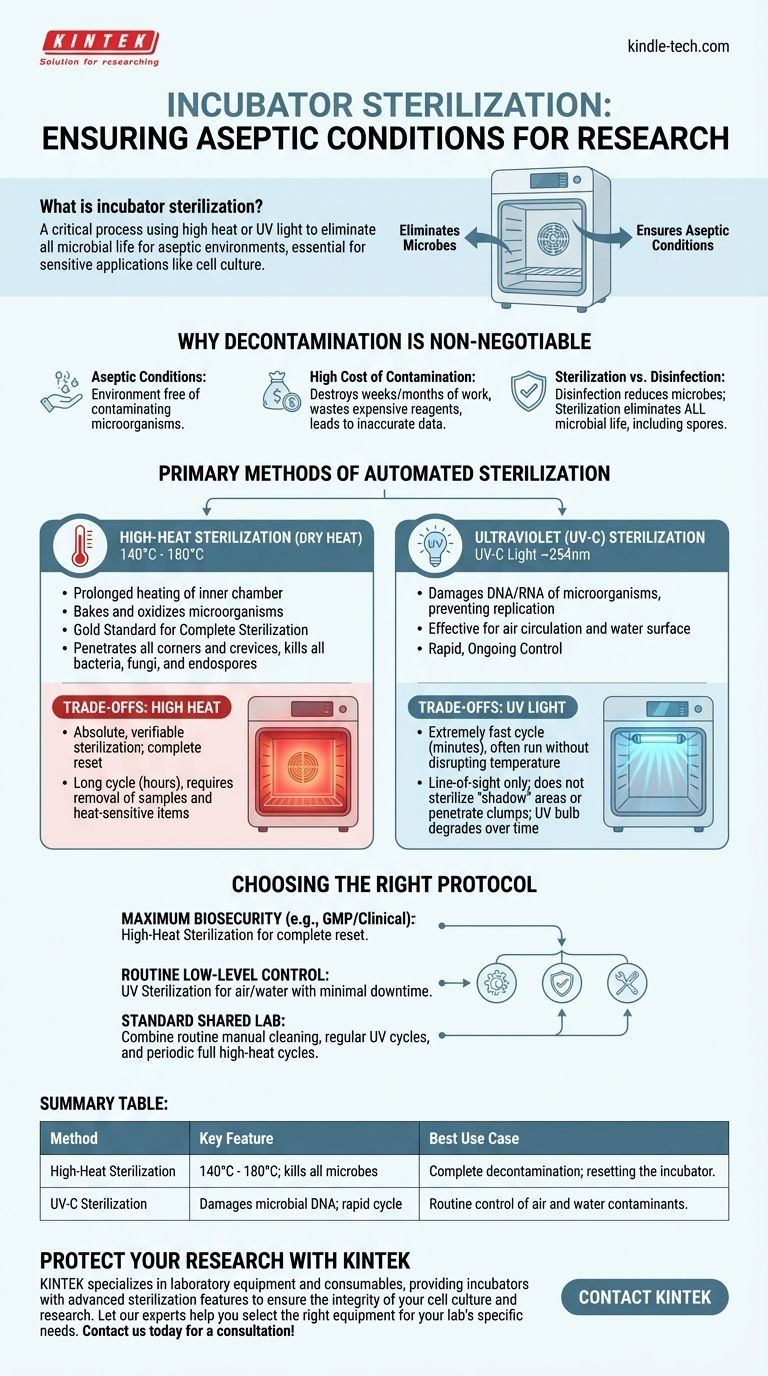
Incubator sterilization is a critical process that uses methods like high heat or ultraviolet light to eliminate all forms of microbial life from the incubator's interior chamber. This procedure is fundamental for creating an aseptic (sterile) environment, which is non-negotiable for sensitive applications like cell culture, where even minor contamination can invalidate entire experiments.
The core decision in incubator sterilization is not about which method is "better," but which is appropriate for your specific need. High-heat sterilization offers complete decontamination for a total reset, while UV light provides rapid, ongoing control of contaminants in the air and water.

Why Incubator Decontamination is Non-Negotiable
An incubator's warm, humid environment is the perfect breeding ground not just for your cells, but also for unwanted bacteria, molds, yeast, and mycoplasma. Failing to control these contaminants has serious consequences.
The Goal: Aseptic Conditions
The primary goal is to maintain aseptic conditions, meaning an environment completely free of contaminating microorganisms. This ensures that the only thing growing in your flasks or plates is the specific cell line you are studying.
The High Cost of Contamination
A single contamination event can destroy weeks or even months of work. It leads to wasted time, expensive reagents, and potentially inaccurate or irreproducible experimental data, which undermines the integrity of your research.
Sterilization vs. Disinfection
It's crucial to understand the difference. Disinfection reduces the number of harmful microbes, which is what you do when you wipe down a surface with 70% ethanol. Sterilization, the goal of an automated cycle, is the complete elimination of all microbial life, including highly resistant bacterial and fungal spores.
The Primary Methods of Automated Sterilization
Modern incubators typically feature one or both of the following automated sterilization methods. They serve different purposes and offer distinct advantages.
High-Heat Sterilization (Dry Heat)
This method involves heating the incubator's inner chamber to very high temperatures, typically between 140°C and 180°C, for a prolonged period. This process effectively bakes and oxidizes any microorganisms present.
High-heat is considered the gold standard for complete sterilization. The intense heat penetrates all corners and crevices, reliably killing all bacteria, fungi, and even the toughest-to-kill endospores.
Ultraviolet (UV-C) Sterilization
This method uses a lamp inside the chamber to generate UV-C light, typically at a wavelength of around 254nm. This specific wavelength of light works by damaging the DNA and RNA of microorganisms, rendering them unable to replicate.
UV is most effective at sterilizing the air as it circulates and the surface of the water in the humidity pan, two common sources of contamination.
Understanding the Trade-offs
Neither method is a perfect solution for every situation. Understanding their respective strengths and weaknesses is key to building a robust contamination control protocol.
High Heat: The Gold Standard
- Benefit: Provides absolute, verifiable sterilization of all internal surfaces. It is the most thorough and reliable method for completely resetting the incubator to a sterile state.
- Drawback: The cycle is very long, often taking several hours from heat-up to cool-down. It also requires the removal of all samples, shelving, and heat-sensitive electronics before running.
UV Light: Speed and Convenience
- Benefit: The cycle is extremely fast, sometimes lasting only a few minutes. It can often be run without disrupting the incubator's temperature, providing a quick way to decontaminate the air and water between regular cleanings.
- Drawback: UV light works on a line-of-sight basis. It cannot sterilize any surface in a "shadow" and is less effective at penetrating clumps of cells or debris. Furthermore, the effectiveness of the UV bulb degrades over time and requires periodic replacement.
Automated Cycles Do Not Replace Manual Cleaning
It is critical to remember that automated sterilization is a supplement to, not a replacement for, routine manual cleaning. Spills from media or buffers must be wiped up immediately with a suitable disinfectant. This physical removal of potential nutrients prevents microbes from establishing a foothold where they might be shielded from heat or UV light.
Choosing the Right Sterilization Protocol
Your choice of sterilization method should align directly with your laboratory's needs for security, speed, and workflow.
- If your primary focus is maximum biosecurity and eliminating all potential contaminants (e.g., in a GMP or clinical setting): High-heat sterilization is the definitive standard for ensuring a completely sterile environment after a contamination event or between critical projects.
- If your primary focus is maintaining a low level of background contamination during routine work: UV sterilization is an excellent tool for frequently decontaminating the internal air and water pan with minimal downtime.
- If you are running a standard research lab with shared equipment: A robust protocol combining both is ideal—perform routine manual cleaning, use UV cycles regularly, and schedule a full high-heat sterilization cycle on a periodic basis (e.g., monthly or quarterly).
Ultimately, a consistent and well-understood sterilization protocol is your best defense against the costly and time-consuming threat of contamination.
Summary Table:
| Method | Key Feature | Best Use Case |
|---|---|---|
| High-Heat Sterilization | 140°C - 180°C; kills all microbes, including spores | Complete decontamination; resetting the incubator |
| UV-C Sterilization | Damages microbial DNA; rapid cycle | Routine control of air and water contaminants |
Protect your research investment with reliable contamination control. Contamination can destroy months of work and waste expensive reagents. KINTEK specializes in laboratory equipment and consumables, providing incubators with advanced sterilization features to ensure the integrity of your cell culture and research. Let our experts help you select the right equipment for your lab's specific needs. Contact us today for a consultation!
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Laboratory Sterilizer Lab Autoclave Pulsating Vacuum Desktop Steam Sterilizer
- Laboratory High Pressure Steam Sterilizer Vertical Autoclave for Lab Department
- Portable Digital Display Automatic Laboratory Sterilizer Lab Autoclave for Sterilization Pressure
- Laboratory High Pressure Horizontal Autoclave Steam Sterilizer for Lab Use
- Shaking Incubators for Diverse Laboratory Applications
People Also Ask
- What is the necessity of using an autoclave for pre-treating culture media? Ensure Accurate Ag2O/TiO2 Testing
- What is the primary function of a laboratory Autoclave in seaweed hydrolysates? Sterilize and Optimize Fermentation
- What critical environmental conditions does a laboratory autoclave provide for evaluating wear resistance? - KINTEK
- How does an autoclave ensure the reliability of experimental results? Achieving a Sterile Baseline for Lab Research
- What role do laboratory autoclaves play in pectin extraction? Optimize Prebiotic Yield from Citrus and Apple Biomass



















