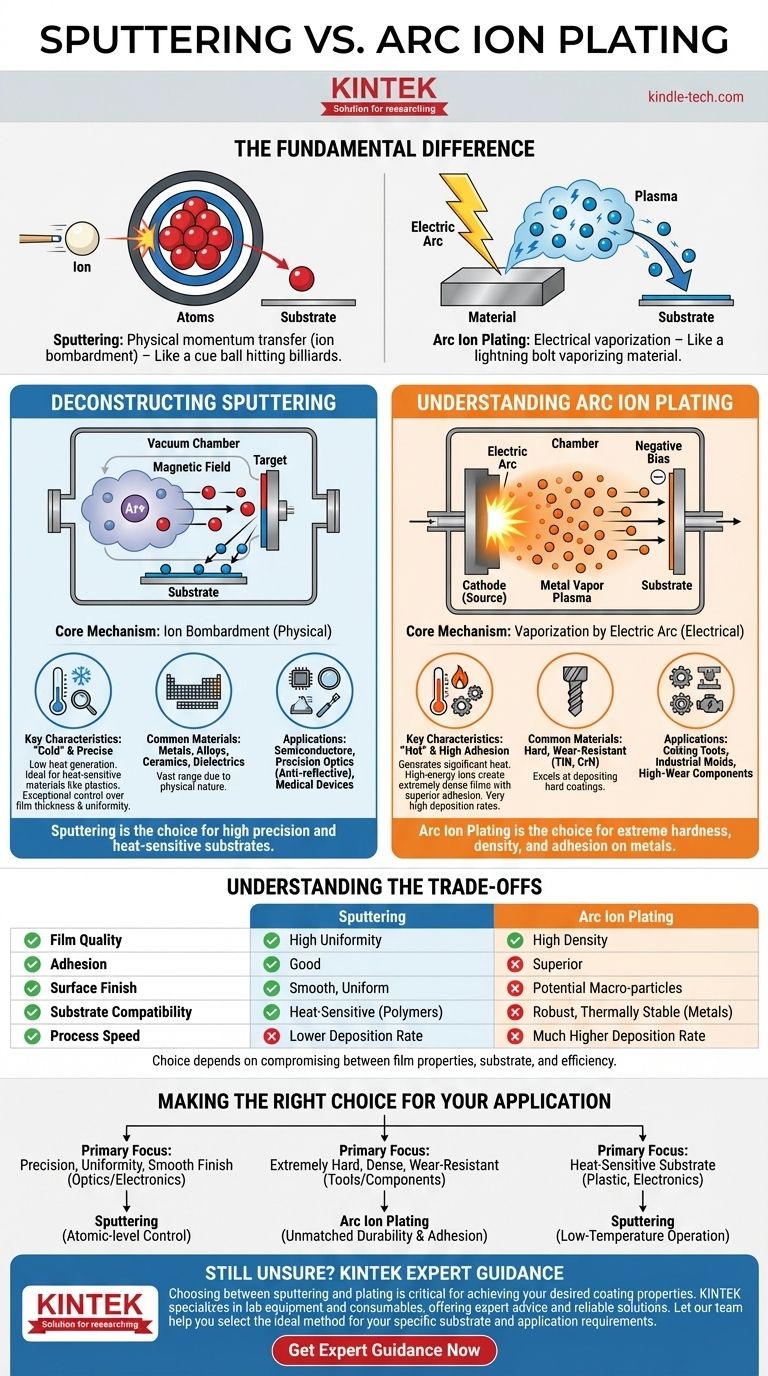
The fundamental difference lies in how atoms are transferred to a surface. Sputtering is a physical momentum transfer process, where ions bombard a target to "knock off" atoms like a cue ball striking a rack of billiard balls. In contrast, a process like arc ion plating uses a high-current electric arc to vaporize a material, creating an energized plasma of ions that are then electrically steered onto the substrate.
While both sputtering and plating are methods of Physical Vapor Deposition (PVD), they operate on entirely different principles. The choice between them is not about which is superior, but about matching the process—physical bombardment versus electrical vaporization—to the specific requirements of the coating and the substrate material.

Deconstructing the Sputtering Process
Sputtering is a highly controlled and versatile coating technique relied upon for applications demanding high precision. It operates in a vacuum chamber filled with an inert gas, typically argon.
The Core Mechanism: Ion Bombardment
A high voltage is applied, creating a plasma from the argon gas. These positively charged argon ions are accelerated by a magnetic field and collide with a target made of the desired coating material.
This high-energy collision physically ejects, or "sputters," atoms from the target. These ejected atoms then travel through the vacuum and deposit onto the substrate, forming a thin, uniform film.
Key Characteristics: A "Cold" and Precise Process
Sputtering is considered a "cold" process because it generates relatively little heat. This makes it ideal for coating heat-sensitive materials like plastics or complex electronics.
The process offers exceptional control over film thickness, uniformity, and composition, often down to the atomic level.
Common Materials and Applications
Because it's a physical rather than chemical process, sputtering can deposit a vast range of materials, including metals, alloys, ceramics, and dielectrics.
It is the cornerstone of industries like semiconductor manufacturing, precision optics (anti-reflective coatings), and medical device coatings.
Understanding Arc Ion Plating
Arc ion plating is a high-energy deposition process known for creating exceptionally hard and dense coatings. It is a more aggressive and faster method compared to sputtering.
The Core Mechanism: Vaporization by Electric Arc
This technique uses a powerful, low-voltage electric arc to strike a solid, metallic source material (the cathode).
The intense energy of the arc spot vaporizes the metal, creating a dense plasma of highly ionized metal vapor. These ions are then accelerated toward the substrate, which is given a negative bias, causing a high-energy deposition.
Key Characteristics: A "Hot" and High-Adhesion Process
The high kinetic energy of the arriving ions results in extremely dense films with superior adhesion to the substrate. The process itself generates significant heat.
Arc ion plating is known for its very high deposition rates, making it much faster than sputtering for building up thick, functional coatings.
Common Materials and Applications
This method excels at depositing hard, wear-resistant coatings like Titanium Nitride (TiN) and Chromium Nitride (CrN).
Its primary application is for improving the durability and lifespan of cutting tools, industrial molds, and mechanical components that experience high wear.
Understanding the Trade-offs
Choosing the right process requires understanding the inherent compromises between film properties, substrate compatibility, and process efficiency.
Film Quality and Adhesion
Arc ion plating generally produces coatings with higher density and superior adhesion due to the high energy of the depositing ions.
However, a known drawback of arc plating is the formation of "macro-particles" or droplets, which can negatively impact surface finish. Sputtering produces a much smoother, more uniform surface.
Substrate Compatibility
Sputtering's low-temperature nature gives it a significant advantage for coating polymers, composites, and other materials that cannot withstand the heat generated by an electric arc.
Arc ion plating is typically restricted to robust, thermally stable substrates, primarily metals.
Process Speed and Simplicity
Arc ion plating has a much higher deposition rate, making it more efficient for applying thick, protective coatings on an industrial scale.
As the references note, sputtering equipment can be mechanically simpler and require less maintenance, although the vacuum systems they rely on can be complex.
Making the Right Choice for Your Application
Your final decision should be guided entirely by your primary goal for the coating and the nature of the object being coated.
- If your primary focus is precision, uniformity, and a smooth finish for optics or electronics: Sputtering is the definitive choice for its atomic-level control.
- If your primary focus is creating an extremely hard, dense, and wear-resistant coating on metal tools or components: Arc ion plating provides unmatched durability and adhesion.
- If your primary focus is coating a heat-sensitive substrate like plastic or a delicate electronic assembly: Sputtering is the only viable option due to its low-temperature operation.
Ultimately, understanding the core mechanism of each process empowers you to select the tool that best achieves your specific engineering goal.
Summary Table:
| Feature | Sputtering | Arc Ion Plating |
|---|---|---|
| Core Mechanism | Physical momentum transfer (ion bombardment) | Electrical vaporization (electric arc) |
| Process Temperature | Low ("Cold" process) | High ("Hot" process) |
| Ideal For | Heat-sensitive substrates, precision optics, electronics | Hard, wear-resistant coatings on metal tools/components |
| Key Advantage | Exceptional control, smooth finish, low temperature | Superior adhesion, high density, fast deposition rate |
Still Unsure Which PVD Process is Right for Your Project?
Choosing between sputtering and plating is critical for achieving your desired coating properties, whether it's precision for electronics or extreme durability for tools. KINTEK specializes in lab equipment and consumables, serving laboratory needs with expert advice and reliable solutions.
Our team can help you select the ideal method for your specific substrate and application requirements. Contact us today to discuss your project and ensure optimal results.
Visual Guide
Related Products
- HFCVD Machine System Equipment for Drawing Die Nano-Diamond Coating
- Vacuum Hot Press Furnace Machine for Lamination and Heating
- 915MHz MPCVD Diamond Machine Microwave Plasma Chemical Vapor Deposition System Reactor
- Laboratory Sterilizer Lab Autoclave Pulse Vacuum Lifting Sterilizer
- Laboratory Sterilizer Lab Autoclave Vertical Pressure Steam Sterilizer for Liquid Crystal Display Automatic Type
People Also Ask
- How are reactants introduced into the reaction chamber during a CVD process? Mastering Precursor Delivery Systems
- What are the advantages of using HFCVD for BDD electrodes? Scaling Industrial Diamond Production Efficiently
- What machine is used to make lab-grown diamonds? Discover the HPHT & CVD Technologies
- What is microwave plasma CVD? A Guide to High-Purity Diamond and Material Synthesis
- What is the specific function of the metal filament in HF-CVD? Key Roles in Diamond Growth



















