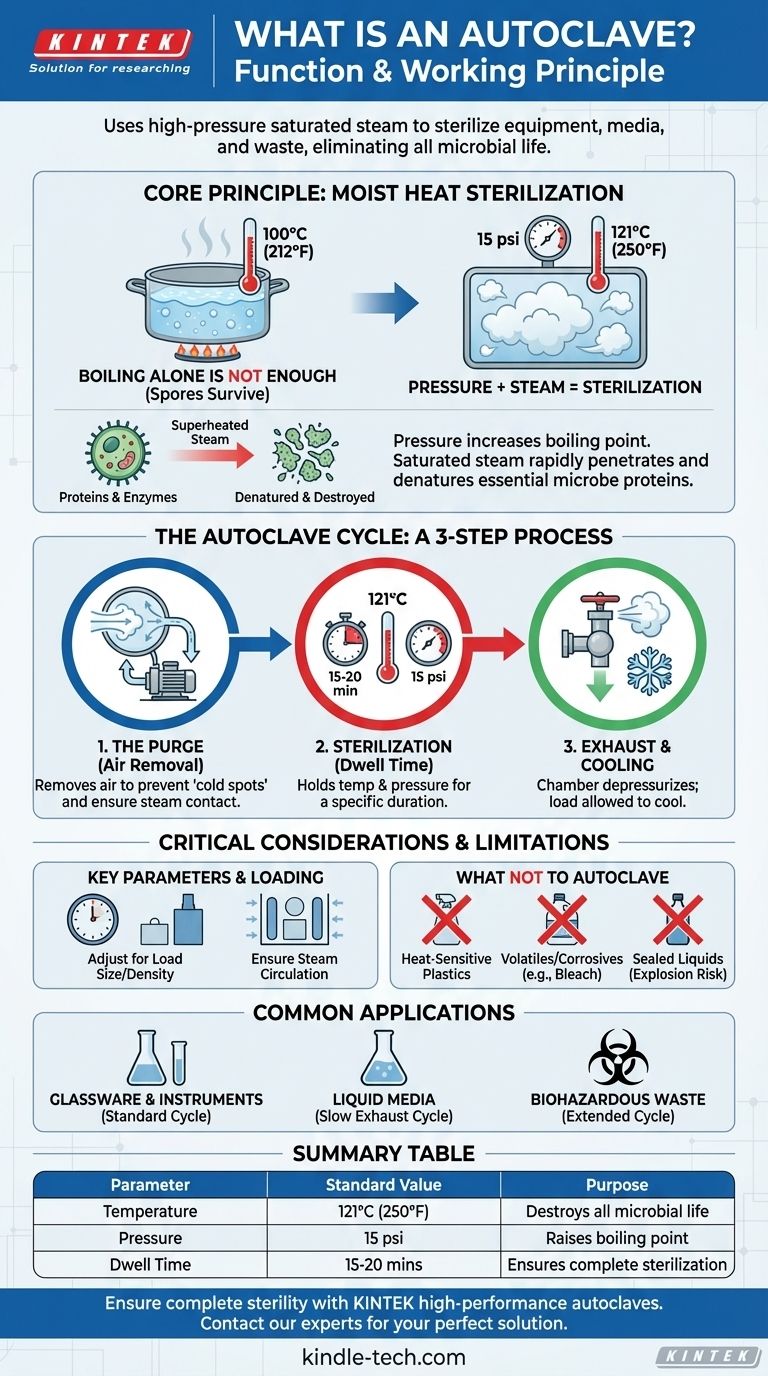
An autoclave is a machine that uses high-pressure saturated steam to sterilize equipment, media, and waste. Its primary function is to eliminate all forms of microbial life, including bacteria, viruses, fungi, and highly resistant bacterial spores, by subjecting them to a specific temperature and pressure for a set duration. This process is a cornerstone of safety and quality control in laboratories, medical facilities, and various industrial settings.
The core principle of an autoclave is its ability to use pressure to increase the boiling point of water. This creates superheated steam that can rapidly penetrate materials and destroy microorganisms by irreversibly damaging their essential proteins and enzymes.
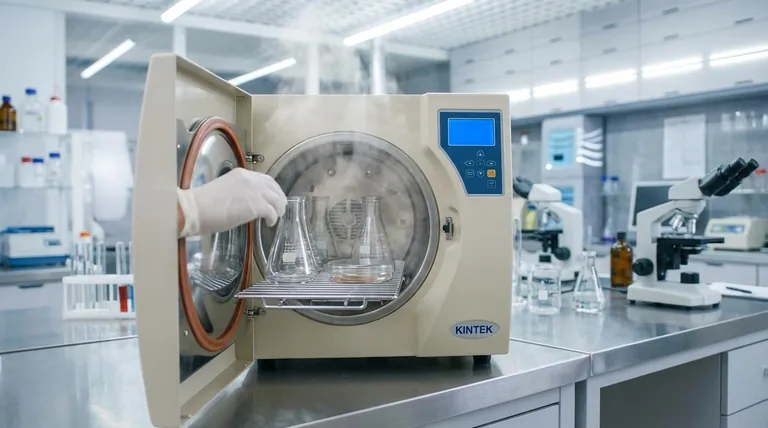

The Core Principle: Moist Heat Sterilization
The effectiveness of an autoclave relies on the physics of water and the biology of microorganisms. Simply boiling items in water is not enough for true sterilization.
The Problem with Boiling Water
At standard atmospheric pressure, water boils at 100°C (212°F). While this temperature can kill many active bacteria, it is often insufficient to eliminate resilient bacterial spores, which can survive and reactivate under favorable conditions.
The Critical Role of Pressure
An autoclave is a sealed chamber, allowing it to manipulate the relationship between pressure and temperature. By increasing the internal pressure, the autoclave raises the boiling point of water far beyond 100°C.
This is the key to its function. For example, at a pressure of about 15 psi (pounds per square inch) above atmospheric pressure, the boiling point of water reaches 121°C (250°F).
The Power of Saturated Steam
The "superheated" steam created under pressure is a highly efficient vehicle for transferring thermal energy. It holds significantly more energy than dry air at the same temperature, allowing it to rapidly heat and penetrate the entire load, including the deepest parts of instruments or dense media.
How Steam Kills Microbes
This intense, moist heat works by denaturing and coagulating the essential proteins and enzymes within microorganisms. This process is irreversible, effectively destroying the cellular machinery required for survival and reproduction, ensuring complete sterilization.
A Step-by-Step Breakdown of an Autoclave Cycle
A modern autoclave automates the sterilization process into distinct phases to ensure safety and effectiveness.
Phase 1: The Purge (Air Removal)
Before sterilization can begin, all air must be removed from the chamber. Air is a poor conductor of heat and its presence creates "cold spots" that prevent steam from reaching all surfaces, leading to sterilization failure. This is typically done using a vacuum system or by displacing the air with flowing steam.
Phase 2: Sterilization (Pressurization and Dwell Time)
Once the air is purged, steam is injected into the chamber, increasing both the pressure and temperature to the desired setpoint (e.g., 121°C and 15 psi). The autoclave holds these conditions for a specific duration known as the dwell time or holding time, which is typically 15-20 minutes for standard loads.
Phase 3: Exhaust and Cooling
After the dwell time is complete, the chamber is depressurized by releasing the steam through an exhaust valve. The load is then allowed to cool. In many units, a cooling system rapidly cools the exhausted steam and water before it enters the facility's drainage system.
Understanding Key Parameters and Limitations
To use an autoclave correctly, you must understand the variables and what the machine cannot handle.
Time, Temperature, and Load
The standard 121°C for 15-20 minutes is a guideline. Larger, denser, or heavily wrapped loads require longer dwell times to ensure the steam fully penetrates the entire volume. Always follow validated protocols specific to the material being sterilized.
What You Cannot Autoclave
Autoclaves are not suitable for all materials. You should never autoclave heat-sensitive plastics that can melt, volatile or corrosive chemicals (like bleach), or any liquids in a sealed container, as this creates a significant explosion risk.
The Importance of Proper Loading
Overloading the chamber or packing items too tightly will impede steam circulation. This is a common cause of sterilization failure. Ensure there is adequate space between items to allow steam to move freely and contact every surface.
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
Your sterilization protocol will depend on the material you are processing.
- If your primary focus is sterilizing laboratory glassware and instruments: Use a standard gravity or vacuum cycle at 121°C for 15-20 minutes after ensuring items are properly cleaned.
- If your primary focus is sterilizing liquid media: Use a specific "liquids" cycle, which employs a slower exhaust rate to prevent the media from boiling over as the pressure drops.
- If your primary focus is decontaminating biohazardous waste: Ensure you are using validated autoclave bags that allow steam penetration and extend the cycle time to handle the density of the waste material.
Ultimately, the autoclave provides a reliable and automated method for achieving the highest level of sterility required in modern science and medicine.
Summary Table:
| Key Autoclave Parameter | Standard Value | Purpose |
|---|---|---|
| Sterilization Temperature | 121°C (250°F) | Destroys all microbial life |
| Chamber Pressure | 15 psi above atmospheric | Raises water's boiling point |
| Dwell Time | 15-20 minutes | Ensures complete sterilization |
| Primary Function | Moist heat sterilization | Denatures microbial proteins |
Ensure complete sterility and safety in your lab with the right autoclave. KINTEK specializes in high-performance laboratory autoclaves designed for reliable sterilization of instruments, media, and biohazardous waste. Our equipment ensures precise temperature and pressure control for consistent, validated results. Contact our sterilization experts today to find the perfect autoclave solution for your laboratory's specific needs and protocols.
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Desktop Fast Laboratory Autoclave Sterilizer 35L 50L 90L for Lab Use
- Portable High Pressure Laboratory Autoclave Steam Sterilizer for Lab Use
- Portable Digital Display Automatic Laboratory Sterilizer Lab Autoclave for Sterilization Pressure
- Laboratory Sterilizer Lab Autoclave Herbal Powder Sterilization Machine for Plant
- Laboratory High Pressure Steam Sterilizer Vertical Autoclave for Lab Department
People Also Ask
- What is an example of autoclave in laboratory? Essential Sterilization for Reliable Science
- What are the guidelines when sterilizing items with a steam autoclave? Master the 3 Pillars for Guaranteed Sterility
- What is the normal temperature of an autoclave? Achieve Sterile Confidence with Precise Control
- What equipment is used for laboratory sterilization? A Guide to Autoclaves, Ovens & Filtration
- What is the use of autoclave in research? Ensure Sterile Conditions for Valid Scientific Results



















