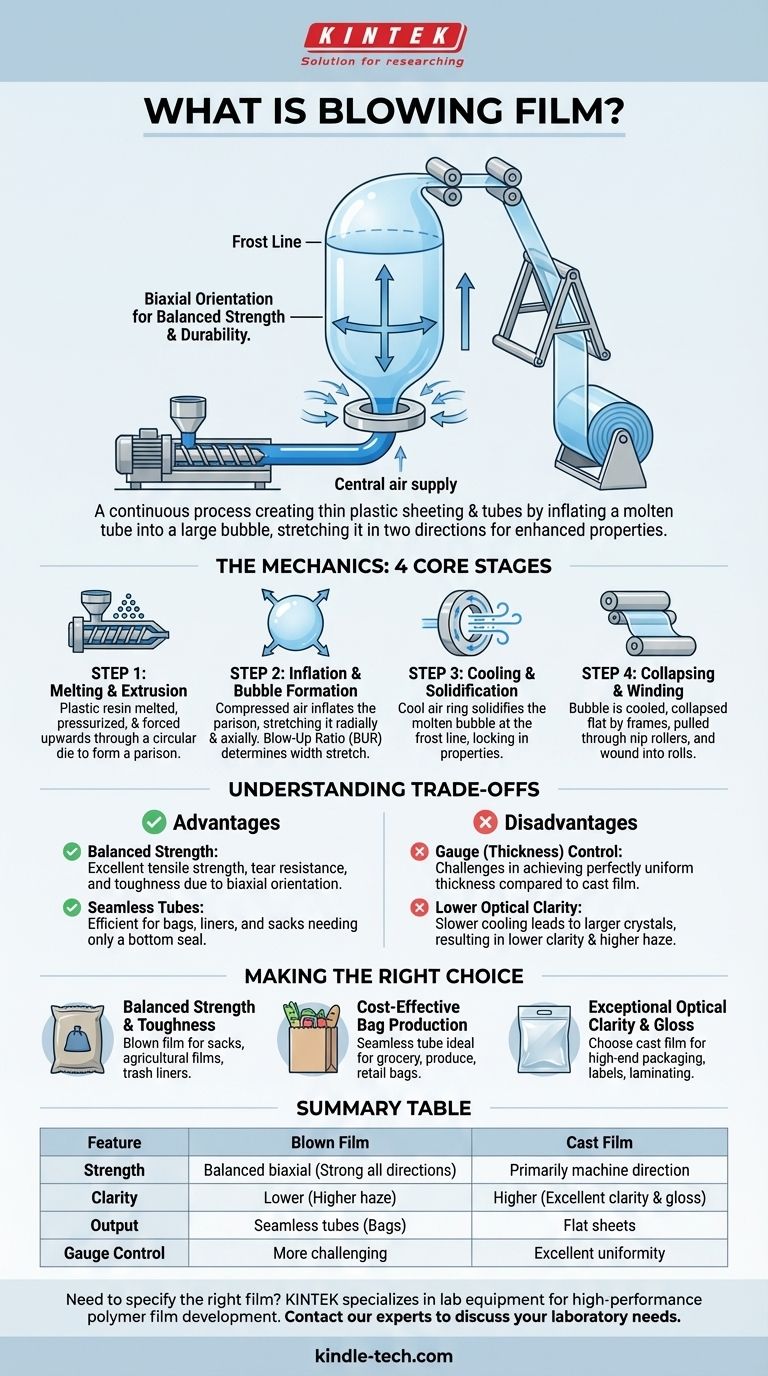
Blowing film, technically known as blown film extrusion, is a continuous manufacturing process for creating thin plastic sheeting and tubes. It works by melting plastic resin, extruding it vertically through a circular die to form a thick tube, and simultaneously inflating that tube with air into a large, thin-walled bubble. This bubble is then cooled, collapsed flat, and wound into rolls.
The core purpose of blowing film is not merely to make plastic sheets, but to stretch the molten plastic in two directions at once. This biaxial orientation creates a film with balanced mechanical properties, making it significantly stronger and more durable for its thickness than films made by other methods.

The Mechanics of the Blown Film Process
To understand why this process is so widely used, it's essential to break it down into its core stages. Each step is a control point that determines the final properties of the film.
Step 1: Melting and Extrusion
The process begins with solid plastic pellets (resin), typically polyethylene (LDPE, LLDPE, HDPE), which are fed into the barrel of an extruder. A rotating screw inside the barrel heats, melts, and pressurizes the plastic, ensuring it becomes a homogenous, consistent fluid.
This molten plastic is then forced upwards through a circular die, emerging as a thick-walled tube of plastic called a parison.
Step 2: Inflation and Bubble Formation
As the parison exits the die, compressed air is injected into the center of the tube. This air pressure inflates the tube, stretching it both radially (outwards) and axially (upwards).
The ratio between the final bubble diameter and the die diameter is a critical parameter known as the Blow-Up Ratio (BUR). A higher BUR results in more stretching in the transverse (width) direction.
Step 3: Cooling and Solidification
An air ring mounted above the die blows a high volume of cool air onto the exterior of the bubble. This cooling process solidifies the plastic, locking its molecular structure into place.
The point at which the molten, transparent bubble becomes a solid, hazy film is called the frost line. The height of this frost line is a key variable that affects the film's clarity, strength, and toughness.
Step 4: Collapsing and Winding
After cooling, the bubble continues to travel upwards, sometimes for several stories in a large production facility, before being guided through a set of collapsing frames that gently flatten it into a lay-flat tube.
This flattened tube is then pulled through a set of nip rollers, which control the speed of the entire process. Finally, the lay-flat tube is wound onto large rolls. It can be kept as a tube or slit along one or both edges to create one or two flat sheets of film.
Understanding the Trade-offs
While incredibly versatile, blown film extrusion is not the ideal solution for every application. Understanding its limitations is key to making informed decisions.
Advantage: Balanced Strength
The primary advantage is biaxial orientation. By stretching the plastic in two directions, the polymer chains are interlocked, resulting in a film with excellent tensile strength, tear resistance, and toughness in both the machine and transverse directions.
Advantage: Seamless Tubes
The process naturally creates seamless tubes, making it the most efficient method for producing plastic bags, liners, and sacks that require only a bottom seal.
Disadvantage: Gauge (Thickness) Control
Compared to cast film (where plastic is extruded onto a chilled roller), blown film has a greater tendency for thickness variations. Achieving perfectly uniform gauge across the entire width of the film is a significant technical challenge.
Disadvantage: Lower Optical Clarity
The slower cooling rate in the blown film process allows for the formation of larger crystal structures in the plastic, which scatters more light. This typically results in a film with lower clarity and higher haze than cast film.
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
Selecting the correct manufacturing process depends entirely on the end-use requirements for the film.
- If your primary focus is balanced strength and toughness: Blown film is the clear choice for applications like heavy-duty sacks, agricultural films, and trash can liners.
- If your primary focus is cost-effective bag production: The seamless tube formed by the blown film process is unmatched for making grocery, produce, and other retail bags.
- If your primary focus is exceptional optical clarity and gloss: You should specify cast film, which is better suited for high-end flexible packaging, labels, and laminating applications.
By understanding how the blowing film process creates its unique properties, you can better specify the right material that balances performance, cost, and aesthetics for your specific need.
Summary Table:
| Feature | Blown Film | Cast Film |
|---|---|---|
| Strength | Balanced biaxial orientation (strong in all directions) | Primarily machine direction strength |
| Clarity | Lower (higher haze) | Higher (excellent clarity and gloss) |
| Output | Seamless tubes (ideal for bags) | Flat sheets |
| Gauge Control | More challenging to control uniformly | Excellent uniformity |
Need to specify the right film for your application? The blown film process is ideal for creating strong, durable plastic sheeting and seamless tubes for bags and liners. At KINTEK, we specialize in providing the lab equipment and consumables necessary for developing and testing high-performance polymer films. Whether you're in R&D or quality control, our solutions help you achieve the perfect balance of strength, clarity, and cost-effectiveness. Contact our experts today to discuss your laboratory needs and how we can support your projects.
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Lab Plastic PVC Calender Stretch Film Casting Machine for Film Testing
- Twin Screw Extruder Plastic Granulation Machine
- HFCVD Machine System Equipment for Drawing Die Nano-Diamond Coating
- Anti-Cracking Press Mold for Lab Use
- Benchtop Laboratory Vacuum Freeze Dryer
People Also Ask
- What are the advantages of blown film extrusion? Boost Your Film Production Efficiency
- What is the process of double extrusion? Create Integrated Multi-Material Components
- What are the disadvantages of the extrusion process? High Costs and Geometric Limits Explained
- What products are blown film extrusion? From Grocery Bags to Industrial Sheeting
- What is the difference between calendaring and calendering? Master the Key Spelling and Context



















