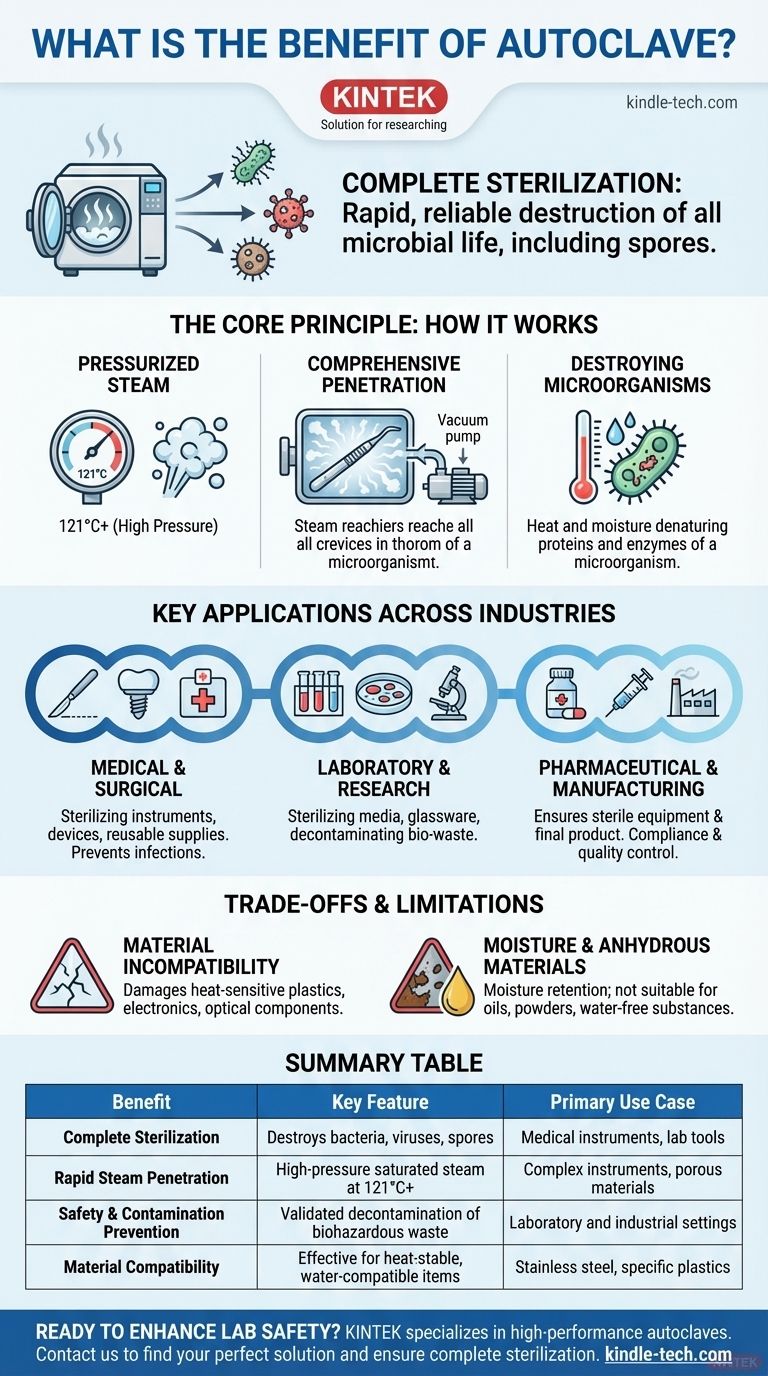
The primary benefit of an autoclave is its ability to provide rapid, reliable, and complete sterilization of materials using high-pressure saturated steam. This method is highly effective at destroying all forms of microbial life, including resilient bacteria and spores, making it an indispensable tool in medical, laboratory, and industrial settings for ensuring safety and preventing contamination.
An autoclave's core value lies in its use of pressurized steam to achieve a level of sterilization that dry heat or chemical agents often cannot. However, its effectiveness is entirely dependent on using it with compatible materials, as its high heat and moisture can damage sensitive items.

The Core Principle: How an Autoclave Achieves Sterilization
An autoclave is more than just a heater; it is a precisely engineered pressure vessel designed to harness the sterilizing power of steam. Its effectiveness comes from a combination of high temperature, direct steam contact, and pressure.
Pressurized Steam as the Active Agent
The key to an autoclave's function is saturated steam under pressure. Increasing the pressure within the chamber allows water to exist as steam at temperatures well above its normal boiling point (100°C or 212°F), typically reaching 121°C or higher.
This high-temperature steam is far more effective at transferring thermal energy than dry air, allowing it to rapidly denature the essential proteins and enzymes that microorganisms need to survive.
Comprehensive Penetration
A critical advantage of steam is its ability to penetrate materials and reach all surfaces of the items being sterilized. Many modern autoclaves include a vacuum system that removes air from the chamber before steam is injected.
This ensures there are no insulating air pockets, allowing steam to make direct contact with every part of complex instruments, hollow tubes, and porous materials like surgical dressings.
Destroying Resilient Microorganisms
The combination of heat and moisture is exceptionally effective at killing a wide spectrum of microbial life. This includes not just active bacteria and viruses but also their highly resistant dormant forms, known as spores, which are often impervious to simple boiling or chemical disinfectants.
Key Applications Across Industries
The autoclave's reliability has made it a foundational piece of equipment in any field where sterility is non-negotiable. Its applications are broad and critical for public and product safety.
Medical and Surgical Environments
In healthcare, autoclaves are used to sterilize surgical instruments, implantable medical devices, and reusable supplies. This process is fundamental to preventing post-operative infections and ensuring patient safety.
Laboratory and Research Settings
Microbiology, veterinary science, and research labs rely on autoclaves for sterilizing microbial growth media, glassware, and laboratory tools. They are also used for the critical step of decontaminating biohazardous waste before disposal.
Pharmaceutical and Manufacturing
In the production of pharmaceuticals and other sterile products, autoclaves ensure that both the equipment and the final product are free from microbial contamination. This is a core component of regulatory compliance and quality control.
Understanding the Trade-offs and Limitations
While highly effective, an autoclave is not a universal solution. Understanding its limitations is crucial for safe and effective operation, as improper use can damage valuable equipment.
Material Incompatibility
The primary drawback is that the high heat and moisture will damage or destroy heat-sensitive materials. This includes most plastics, electronics, and certain optical components. Only stainless steel and specific high-temperature-rated plastics can be safely processed.
The Problem of Moisture
The steam-based process inevitably leaves sterilized items with moisture retention. While often not an issue, it can promote corrosion on susceptible metals like carbon steel and may require a post-sterilization drying phase for certain applications.
Ineffective for Anhydrous Materials
An autoclave is not suitable for sterilizing materials that repel water or cannot be penetrated by steam. This includes oils, powders, and other water-free (anhydrous) substances, which require dry-heat sterilization or other methods instead.
Making the Right Choice for Your Sterilization Needs
Selecting the correct sterilization method depends entirely on the material you are processing and your operational goal. The autoclave is a powerful tool when used within its proper context.
- If your primary focus is sterilizing robust surgical tools or lab glassware: The autoclave is the gold standard, offering unmatched speed, reliability, and penetration.
- If your primary focus is decontaminating biohazardous waste: The autoclave provides a safe, economical, and validated method for rendering biological waste inert before disposal.
- If your primary focus is sterilizing heat-sensitive plastics, electronics, or powders: You must explore alternative methods, as an autoclave will cause irreversible damage to these items.
Ultimately, mastering sterilization requires understanding that the autoclave is the definitive solution for heat-stable, water-compatible materials, but not for everything.
Summary Table:
| Benefit | Key Feature | Primary Use Case |
|---|---|---|
| Complete Sterilization | Destroys bacteria, viruses, and spores | Medical instruments, lab tools |
| Rapid Steam Penetration | High-pressure saturated steam at 121°C+ | Complex instruments, porous materials |
| Safety & Contamination Prevention | Validated decontamination of biohazardous waste | Laboratory and industrial settings |
| Material Compatibility | Effective for heat-stable, water-compatible items | Stainless steel, specific plastics |
Ready to enhance your lab's safety and efficiency with reliable sterilization? KINTEK specializes in high-performance autoclaves and lab equipment designed for medical, research, and industrial applications. Contact us today to find the perfect autoclave solution for your needs and ensure complete peace of mind in your sterilization processes.
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Laboratory Sterilizer Lab Autoclave Vertical Pressure Steam Sterilizer for Liquid Crystal Display Automatic Type
- Laboratory Sterilizer Lab Autoclave Pulse Vacuum Lifting Sterilizer
- Laboratory Test Sieves and Sieving Machines
- Benchtop Laboratory Freeze Dryer for Lab Use
- Benchtop Laboratory Vacuum Freeze Dryer
People Also Ask
- Why is temperature important in sterilization? Achieve Complete Microbial Destruction
- What is the role of high-pressure high-level autoclaves in simulating 9Cr–1Mo steel reactions? Expert Insights
- What is an autoclave laboratory equipment? The Ultimate Guide to Steam Sterilization
- What reaction conditions are provided by a high-pressure autoclave? Unlock Superior Nanocrystal Synthesis Control
- Why are high-temperature and high-pressure reactors (autoclaves) essential for friction and wear tests? Get Real Data
- What is the most effective method for sterilization of laboratory materials? Choose the Right Method for Your Lab
- What are the performance requirements for an autoclave used in OHPMP? Precision Solutions for High-Pressure Synthesis
- What is the usual temperature of an autoclave? Master the 121°C Standard for Effective Sterilization



















