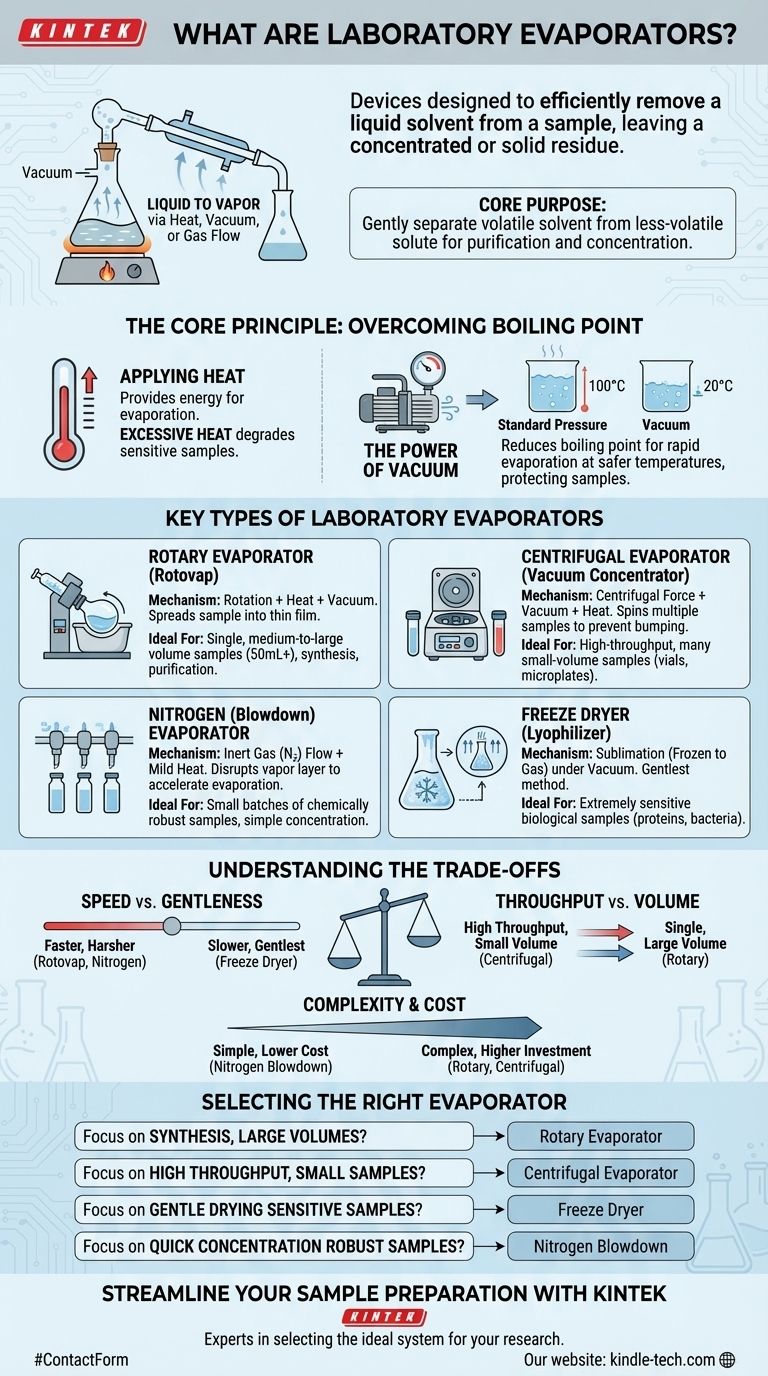
In essence, a laboratory evaporator is a device designed to efficiently remove a liquid solvent from a sample, leaving behind a concentrated or solid residue. They achieve this by converting the liquid into a vapor, a process accelerated through the controlled application of heat, vacuum, or gas flow. This technique is fundamental for purifying compounds, concentrating solutions, and preparing samples for further analysis.
The core purpose of any laboratory evaporator is to gently and efficiently separate a volatile solvent from a less-volatile solute. The key to choosing the right type lies in understanding the trade-offs between sample volume, throughput, required gentleness, and speed.
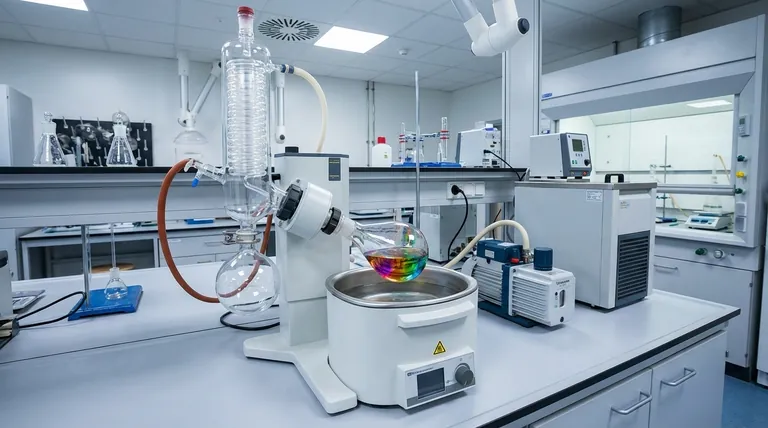

The Core Principle: Overcoming Boiling Point
To understand how evaporators work, you must first understand the challenge they solve: removing a solvent without damaging the compound of interest dissolved within it. This is accomplished by manipulating temperature and pressure.
The Role of Heat
Applying heat provides the energy needed for liquid molecules to escape into the vapor phase, which is the definition of evaporation.
However, excessive heat can degrade sensitive samples. The primary challenge evaporators solve is enabling rapid evaporation at temperatures low enough to protect the sample's integrity.
The Power of Vacuum
The most crucial element for modern evaporators is vacuum. By reducing the atmospheric pressure above the liquid, the solvent's boiling point is significantly lowered.
This allows for rapid evaporation at much safer temperatures. For example, water boils at 100°C (212°F) at standard pressure but boils at just 20°C (68°F) under a moderate vacuum. This protects heat-sensitive compounds like proteins or pharmaceuticals from damage.
Key Types of Laboratory Evaporators
While the goal is the same, different evaporators use distinct mechanisms tailored to specific applications, sample volumes, and throughput needs.
Rotary Evaporators (Rotovaps)
The most common type, a rotary evaporator, uses a rotating flask partially submerged in a heated bath, all connected to a vacuum source.
The rotation continuously spreads the sample into a thin film on the flask's inner surface, dramatically increasing the surface area for evaporation. A condenser then cools the vaporized solvent, collecting it for disposal or reuse.
These are the workhorses for processing single, medium-to-large volume samples, typically ranging from 50 mL to several liters.
Centrifugal Evaporators (Vacuum Concentrators)
A centrifugal evaporator combines vacuum and heat with centrifugal force, spinning multiple samples at high speed.
This force creates a pressure gradient within the sample tubes that prevents the violent boiling (known as "bumping") that can lead to sample loss or cross-contamination.
They are ideal for high-throughput processing of many small-volume samples at once, such as those in microplates or small vials, making them essential in genomics, proteomics, and drug discovery.
Nitrogen (Blowdown) Evaporators
These devices work by directing a steady stream of an inert gas, typically nitrogen, over the surface of the liquid samples.
The gas flow disrupts the layer of air saturated with solvent vapor that forms directly above the liquid, which significantly accelerates the rate of natural evaporation.
This method is often used for concentrating small batches of samples in vials where a full vacuum system is not necessary or practical.
Understanding the Trade-offs
No single evaporator is perfect for every task. The choice involves balancing competing factors of speed, sample integrity, and scale.
Speed vs. Gentleness
Generally, faster evaporation methods involving more heat or a deeper vacuum can be harsher on delicate samples.
A specialized technique like freeze-drying (lyophilization), which removes a frozen solvent via sublimation (solid to gas), is the gentlest method available but is also the slowest and most complex.
Throughput vs. Volume
Centrifugal evaporators excel at high throughput (many small samples), while rotary evaporators are built for processing a single, larger volume sample.
Nitrogen blowdown systems fall in between, handling a moderate number of small-volume samples simultaneously without the complexity of a high-vacuum system.
Complexity and Cost
A simple nitrogen blowdown system is relatively inexpensive and easy to operate.
Rotary and centrifugal systems represent a larger investment, requiring integrated vacuum pumps, chillers, and more complex glassware that reflect their enhanced capabilities and control.
Selecting the Right Evaporator for Your Application
Choosing the correct technology depends entirely on the nature of your sample and your experimental goal.
- If your primary focus is synthesizing or purifying a single compound in volumes over 50 mL: A rotary evaporator (rotovap) is the standard and most effective tool.
- If your primary focus is concentrating dozens or hundreds of small samples from microplates or vials: A centrifugal evaporator is the superior choice for high throughput and preventing cross-contamination.
- If your primary focus is gently drying highly sensitive biological samples like proteins or bacteria: A freeze dryer (lyophilizer) is essential to preserve their structure and activity.
- If your primary focus is quickly concentrating a small batch of chemically robust samples: A nitrogen blowdown evaporator offers a simple and cost-effective solution.
By matching the evaporator's mechanism to your specific needs for volume, throughput, and sample sensitivity, you ensure efficient and reliable results in your work.
Summary Table:
| Evaporator Type | Ideal For | Key Mechanism |
|---|---|---|
| Rotary Evaporator (Rotovap) | Single, medium-to-large volume samples (50mL+), synthesis, purification | Rotation + Heat + Vacuum |
| Centrifugal Evaporator | High-throughput, many small-volume samples (vials, microplates) | Centrifugal Force + Vacuum + Heat |
| Nitrogen Blowdown | Small batches of chemically robust samples, simple concentration | Inert Gas (N₂) Flow + Mild Heat |
| Freeze Dryer (Lyophilizer) | Extremely sensitive biological samples (proteins, bacteria) | Sublimation (Frozen to Gas) under Vacuum |
Streamline Your Sample Preparation with KINTEK
Choosing the right evaporation technology is critical for the integrity of your samples and the efficiency of your workflow. Whether you are purifying compounds, concentrating solutions for analysis, or preparing sensitive biological samples, KINTEK has the right laboratory evaporator for your needs.
Our experts are ready to help you select the ideal system—from robust rotary evaporators to high-throughput centrifugal concentrators—ensuring you achieve reliable and gentle solvent removal.
Contact us today to discuss your application and get a personalized recommendation. Let KINTEK, your trusted partner in lab equipment, enhance your research capabilities.
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Evaporation Crucible for Organic Matter
- Circulating Water Vacuum Pump for Laboratory and Industrial Use
- Molybdenum Tungsten Tantalum Evaporation Boat for High Temperature Applications
- Ceramic Evaporation Boat Set Alumina Crucible for Laboratory Use
- Electron Beam Evaporation Coating Conductive Boron Nitride Crucible BN Crucible
People Also Ask
- How is the concept of a vessel utilized to define the boundary of a contained substance in laboratory equipment?
- What are the factors that affect heat transfer? Master the Key Variables for Optimal Thermal Performance
- What are the risks associated with the sintering process? Key Strategies to Prevent Failure & Maximize Quality
- How is sputtering done? A Step-by-Step Guide to Thin Film Deposition
- What are the applications of stainless steel? Unlock Its Versatility for Your Project
- How does sintering work? A Guide to Atomic Bonding and Material Densification
- What thickness is magnetron sputtering for coating? Achieve Precise, Functional Thin Films
- What is the difference between induction heating and resistance heating? A Guide to Choosing the Right Method



















