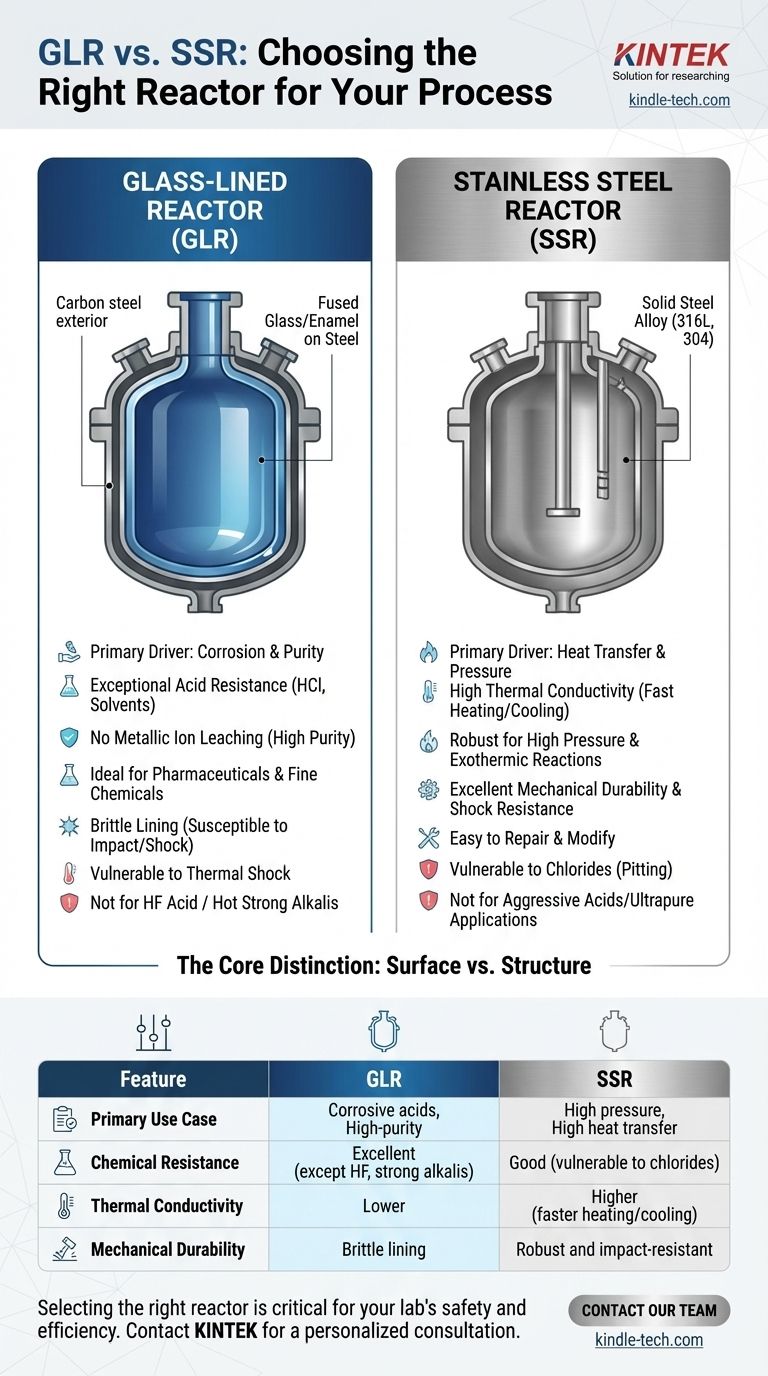
The fundamental difference between a Glass-Lined Reactor (GLR) and a Stainless Steel Reactor (SSR) lies in their material of construction, which dictates their ideal use cases. A GLR leverages a fused glass or enamel layer on an interior steel surface for supreme chemical resistance, while an SSR is built entirely from a steel alloy, offering superior thermal and mechanical performance.
The choice between a GLR and an SSR is not a matter of which is superior overall, but a critical decision based on your specific process chemistry. You are trading the near-universal corrosion resistance and product purity of glass for the mechanical robustness and thermal efficiency of stainless steel.

The Core Distinction: Surface vs. Structure
A chemical reactor is fundamentally a containment vessel for a controlled reaction. The material that touches your chemical reactants—the "wetted" surface—is the most critical design choice.
What is a Glass-Lined Reactor (GLR)?
A GLR is a composite vessel. It has a carbon steel or stainless steel exterior that provides the necessary mechanical strength to handle pressure and structural loads.
The interior surfaces are coated with a layer of specialized glass or enamel. This coating is fused to the steel at very high temperatures, creating a strong, inert, and non-porous barrier between your process chemicals and the base metal.
What is a Stainless Steel Reactor (SSR)?
An SSR is a homogenous vessel constructed from a solid stainless steel alloy, most commonly types 316L or 304.
The entire structure, from the shell to the nozzles and agitator, is made of this alloy. Its properties are uniform throughout, and its resistance to chemicals and temperature is an inherent characteristic of the metal itself.
Key Decision Factors: Chemistry vs. Physics
Your choice will almost always hinge on balancing the demands of your chemical process against the physical operating conditions required.
When to Prioritize GLR: Corrosion & Purity
The primary driver for choosing a GLR is its exceptional corrosion resistance. The glass lining is inert to nearly all acids (except hydrofluoric acid) and solvents, even at elevated temperatures.
This makes GLRs essential for processes involving highly corrosive media like hydrochloric acid, which would quickly destroy most stainless steels. Furthermore, because glass is non-metallic, it prevents metallic ion leaching, ensuring the highest product purity for pharmaceuticals, fine chemicals, and food-grade applications.
When to Prioritize SSR: Heat Transfer & Pressure
Stainless steel's main advantage is its physical performance. It has significantly higher thermal conductivity than glass, allowing for much faster and more efficient heating and cooling. This is critical for exothermic reactions that require rapid heat removal.
Additionally, the inherent strength and ductility of steel make SSRs far more suitable for high-pressure applications, such as hydrogenation. They are also much more resistant to mechanical and thermal shock than the brittle glass lining of a GLR.
Understanding the Critical Trade-offs
Neither reactor type is without limitations. Understanding their weaknesses is key to preventing catastrophic failure and ensuring process success.
Thermal Performance and Shock
An SSR can handle rapid temperature changes with ease. A GLR, however, is highly susceptible to thermal shock. Applying a hot fluid to a cold vessel wall (or vice-versa) can cause the glass lining to crack due to the different expansion rates of glass and steel, leading to immediate failure.
Mechanical Durability and Repair
An SSR is a robust, solid metal vessel. It can withstand accidental impacts and is relatively easy to modify or repair through standard welding procedures.
A GLR's lining is fundamentally brittle. A dropped tool or an accidental impact from the outside can cause the internal glass to fracture or chip. Repairing a glass lining, known as re-glassing, is a highly specialized and expensive process that often requires sending the entire vessel back to the manufacturer.
Chemical Limitations
While excellent, the resistance of each material is not absolute. GLRs are attacked by hydrofluoric acid and are not recommended for sustained use with hot, highly alkaline solutions (pH > 12), which can dissolve the silicate glass.
SSRs are particularly vulnerable to corrosion from halides, especially chlorides. This can lead to localized "pitting corrosion," which is difficult to detect and can cause a vessel to fail unexpectedly.
Making the Right Choice for Your Process
Base your decision on the non-negotiable requirements of your chemical process.
- If your primary focus is ultimate purity or handling aggressive acids (like HCl): A GLR is almost certainly the correct choice to ensure product integrity and vessel longevity.
- If your primary focus is high-pressure operation or managing highly exothermic reactions: An SSR provides the necessary mechanical strength and thermal efficiency for safe and effective control.
- If your primary focus is general-purpose organic synthesis with common solvents and moderate conditions: An SSR (typically 316L) is often the more durable and cost-effective default option.
- If your primary focus is a process involving hot, caustic solutions or fluorides: You must avoid a GLR and select a suitable SSR or a more exotic alloy reactor.
Ultimately, selecting the right reactor is about matching the material's inherent properties directly to the demands of your chemistry.
Summary Table:
| Feature | Glass-Lined Reactor (GLR) | Stainless Steel Reactor (SSR) |
|---|---|---|
| Primary Use Case | Corrosive acids, high-purity applications | High pressure, high heat transfer, general synthesis |
| Chemical Resistance | Excellent (except HF acid & hot strong alkalis) | Good (vulnerable to chlorides) |
| Thermal Conductivity | Lower | Higher (faster heating/cooling) |
| Mechanical Durability | Brittle lining (susceptible to impact/shock) | Robust and impact-resistant |
| Ideal For | Pharmaceuticals, fine chemicals, HCl processes | Hydrogenation, exothermic reactions, high-pressure processes |
Selecting the right reactor is critical for your lab's safety and efficiency. KINTEK specializes in high-quality lab equipment, including GLR and SSR reactors, to meet your specific process chemistry needs. Our experts can help you navigate the trade-offs between corrosion resistance and thermal performance to ensure you get the perfect vessel for your application. Contact our team today for a personalized consultation and discover how KINTEK can support your laboratory's success.
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Customizable High Pressure Reactors for Advanced Scientific and Industrial Applications
- Mini SS High Pressure Autoclave Reactor for Laboratory Use
- High Pressure Laboratory Autoclave Reactor for Hydrothermal Synthesis
- Stainless High Pressure Autoclave Reactor Laboratory Pressure Reactor
- Cylindrical Resonator MPCVD Machine System Reactor for Microwave Plasma Chemical Vapor Deposition and Lab Diamond Growth
People Also Ask
- What are the different types of laboratory reactors? Choose the Right Tool for Your Chemical Research
- What is the core function of a high-pressure static autoclave in PWR simulation? Precise Material Validation
- How do precision reactors control product quality in Mannich amination of lignin? Achieve Superior Site-Specific Accuracy
- What is the function of a high-pressure stainless steel autoclave in the catalytic conversion of cellulose into sugar alcohols?
- What is the significance of SCPW reactors for ODS steel? Evaluate Corrosion Resistance in Fusion Environments
- What is a fluidized bed reactor? Master Temperature Control for Superior Chemical Processing
- What are the pros and cons of batch reactor? Balancing Flexibility vs. Efficiency for Your Lab
- What are the core technical requirements for high-pressure reactors? Expert Specs for Polyamide Depolymerization



















