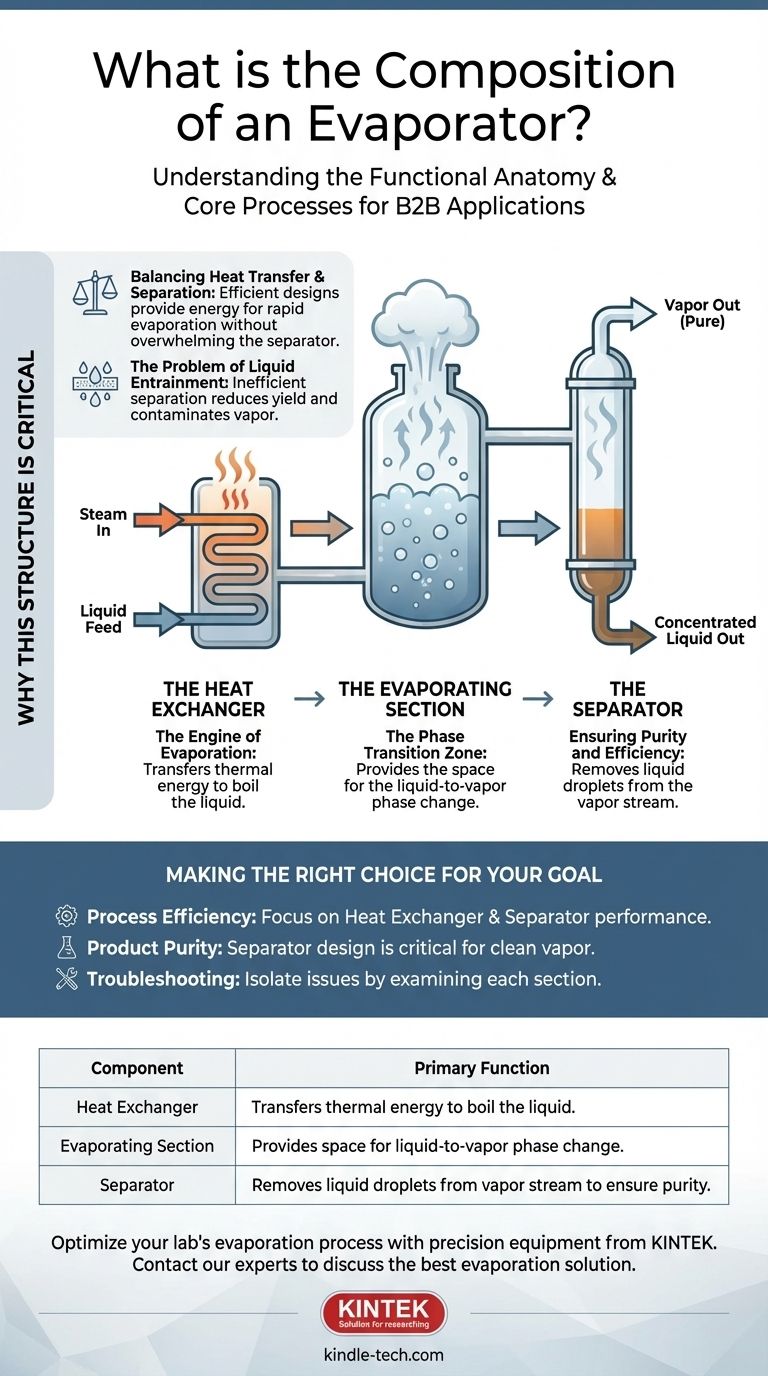
At its core, an evaporator is a purpose-built system designed to transform a liquid into a vapor. A typical evaporator is not a single component but is composed of three primary functional sections: the heat exchanger, the evaporating section where the liquid boils, and the separator, which divides the resulting vapor from the remaining liquid.
An evaporator is best understood as a coordinated process, not just a piece of equipment. Its design is singularly focused on two critical tasks: first, efficiently injecting energy to create vapor, and second, cleanly separating that vapor from the liquid it came from.

The Functional Anatomy of an Evaporator
While designs vary, the operation of any evaporator relies on three distinct functional stages. Understanding the role of each stage is key to understanding the entire process of concentration and separation.
The Heat Exchanger: The Engine of Evaporation
The heat exchanger is the component responsible for supplying the thermal energy required for evaporation. It transfers heat from a heating medium, often steam, into the liquid solution that needs to be concentrated.
Its sole purpose is to raise the temperature of the liquid to its boiling point, providing the latent heat necessary for the phase change from liquid to vapor.
The Evaporating Section: The Phase Transition Zone
This is the physical space where the actual boiling and evaporation occur. Once the heat exchanger has brought the liquid to its boiling point, this section provides the volume for vapor bubbles to form and rise.
In many common designs, the heat exchanger and the evaporating section are tightly integrated. For example, in a shell-and-tube evaporator, the liquid boils inside the tubes, which are themselves the heat exchange surface.
The Separator: Ensuring Purity and Efficiency
The separator performs the final, critical step: physically partitioning the vapor stream from the now-concentrated liquid. As the mixture boils, droplets of liquid can become suspended in the vapor stream, a phenomenon known as entrainment.
The separator is designed to remove these entrained droplets, ensuring that the vapor leaving the system is pure and that the valuable concentrated liquid is not lost. This component is essential for both product quality and process efficiency.
Why This Three-Part Structure is Critical
The effectiveness of any evaporator hinges on how well these three sections work in concert. The design is a careful balance of competing physical demands that dictate the overall performance of the system.
Balancing Heat Transfer and Separation
A primary design challenge is to maximize the rate of heat transfer to induce rapid boiling. However, overly vigorous boiling can make it much more difficult for the separator to effectively remove liquid droplets from the vapor stream.
An efficient design provides enough energy for rapid evaporation without overwhelming the separation process.
The Problem of Liquid Entrainment
If the separator is inefficient or improperly designed, liquid is carried away with the vapor. This directly reduces the yield of the concentrated product and contaminates the vapor stream, which might be condensed for reuse as pure water.
Therefore, the separator's role is just as important as the heat exchanger's. One creates the vapor, and the other ensures its quality.
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
Understanding these core functions allows you to analyze and troubleshoot evaporator performance based on your specific objective.
- If your primary focus is process efficiency: Pay closest attention to the heat exchanger's performance and the separator's ability to prevent product loss through entrainment.
- If your primary focus is product purity: The design and operation of the separator are the most critical factors for ensuring a clean vapor output.
- If your primary focus is troubleshooting: Isolate the problem by examining each section—is the heat transfer insufficient, is there excessive foaming in the evaporation section, or is the separator failing to capture liquid?
By viewing an evaporator as these three distinct yet interconnected systems, you can effectively manage and optimize any evaporation process.
Summary Table:
| Component | Primary Function |
|---|---|
| Heat Exchanger | Transfers thermal energy to boil the liquid. |
| Evaporating Section | Provides the space for the liquid-to-vapor phase change. |
| Separator | Removes liquid droplets from the vapor stream to ensure purity. |
Optimize your lab's evaporation process with precision equipment from KINTEK.
Whether your goal is maximizing process efficiency, ensuring product purity, or troubleshooting an existing system, understanding the core components is the first step. KINTEK specializes in high-quality lab equipment and consumables, providing reliable evaporators and expert support to meet your specific laboratory needs.
Contact our experts today to discuss the best evaporation solution for your application.
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Laboratory Sterilizer Lab Autoclave Vertical Pressure Steam Sterilizer for Liquid Crystal Display Automatic Type
- Laboratory Sterilizer Lab Autoclave Pulse Vacuum Lifting Sterilizer
- Engineering Advanced Fine Ceramics Aluminum Oxide Al2O3 Heat Sink for Insulation
- 915MHz MPCVD Diamond Machine Microwave Plasma Chemical Vapor Deposition System Reactor
- Anti-Cracking Press Mold for Lab Use
People Also Ask
- What experimental conditions do stainless steel autoclaves provide for PCT-A leaching? Optimize Phosphate Glass Testing
- What are the standard operating parameters for an autoclave? Master Temperature, Pressure, and Time for Sterilization
- What critical environmental conditions does a laboratory autoclave provide for evaluating wear resistance? - KINTEK
- What role do laboratory autoclaves play in pectin extraction? Optimize Prebiotic Yield from Citrus and Apple Biomass
- What is the necessity of using an autoclave for pre-treating culture media? Ensure Accurate Ag2O/TiO2 Testing
















