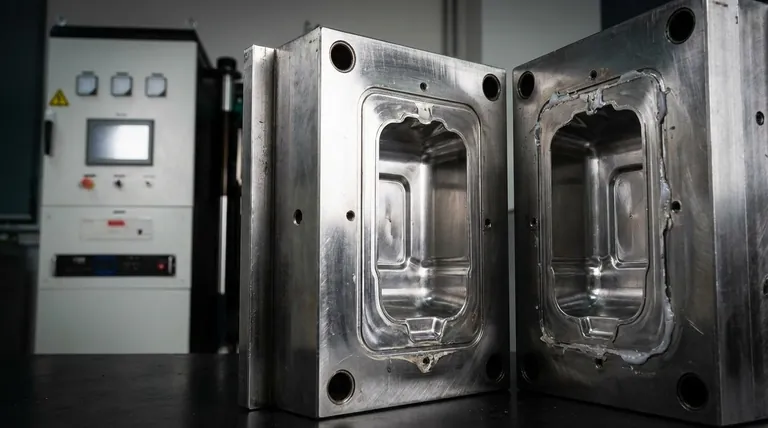
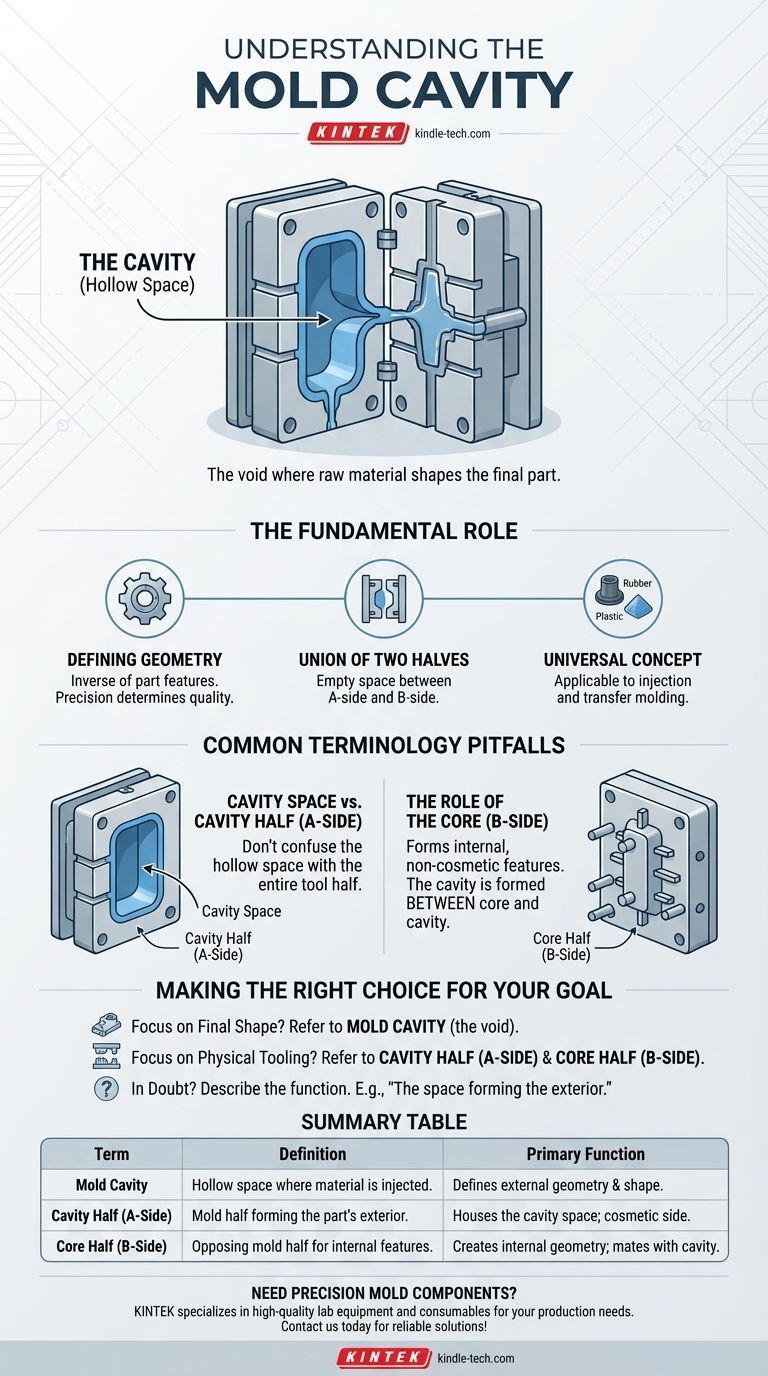
The hollow space inside a mold is called the cavity. This is the void where molten plastic, liquid silicone, or another raw material is injected or forced in order to form the final shape of a part. Essentially, the cavity is the negative space that defines the product's external geometry.
The core principle to understand is that "cavity" can refer to two distinct but related things: the three-dimensional space that forms the part, and the entire half of the mold tool that typically shapes the part's cosmetic exterior.

The Fundamental Role of the Mold Cavity
Defining the Part's Geometry
The primary function of the mold cavity is to give the final product its shape. The walls of the cavity are the inverse of the part's features, and their precision directly determines the quality and accuracy of the molded component.
The Union of Two Halves
In most common processes like injection molding, the cavity is the empty space created when two halves of the mold, the A-side and the B-side, are clamped together. The material fills this void between them.
A Universal Manufacturing Concept
The term cavity is not limited to one process. Whether in transfer molding for rubber or injection molding for plastic, the concept remains the same: the cavity is the chamber that contains and shapes the raw material under pressure.
Understanding Common Terminology Pitfalls
Cavity Space vs. Cavity Half (A-Side)
Herein lies a frequent point of confusion. The term cavity is often used as shorthand for the entire A-side of the mold. This half is also called the "cavity half" because it usually forms the primary cosmetic or exterior surface of the part.
The Role of the Core (B-Side)
The other half of the mold is known as the core, or the B-side. The core typically forms the internal, non-cosmetic features of a part, such as ribs, bosses, or posts. The cavity space is formed between the core and the cavity half.
Why Precision Matters
Distinguishing between "the mold cavity" (the space) and "the cavity half" (the tool) is critical. In technical discussions with designers, engineers, and toolmakers, this precision prevents costly misunderstandings about which part of the mold or product feature is being discussed.
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
To ensure your intent is perfectly clear, use the term that best fits the context of your discussion.
- If your primary focus is the final part's shape: Refer to the mold cavity, which is the void where the material solidifies.
- If your primary focus is the physical tooling: Refer to the cavity half (A-side) and the core half (B-side) to differentiate between the two sides of the mold.
- If you are ever in doubt: Describe the function to avoid ambiguity, such as "the space that forms the part's exterior" or "the stationary half of the mold tool."
Using this precise language ensures your design intent is perfectly understood from concept to production.
Summary Table:
| Term | Definition | Primary Function |
|---|---|---|
| Mold Cavity | The hollow space inside a mold where material is injected. | Defines the external geometry and shape of the final part. |
| Cavity Half (A-Side) | The half of the mold tool that typically forms the part's exterior surface. | Houses the cavity space; often the cosmetic side. |
| Core Half (B-Side) | The opposing half of the mold that forms internal features (ribs, posts). | Creates internal part geometry; mates with the cavity half. |
Need precision mold components or lab equipment for your production? KINTEK specializes in high-quality lab equipment and consumables, serving laboratories and manufacturing needs with reliable solutions. Let our expertise support your molding projects—contact us today to discuss how we can enhance your process efficiency and part quality!
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Vacuum Heat Treat and Molybdenum Wire Sintering Furnace for Vacuum Sintering
- Three-dimensional electromagnetic sieving instrument
- Lab Internal Rubber Mixer Rubber Kneader Machine for Mixing and Kneading
- Hydraulic Diaphragm Lab Filter Press for Laboratory Filtration
- 1800℃ Muffle Oven Furnace for Laboratory
People Also Ask
- Why is a high vacuum required for sintering Ti-43Al-4Nb-1Mo-0.1B? Ensure Purity & Fracture Toughness
- How does a high-temperature vacuum sintering furnace facilitate the post-treatment of Zirconia coatings?
- How does precise temperature control affect FeCoCrNiMnTiC high-entropy alloys? Master Microstructural Evolution
- What is sintering reaction? Transform Powders into Dense Solids Without Melting
- What is vacuum sintering? Achieve Unmatched Purity and Performance for Advanced Materials















