In simple terms, the industrial process of evaporation is a highly controlled method for creating ultra-thin films on a surface. It works by heating a source material inside a high-vacuum chamber until it turns into a vapor, which then travels and condenses onto a target object (called a substrate), forming a precise and uniform coating.
Industrial evaporation is not about boiling water; it is a cornerstone of Physical Vapor Deposition (PVD), an engineering process used to build functional, high-purity coatings atom by atom. The core challenge and key differentiator between methods is how you efficiently transfer energy to the source material to turn it into a vapor.

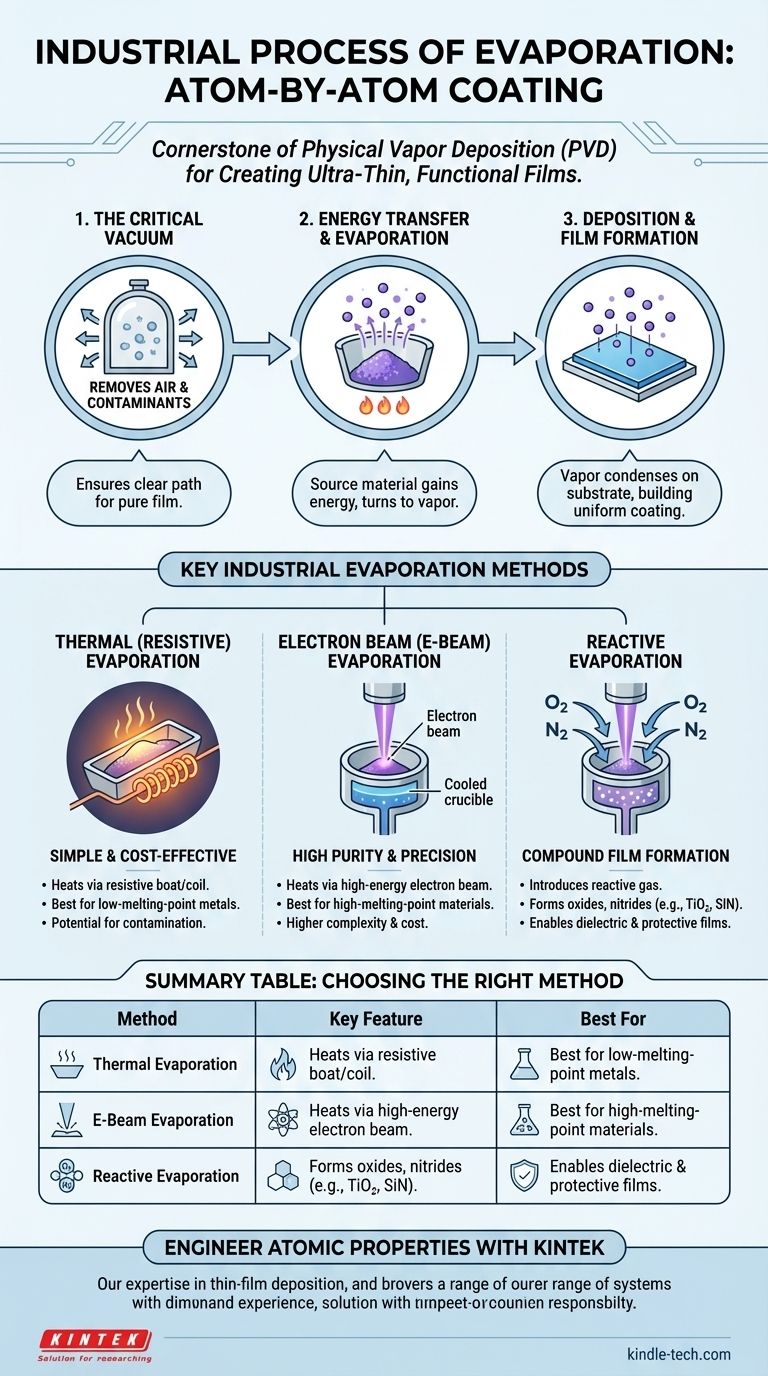
The Fundamental Principle: From Solid to Vapor to Film
Industrial evaporation relies on a three-step physical process that happens inside a carefully controlled environment. Understanding this sequence is key to appreciating its applications.
The Critical Role of the Vacuum
The entire process occurs in a high-vacuum chamber. This is non-negotiable.
The vacuum removes air and other gas molecules that would otherwise collide with the vaporized material atoms. This ensures the atoms have a clear, direct path to the substrate, preventing contamination and guaranteeing a pure film.
The Energy Transfer
To begin, the source material must gain enough energy to transition from a solid or liquid into a gaseous vapor. This is the "evaporation" step.
The method used to deliver this energy is what primarily distinguishes the different industrial evaporation techniques.
The Deposition
Once vaporized, the material's atoms travel through the vacuum until they hit the cooler substrate. Upon contact, they lose energy, condense back into a solid state, and bond to the surface, gradually building the thin film.
Key Industrial Evaporation Methods
While the principle is the same, the method of heating the source material varies significantly. The two most common techniques are Thermal Evaporation and Electron Beam (E-Beam) Evaporation.
Thermal (Resistive) Evaporation
This is the most straightforward method. The source material, often in pellet form, is placed in a small container made of a resistive material, such as a tungsten "boat" or coil.
A high electrical current is passed through this boat. The boat's electrical resistance causes it to heat up intensely, which in turn heats the source material to its evaporation point.
Electron Beam (E-Beam) Evaporation
This is a more advanced and precise technique. It is used for materials that require extremely high temperatures to evaporate or when exceptional film purity is required.
In this process, a high-energy beam of electrons is generated, accelerated by high voltage, and magnetically focused onto the source material held in a crucible. The intense energy from the electron beam melts and vaporizes the material with high efficiency.
Reactive Evaporation
E-beam systems can be enhanced through a process called reactive evaporation. A reactive gas, such as oxygen or nitrogen, is intentionally introduced into the vacuum chamber during deposition.
This allows the vaporized metal atoms to react with the gas as they deposit, forming non-metallic compound films like oxides or nitrides directly on the substrate.
Understanding the Trade-offs
Choosing the right evaporation method involves balancing cost, complexity, and the desired properties of the final film. No single method is universally superior.
Thermal Evaporation: Simplicity vs. Purity
The primary advantage of thermal evaporation is its relative simplicity and lower equipment cost.
However, it is limited to materials with lower evaporation temperatures. A significant drawback is the potential for the heated boat or coil material to contaminate the vapor stream, reducing the purity of the final film.
E-Beam Evaporation: Purity vs. Complexity
E-beam evaporation can deposit materials with very high melting points, such as refractory metals and ceramics, which is impossible with thermal methods.
Because the electron beam heats only the source material and not the crucible holding it, it produces films of exceptionally high purity. The trade-off is significantly higher equipment cost and complexity.
Making the Right Choice for Your Application
Your goal dictates the correct technology. The choice between these methods depends entirely on the material you are depositing and the performance you require from the final film.
- If your primary focus is cost-effective coating with simpler, low-melting-point metals: Thermal (resistive) evaporation offers a proven and economical solution.
- If your primary focus is creating high-purity, high-performance films for advanced optics or electronics: E-beam evaporation is the superior choice due to its precision and ability to handle difficult materials.
- If your primary focus is depositing hard, protective, or dielectric films like titanium nitride or silicon dioxide: Reactive e-beam evaporation provides the necessary control to form these compound materials.
By understanding these core techniques, you can precisely engineer material properties at the atomic level to achieve your specific technical goal.
Summary Table:
| Method | Key Feature | Best For |
|---|---|---|
| Thermal Evaporation | Simple, cost-effective heating via resistive boat | Low-melting-point metals, cost-sensitive applications |
| E-Beam Evaporation | High-purity, focused electron beam heating | Refractory metals, high-performance optics/electronics |
| Reactive Evaporation | Introduces reactive gas (e.g., O₂, N₂) during deposition | Forming compound films like oxides or nitrides |
Ready to engineer your material properties at the atomic level?
Whether you need to deposit simple metal coatings or complex, high-purity films, KINTEK has the expertise and equipment to meet your laboratory's specific thin-film deposition needs. Our range of evaporation systems, including thermal and e-beam solutions, are designed to deliver precision, reliability, and exceptional results for your R&D or production goals.
Contact our experts today to discuss how we can help you achieve your technical objectives with the right evaporation technology.
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Chemical Vapor Deposition CVD Equipment System Chamber Slide PECVD Tube Furnace with Liquid Gasifier PECVD Machine
- RF PECVD System Radio Frequency Plasma-Enhanced Chemical Vapor Deposition RF PECVD
- Electron Beam Evaporation Coating Conductive Boron Nitride Crucible BN Crucible
- Molybdenum Tungsten Tantalum Evaporation Boat for High Temperature Applications
- Vacuum Heat Treat and Sintering Furnace with 9MPa Air Pressure
People Also Ask
- What is the vapor phase deposition technique? A Guide to PVD & CVD Thin-Film Coating Methods
- What is PECVD in semiconductor? Enable Low-Temperature Thin Film Deposition for ICs
- How does PECVD work? Enable Low-Temperature, High-Quality Thin Film Deposition
- What are the different types of thin films? A Guide to Optical, Electrical, and Functional Coatings
- What are the steps of the CVD process? A Guide to Precision Thin Film Deposition


















