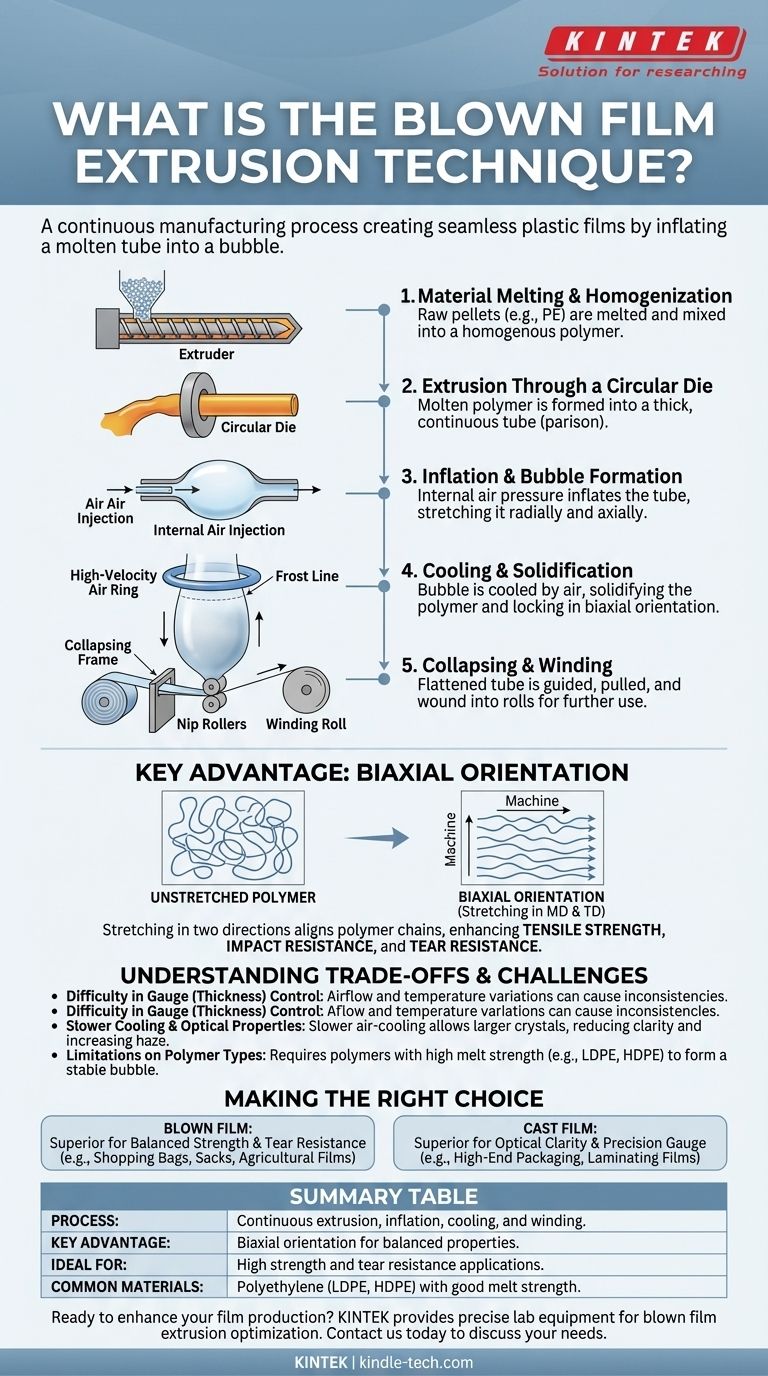
In manufacturing, blown film extrusion is a continuous process used to create seamless plastic films. It involves melting a thermoplastic material, forcing it through a circular die to form a thick tube, and simultaneously inflating that tube with air into a large, thin-walled bubble. This bubble is then cooled, collapsed, and wound onto a roll.
The critical advantage of this method is that it stretches the plastic in two directions at once—radially and axially. This biaxial orientation aligns the polymer chains, creating a film with balanced, superior mechanical properties like strength and tear resistance compared to other processes.

The Step-by-Step Blown Film Process
To understand the unique properties of blown film, it's essential to visualize its journey from raw material to finished product. The entire process occurs vertically, often in towers several stories high.
Step 1: Material Melting and Homogenization
The process begins with raw plastic pellets, typically a polyolefin like polyethylene (PE), being fed from a hopper into the barrel of an extruder. A rotating screw inside the barrel conveys, heats, and melts the plastic, creating a homogenous molten polymer.
Step 2: Extrusion Through a Circular Die
This molten plastic is then forced through a circular die. The die forms the material into a thick-walled, continuous tube of molten polymer, which is known as the parison.
Step 3: Inflation and Bubble Formation
As the tube exits the die, air is injected into its center through an opening in the die. This internal air pressure inflates the molten tube, much like a long, continuous balloon. This step stretches the film both circumferentially (radially) and in the direction of travel (axially).
Step 4: Cooling and Solidification
The bubble travels upward, continuously cooled by a high-velocity air ring mounted on top of the die. The point at which the polymer solidifies is called the frost line—you can often see it as a transition from a clear to a hazy appearance. Cooling locks the polymer molecules into their biaxially oriented state.
Step 5: Collapsing and Winding
After cooling, the bubble is guided through a collapsing frame that carefully flattens the tube. This flattened tube is then pulled through nip rollers and finally wound onto large rolls for subsequent processing, such as printing or bag-making.
Why Biaxial Orientation is the Key Advantage
The simple act of inflating the bubble is what gives blown film its most important characteristics. It's a concept that directly impacts the final product's performance.
The Impact on Molecular Structure
Without stretching, polymer chains are randomly coiled. The two-way stretching during inflation forces these chains to align in both the machine direction (MD) and the transverse direction (TD). This organized structure is what we call biaxial orientation.
The Resulting Material Properties
This molecular alignment dramatically enhances the film's physical properties. It results in a more balanced material with higher tensile strength, impact resistance, and tear resistance in all directions, making it ideal for applications that require durability, such as grocery bags or heavy-duty sacks.
Understanding the Trade-offs and Challenges
While powerful, the blown film process is not without its complexities and limitations. Objectivity requires acknowledging where other methods may be superior.
Difficulty in Gauge (Thickness) Control
Maintaining a perfectly uniform film thickness across the entire width of the bubble is more challenging in blown film than in cast film extrusion. The airflow and temperature variations can lead to slight gauge bands or inconsistencies.
Slower Cooling and Optical Properties
The air-cooling process is significantly slower than the chill-roll quenching used in cast film. This slower cooling allows for larger crystal structures to form in the polymer, which can reduce the film's clarity and increase its haze.
Limitations on Polymer Types
The process requires a polymer with sufficient melt strength to form a stable bubble without collapsing. This is why the technique is dominated by materials like Low-Density Polyethylene (LDPE) and High-Density Polyethylene (HDPE), while materials with low melt strength are unsuitable.
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
The decision between blown film and other processes, like cast film, depends entirely on the end-use requirements of your product.
- If your primary focus is balanced strength and tear resistance: Blown film is the superior choice for applications like shopping bags, construction sheeting, and agricultural films where durability is paramount.
- If your primary focus is exceptional optical clarity and precise thickness control: You should consider cast film extrusion, which is preferred for high-end packaging overwraps and laminating films.
- If your primary focus is producing seamless tubing: Blown film is the only practical method, as it naturally creates a continuous tube ideal for making bags with only a bottom seal.
Ultimately, understanding the relationship between the inflation process and the resulting molecular orientation is the key to leveraging this technique effectively.
Summary Table:
| Key Aspect | Details |
|---|---|
| Process | Continuous extrusion of a molten plastic tube, inflated into a bubble, then cooled and wound. |
| Key Advantage | Biaxial orientation (stretching in two directions) for balanced mechanical properties. |
| Ideal For | Applications requiring high strength and tear resistance (e.g., bags, sacks, agricultural films). |
| Common Materials | Polyethylene (LDPE, HDPE) and other polymers with good melt strength. |
Ready to enhance your film production with superior strength and durability?
The blown film process is key to creating high-performance plastic films. At KINTEK, we specialize in providing the precise lab equipment and consumables needed to develop, test, and optimize your blown film extrusion processes. Whether you are researching new materials or ensuring quality control, our solutions help you achieve the perfect balance of properties for your target application.
Contact us today using the form below to discuss how we can support your laboratory's specific needs in polymer processing and film analysis.
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Lab Plastic PVC Calender Stretch Film Casting Machine for Film Testing
- Anti-Cracking Press Mold for Lab Use
- HFCVD Machine System Equipment for Drawing Die Nano-Diamond Coating
- Laboratory Sterilizer Lab Autoclave Vertical Pressure Steam Sterilizer for Liquid Crystal Display Automatic Type
- Laboratory Test Sieves and Sieving Machines
People Also Ask
- What is the process of double extrusion? Create Integrated Multi-Material Components
- What is the meaning of blowing film? A Guide to Biaxial Orientation and Stronger Plastic Films
- What products are blown film extrusion? From Grocery Bags to Industrial Sheeting
- What is the difference between calendaring and calendering? Master the Key Spelling and Context
- What is the cost of blown film extrusion? From $20K to High-End Systems



















