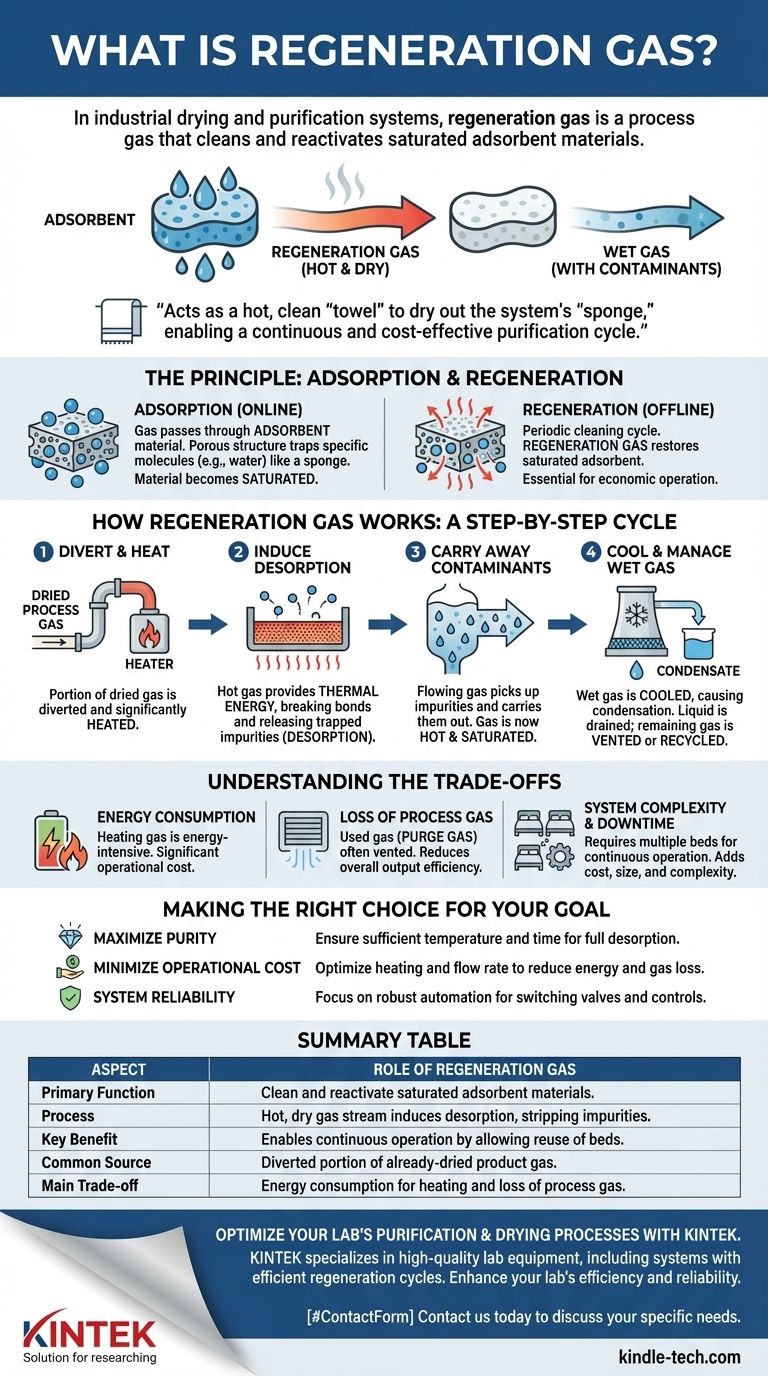
In industrial drying and purification systems, regeneration gas is a specific stream of gas used to clean and reactivate a material that has become saturated with contaminants. Typically, a portion of the already-dried product gas is diverted, heated, and then passed over a saturated filter bed (like a desiccant). This hot, dry gas strips away the trapped impurities, such as water, effectively "regenerating" the filter bed so it can be used again.
Regeneration gas is not a unique chemical substance, but rather a process gas assigned a specific task: to restore a saturated adsorbent material. It acts as a hot, clean "towel" to dry out the system's "sponge," enabling a continuous and cost-effective purification cycle.

The Principle: Adsorption and Regeneration
To understand regeneration gas, you must first understand the process it enables. Most large-scale gas drying systems use a process called adsorption, which requires a periodic cleaning or "regeneration" cycle.
The Role of Adsorbent Materials
Many industrial processes require removing impurities, like water vapor, from a gas stream. This is often done by passing the gas through a vessel filled with an adsorbent material, such as a desiccant or molecular sieve.
These materials have a porous structure that acts like a sponge, trapping specific molecules (the adsorbate, e.g., water) on their surface while letting the desired process gas pass through.
Reaching Saturation
This adsorbent "sponge" has a finite capacity. Over time, its surface becomes filled with the trapped impurity molecules. When it can't hold any more, it is considered saturated.
At this point, the adsorbent bed is no longer effective, and unwanted impurities will begin to pass through with the product gas.
The Need for Regeneration
Replacing the saturated adsorbent material after every cycle would be extremely expensive. Instead, it is far more economical to clean and reuse it.
This process of cleaning the adsorbent bed by removing the trapped contaminants is called regeneration. This is the critical function performed by the regeneration gas.
How Regeneration Gas Works: A Step-by-Step Cycle
The regeneration process is a carefully controlled cycle that temporarily takes an adsorbent bed offline to restore it.
Step 1: Divert and Heat the Gas
A small portion of the main process gas that has already been dried is diverted from the primary flow. This dry gas stream is then passed through a heater, significantly raising its temperature.
Step 2: Induce Desorption
This hot, extremely dry gas is then channeled through the saturated adsorbent bed. The heat provides the thermal energy required to break the bonds between the trapped impurity molecules (e.g., water) and the adsorbent surface.
This release of trapped molecules is called desorption.
Step 3: Carry Away Contaminants
As the impurities are released, the flowing regeneration gas picks them up and carries them out of the adsorbent vessel. The gas, which entered hot and dry, is now hot and saturated with the very contaminants it removed.
Step 4: Cool and Manage the Wet Gas
After exiting the vessel, this wet regeneration gas is cooled. As it cools, the water vapor it was carrying condenses into a liquid and can be drained from the system. The remaining gas is then either vented or recompressed and returned to the main process upstream.
Understanding the Trade-offs
While regeneration is essential for economic operation, it comes with inherent costs and design considerations that must be managed.
Energy Consumption
Heating the regeneration gas is an energy-intensive process. This represents one of the most significant operational costs for a gas dehydration unit. The temperature, pressure, and flow rate must be carefully optimized to ensure complete regeneration without wasting energy.
Loss of Process Gas
The gas used for regeneration is often called purge gas. In many systems, this gas is vented from the process after use. This constitutes a direct loss of valuable product and reduces the overall output efficiency of the plant. More complex systems may include equipment to recover and recycle this gas, but that adds capital cost.
System Complexity and Downtime
Because an adsorbent bed cannot dry the process gas while it is being regenerated, these systems almost always require at least two parallel beds. One bed is "online" performing adsorption, while the other is "offline" undergoing regeneration. This dual-bed design adds to the system's cost, size, and complexity.
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
The design and operation of a regeneration gas system depend entirely on balancing performance, cost, and efficiency.
- If your primary focus is maximizing purity: Ensure the regeneration temperature and time are sufficient to fully desorb contaminants, preventing them from impacting your product during the next operational cycle.
- If your primary focus is minimizing operational cost: The key is to optimize the heating and flow rate of the regeneration gas to reduce energy consumption and purge gas loss.
- If your primary focus is system reliability: Focus on robust automation for the switching valves and controls that manage the cycle between the online and regenerating beds, as this is a frequent point of failure.
Ultimately, mastering the use of regeneration gas is fundamental to running an efficient and effective continuous purification system.
Summary Table:
| Aspect | Role of Regeneration Gas |
|---|---|
| Primary Function | To clean and reactivate saturated adsorbent materials (e.g., desiccants). |
| Process | A hot, dry gas stream induces desorption, stripping away trapped impurities like water. |
| Key Benefit | Enables continuous operation by allowing adsorbent beds to be reused instead of replaced. |
| Common Source | A diverted portion of the already-dried product gas. |
| Main Trade-off | Involves energy consumption for heating and a loss of process gas (purge gas). |
Optimize your lab's purification and drying processes with KINTEK.
Just as industrial systems rely on regeneration gas for efficient, continuous operation, your laboratory needs reliable equipment to maintain purity and control costs. KINTEK specializes in high-quality lab equipment and consumables, including systems that incorporate efficient regeneration cycles for desiccants and filters.
We understand the balance between achieving superior purity and managing operational expenses. Our solutions are designed to enhance your lab's efficiency and reliability.
Contact us today using the form below to discuss how we can support your specific laboratory needs.
[#ContactForm]
Visual Guide
Related Products
- RF PECVD System Radio Frequency Plasma-Enhanced Chemical Vapor Deposition RF PECVD
- Single Punch Electric Tablet Press Machine Laboratory Powder Tablet Punching TDP Tablet Press
- Cylindrical Resonator MPCVD Machine System Reactor for Microwave Plasma Chemical Vapor Deposition and Lab Diamond Growth
- Gold Disc Electrode
- Molybdenum Disilicide (MoSi2) Thermal Elements Electric Furnace Heating Element
People Also Ask
- What is the plasma CVD process? Achieve Low-Temperature Thin Film Deposition
- What is plasma enhanced? A Guide to Low-Temperature, High-Precision Manufacturing
- What is the temperature of PECVD deposition? Achieve High-Quality Films at Low Temperatures
- Why does PECVD commonly use RF power input? For Precise Low-Temperature Thin Film Deposition
- What are the uses of PECVD? A Guide to Low-Temperature Thin-Film Deposition













