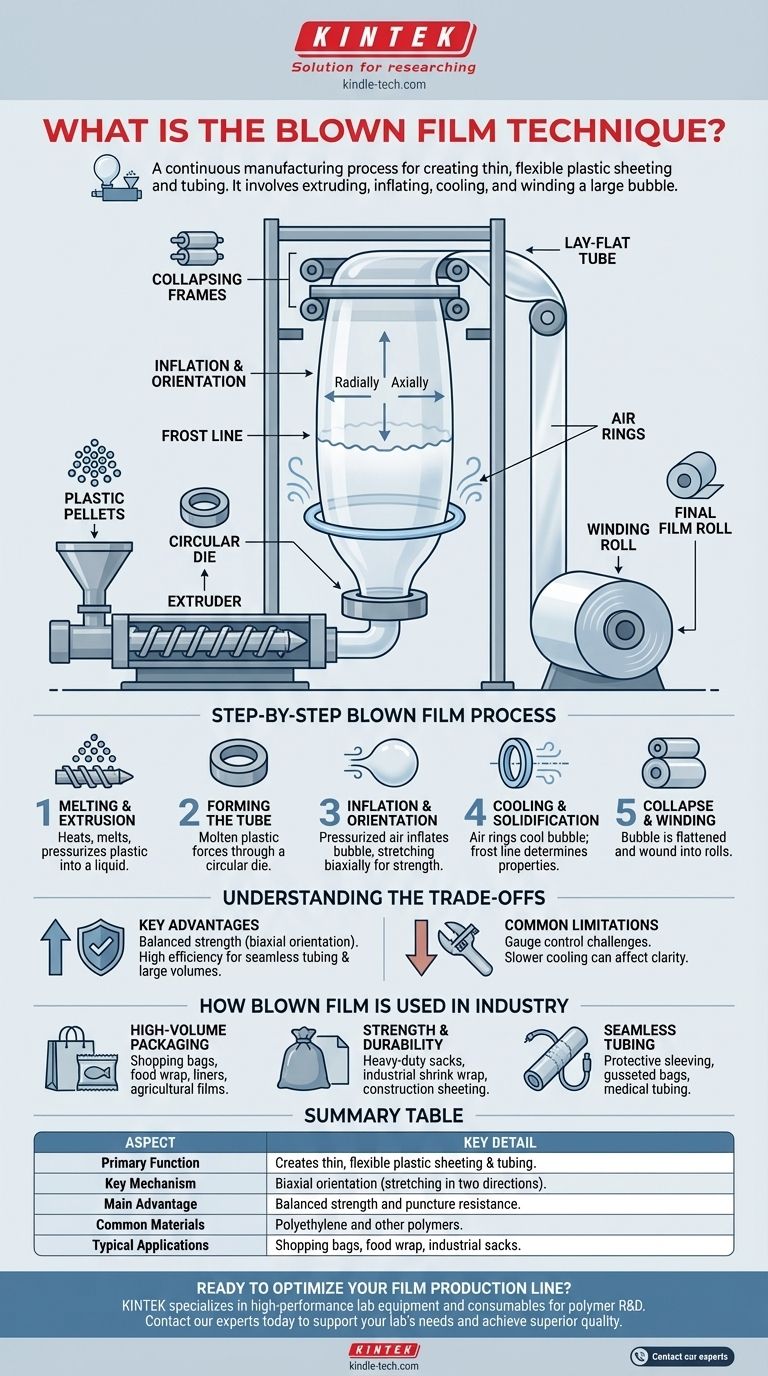
At its core, the blown film technique is a continuous manufacturing process used to create thin, flexible plastic sheeting and tubing. It involves extruding molten plastic through a circular die, inflating it with air to form a large, thin-walled bubble, and then cooling and collapsing this bubble to be collected on a roll.
The true significance of the blown film process lies in how it simultaneously forms and orients the plastic. By stretching the material in two directions as the bubble expands, the process imparts balanced mechanical strength, making it ideal for a vast range of high-volume packaging applications.

The Step-by-Step Blown Film Process
To understand how blown film works, it's best to visualize it as a controlled, continuous method of blowing and solidifying a plastic bubble vertically.
Step 1: Melting and Extrusion
The process begins with solid plastic pellets, typically a polymer like polyethylene. These pellets are fed into an extruder, where a rotating screw heats, melts, and pressurizes the plastic into a consistent, homogenous liquid.
Step 2: Forming the Tube
This molten plastic is then forced upwards through a circular die. The die shapes the melt into a thick-walled tube, which is the initial form of the final film.
Step 3: Inflation and Orientation
As the tube exits the die, pressurized air is injected into its center. This air inflates the tube, much like blowing a soap bubble. This expansion stretches the plastic both radially (around its circumference) and axially (along its length).
This biaxial orientation is the most critical part of the process. It aligns the long-chain polymer molecules in two directions, which is what gives the final film its characteristic strength and flexibility.
Step 4: Cooling and Solidification
As the bubble expands upwards, it is cooled by one or more external air rings that blow a high volume of air onto its surface. The point where the plastic solidifies and turns from transparent to hazy is known as the frost line.
The height of this frost line is a critical control parameter. It determines the final properties of the film, such as its clarity, stiffness, and tear resistance.
Step 5: Collapse and Winding
Once the bubble is sufficiently cooled and solidified, it continues to travel upwards, often for several stories in a production tower. At the top, collapsing frames or nip rollers gently flatten the bubble into a lay-flat tube.
This flattened tube is then wound into large rolls. It can be kept as a seamless tube for applications like liners or bags, or it can be slit along one or both edges to create one or two sheets of flat film.
Understanding the Trade-offs
Like any manufacturing process, blown film has distinct advantages and limitations that make it suitable for specific applications.
Key Advantages
The primary benefit is balanced strength. The biaxial orientation provides excellent tensile strength and puncture resistance in both the machine and transverse directions.
This process is also highly efficient for producing seamless tubing and can achieve very high output rates, making it cost-effective for large-volume products.
Common Limitations
Achieving a perfectly uniform film thickness, or gauge control, can be more challenging with blown film compared to other methods like cast film.
The cooling process is also slower than in casting. This can sometimes result in lower optical clarity and a softer feel, though modern techniques have significantly improved these properties.
How Blown Film is Used in Industry
The unique properties imparted by this process make it a cornerstone of the flexible packaging and construction industries. Your choice to use it depends entirely on your end-product requirements.
- If your primary focus is high-volume packaging: Blown film is the dominant method for creating shopping bags, food wrap, trash can liners, and agricultural films.
- If your primary focus is material strength and durability: The process is ideal for heavy-duty sacks, industrial shrink wrap, and construction sheeting where puncture resistance is critical.
- If your primary focus is seamless tubing: It is the go-to method for producing protective sleeving for products, gusseted bags, and medical tubing.
By controlling the inflation and cooling of a simple plastic tube, the blown film process provides an elegant and efficient solution for creating essential materials that define modern commerce.
Summary Table:
| Aspect | Key Detail |
|---|---|
| Primary Function | Creates thin, flexible plastic sheeting and tubing. |
| Key Mechanism | Biaxial orientation (stretching in two directions). |
| Main Advantage | Balanced strength and puncture resistance. |
| Common Materials | Polyethylene and other polymers. |
| Typical Applications | Shopping bags, food wrap, industrial sacks, construction sheeting. |
Ready to optimize your film production line? KINTEK specializes in high-performance lab equipment and consumables for polymer research and development. Whether you are testing new materials or scaling up your blown film process, our solutions deliver the precision and reliability you need. Contact our experts today to discuss how we can support your laboratory's specific requirements and help you achieve superior product quality.
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Lab Blown Film Extrusion Three Layer Co-Extrusion Film Blowing Machine
- Lab Plastic PVC Calender Stretch Film Casting Machine for Film Testing
- Aluminum-Plastic Flexible Packaging Film for Lithium Battery Packaging
- Inclined Rotary Plasma Enhanced Chemical Vapor Deposition PECVD Equipment Tube Furnace Machine
- Powerful Plastic Crusher Machine
People Also Ask
- What does a blown film machine do? Transform Plastic Pellets into Versatile Film
- How does extrusion work step by step? A Guide to the Continuous Manufacturing Process
- What is multilayer blown film? Engineered Packaging for Superior Performance
- What is the use of a blown film machine? To Produce Strong, Versatile Plastic Films for Packaging
- What are the disadvantages of the extrusion process? High Costs and Geometric Limits Explained



















