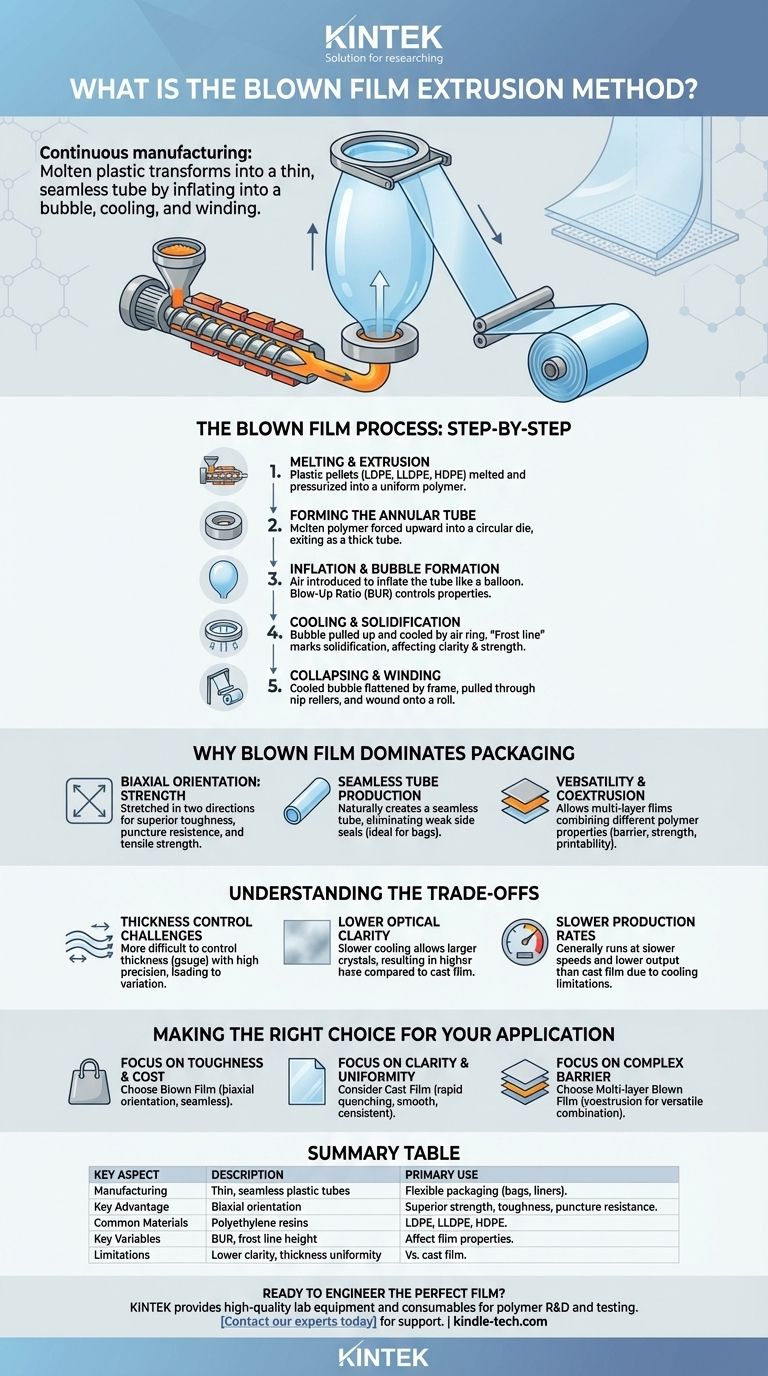
At its core, blown film extrusion is a continuous manufacturing process that transforms molten plastic into a thin, seamless tube of film. This is achieved by melting plastic resin, forcing it through a circular die to form a thin-walled tube, and then inflating this tube with air into a large bubble. This bubble is then cooled, collapsed, and wound into rolls.
The essence of blown film extrusion is not just melting and forming plastic, but simultaneously stretching it in two directions. This biaxial orientation is what gives the final film its characteristic strength and toughness, making it indispensable for flexible packaging applications.

The Blown Film Process: A Step-by-Step Breakdown
To truly understand the method, it's best to visualize it as a vertical assembly line, moving from the ground up. Each stage directly impacts the final properties of the film.
Step 1: Melting and Extrusion
Plastic pellets, typically polyethylene (LDPE, LLDPE, HDPE), are fed from a hopper into the barrel of an extruder. A rotating screw inside the heated barrel conveys, melts, and pressurizes the plastic resin into a uniform molten polymer.
Step 2: Forming the Annular Tube
The molten polymer is then forced upward into an annular (circular) die. As it exits the die lips, it forms a thick, continuous tube of molten plastic.
Step 3: Inflation and Bubble Formation
Air is introduced through a hole in the center of the die, inflating the molten tube like a long, continuous balloon. The ratio of the final bubble diameter to the die diameter is known as the Blow-Up Ratio (BUR), a critical parameter for controlling film properties.
Step 4: Cooling and Solidification
As the bubble is pulled upward, it is cooled by a high-velocity air ring mounted on top of the die. The point at which the molten polymer crystallizes and becomes a solid film is visible as a "frost line." The height of this frost line is another key variable affecting the film's clarity and strength.
Step 5: Collapsing and Winding
Further up the tower, the cooled bubble is guided through a collapsing frame that flattens it into a lay-flat tube. This flat tube is then pulled through a set of nip rollers and wound onto a large roll for subsequent processing, like printing or bag-making.
Why Blown Film Dominates Packaging
The popularity of this method is not accidental; it is a direct result of the unique properties it imparts to the film.
Biaxial Orientation: The Source of Strength
By stretching the film both in the machine direction (pulling it upward) and the transverse direction (inflating it), the polymer chains become oriented in two directions. This biaxial orientation creates a film with balanced, superior toughness, puncture resistance, and tensile strength compared to non-oriented films.
Seamless Tube Production
The process naturally creates a seamless tube. This is a major advantage for producing items like grocery sacks, trash bags, and industrial liners, as it eliminates the need for side seals, which are often the weakest point of a bag.
Versatility and Coextrusion
Modern blown film lines can use multiple extruders feeding a single die to produce multi-layer films. This process, called coextrusion, allows manufacturers to combine the properties of different polymers—for example, a barrier layer for food preservation, a strength layer for durability, and a print-receptive outer layer.
Understanding the Trade-offs
No process is perfect. Objectivity requires acknowledging where blown film has limitations compared to its primary alternative, cast film extrusion.
Thickness Control Challenges
Due to the nature of inflating a free-standing bubble, controlling the film's thickness (gauge) with high precision is more difficult than in other processes. This results in greater gauge variation across the film web.
Lower Optical Clarity
The relatively slow air-cooling process allows for larger crystal structures to form within the polymer. This increased crystallinity leads to higher haze and lower clarity compared to cast film, which is rapidly quenched on a chilled roller.
Slower Production Rates
Generally, blown film lines run at slower speeds and have lower output rates than cast film lines of a similar width. The cooling process is often the limiting factor.
Making the Right Choice for Your Application
Selecting the correct film manufacturing process depends entirely on the performance requirements of your final product.
- If your primary focus is toughness and cost-effective bag production: Blown film is the superior choice due to its biaxial orientation and seamless tube format.
- If your primary focus is optical clarity and precise thickness uniformity: You should consider cast film extrusion, as its rapid quenching provides a smoother, clearer, and more consistent product.
- If your primary focus is creating a complex barrier film: Multi-layer blown film (coextrusion) offers a versatile and cost-effective way to combine different polymer functions into a single structure.
Ultimately, mastering the blown film process means manipulating a delicate balance of heat, air, and speed to engineer the precise film properties your application demands.
Summary Table:
| Key Aspect | Description |
|---|---|
| Primary Use | Manufacturing thin, seamless plastic tubes for flexible packaging (e.g., bags, liners). |
| Key Advantage | Biaxial orientation for superior strength, toughness, and puncture resistance. |
| Common Materials | Polyethylene resins (LDPE, LLDPE, HDPE). |
| Key Process Variables | Blow-Up Ratio (BUR), frost line height. |
| Limitations | Lower optical clarity and thickness uniformity vs. cast film. |
Ready to engineer the perfect film for your packaging needs? The blown film process requires precise control of materials and equipment to achieve optimal strength and performance. At KINTEK, we specialize in supplying high-quality laboratory equipment and consumables essential for polymer research and development, including testing and analysis tools that help optimize your extrusion process. Whether you're developing new film formulations or ensuring quality control, our solutions support your innovation from lab to production. Contact our experts today to discuss how we can support your laboratory's contribution to advanced packaging solutions.
Visual Guide
Related Products
- HFCVD Machine System Equipment for Drawing Die Nano-Diamond Coating
- Anti-Cracking Press Mold for Lab Use
- Benchtop Laboratory Vacuum Freeze Dryer
- Small Injection Molding Machine for Lab Use
- Laboratory Test Sieves and Sieving Machines
People Also Ask
- What is the use of two roll mill? Essential for Polymer Mixing, R&D, and Quality Control
- Is co-extrusion the same as dual extrusion? Unlock the Power of Multi-Material Plastic Profiles
- What is the process of double extrusion? Create Integrated Multi-Material Components
- What are the different types of internal mixers? Choose Between Tangential & Intermeshing Rotors
- What is the process of multilayer co extrusion? Engineer High-Performance Composite Materials
- What are the disadvantages of blown film extrusion? Overcoming Precision and Speed Limitations
- What machine makes molding? Injection Molding Machines for Mass Production
- How many types of rolling mills are there? A Guide to Roll Configurations & Capabilities



















