In short, the rubber milling process is a mechanical method for transforming raw, tough natural or synthetic rubber into a soft, pliable, and uniform compound ready for manufacturing. It is accomplished by repeatedly passing the rubber through a set of powerful rollers to first break it down and then blend it with various additives.
Rubber milling is not simply about grinding rubber. It is a precise engineering process designed to first reduce the rubber's natural elasticity through mechanical work (mastication) and then thoroughly incorporate additives (compounding) to create a homogenous material with specific, desired properties for the final product.

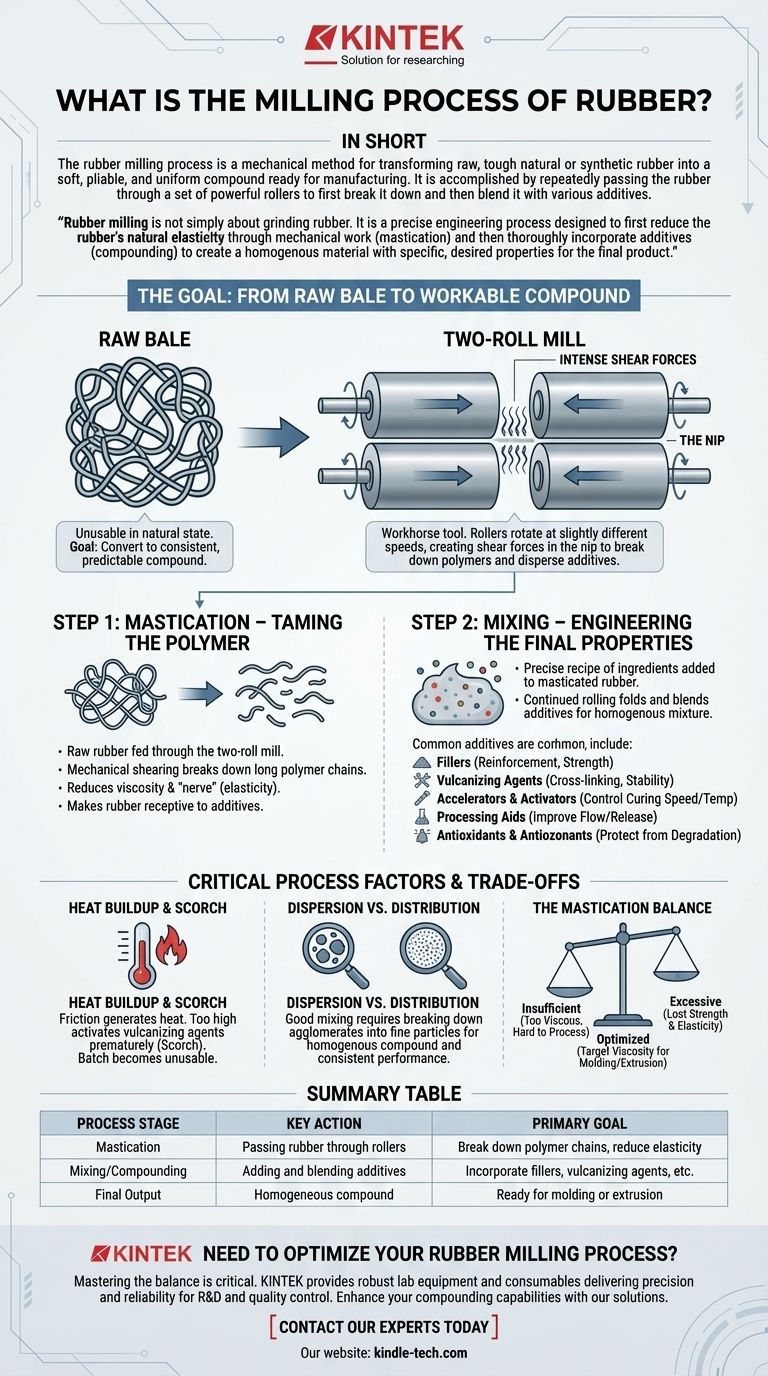
The Goal: From Raw Bale to Workable Compound
The journey of a rubber product begins with a raw polymer, often in the form of a large, tough, and highly elastic bale. This material is unusable in its natural state.
The primary objective of milling is to convert this raw bale into a consistent and predictable compound that can be easily shaped into a final product through processes like molding or extrusion.
Step 1: Mastication – Taming the Polymer
The first and most critical stage of milling is mastication. This involves feeding the raw rubber through a two-roll mill.
The mechanical shearing and tearing action of the rollers breaks down the long, entangled polymer chains that give raw rubber its high elasticity and strength.
Think of it like kneading a very tough dough. The more you work it, the softer and more pliable it becomes. Mastication reduces the rubber's viscosity and "nerve" (its tendency to snap back), making it receptive to additives.
Step 2: Mixing – Engineering the Final Properties
Once the rubber has been sufficiently masticated, the mixing or compounding stage begins. Here, a precise recipe of ingredients is added directly onto the mill.
The rolling action continues, folding and blending the additives into the rubber mass until a completely homogenous mixture is achieved.
Common additives include:
- Fillers: Materials like carbon black or silica are added to reinforce the rubber, increasing its strength, durability, and wear resistance.
- Vulcanizing Agents: Sulfur is the most common agent. It creates cross-links between polymer chains during the final curing stage (post-milling), giving the rubber its final stable form.
- Accelerators & Activators: These chemicals control the speed and temperature of the subsequent curing process.
- Processing Aids: These improve the flow and release of the compound from molds.
- Antioxidants & Antiozonants: These protect the final product from degradation due to heat, oxygen, and ozone.
The Central Tool: The Two-Roll Mill
The workhorse of rubber milling is the two-roll mill. Understanding its function is key to understanding the process.
How It Works
A two-roll mill consists of two large, horizontal, hardened steel rollers positioned side-by-side. These rollers rotate towards each other at slightly different speeds.
This speed differential creates intense shear forces in the small gap between the rollers, known as the nip. It is this shearing action that breaks down the polymer chains during mastication and disperses the additives during mixing.
The Importance of Process Control
Milling is a highly skilled operation. An operator must constantly manage several factors to ensure a quality compound.
Key variables include the nip gap, the temperature of the rollers (which are cored for cooling), the mixing time, and the sequence in which additives are introduced.
Critical Process Factors and Trade-offs
Achieving the perfect rubber compound involves balancing several competing factors. Mismanagement at the milling stage can ruin an entire batch.
Heat Buildup and Scorch
The friction from milling generates significant heat. If the temperature becomes too high, the vulcanizing agents can activate prematurely.
This phenomenon, known as scorch, causes the rubber to begin curing on the mill. A scorched batch is unusable and must be discarded.
Dispersion vs. Distribution
Good mixing is about more than just distributing additives evenly. It requires excellent dispersion, which means breaking down agglomerates of fillers (like carbon black) into fine particles.
Poor dispersion results in a non-homogenous compound with weak points, leading to inconsistent performance and premature failure of the final product.
The Mastication Balance
The degree of mastication is a critical trade-off. Insufficient mastication results in a compound that is too viscous and difficult to process.
Conversely, excessive mastication can break down the polymer chains too much, causing the rubber to lose its strength and elasticity, which cannot be fully recovered during curing.
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
The specifics of the milling process are tailored to the desired outcome of the final rubber product.
- If your primary focus is high performance and durability: The process must prioritize the excellent dispersion of reinforcing fillers like carbon black and silica.
- If your primary focus is efficient manufacturing: The key is to achieve a target viscosity through controlled mastication, ensuring the compound flows smoothly during molding or extrusion.
- If your primary focus is cost reduction: The formulation may include higher levels of inexpensive, non-reinforcing fillers, but milling must still ensure adequate dispersion to avoid catastrophic drops in physical properties.
Ultimately, mastering the milling process is fundamental to engineering rubber compounds that meet precise performance specifications.
Summary Table:
| Process Stage | Key Action | Primary Goal |
|---|---|---|
| Mastication | Passing rubber through rollers | Break down polymer chains, reduce elasticity |
| Mixing/Compounding | Adding and blending additives | Incorporate fillers, vulcanizing agents, etc. |
| Final Output | Homogeneous compound | Ready for molding or extrusion |
Need to Optimize Your Rubber Milling Process?
Mastering the balance between mastication, dispersion, and heat control is critical for producing high-performance rubber compounds. KINTEK specializes in providing robust lab equipment and consumables that deliver the precision and reliability your laboratory requires for R&D and quality control.
Whether you are developing high-durability products or optimizing for manufacturing efficiency, our solutions can help you achieve consistent, high-quality results. Contact our experts today to discuss how we can support your specific laboratory needs and enhance your rubber compounding capabilities.
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Laboratory Single Horizontal Jar Mill
- Laboratory Planetary Ball Mill Rotating Ball Milling Machine
- High Energy Vibratory Laboratory Ball Mill Double Tank Type
- Laboratory Horizontal Planetary Ball Mill Milling Machine
- High Energy Planetary Ball Mill for Laboratory Horizontal Tank Type Milling Machine
People Also Ask
- What is the ball mill based on the principle of? Impact and Attrition for Efficient Grinding
- Why are silicon nitride or zirconia preferred for milling iodo-vanadate-lead precursors? Ensure High Purity Results
- How do stainless steel grinding jars and balls contribute to mechanical alloying? Optimize HEA Powder Synthesis
- Why use zirconia ball milling jars for SiC/ZTA composite powders? Ensure High Purity & Efficient Particle Refinement
- Why are excellent sealing and corrosion resistance required for WC-10Co ball milling? Ensure High-Purity Mixing Results



















