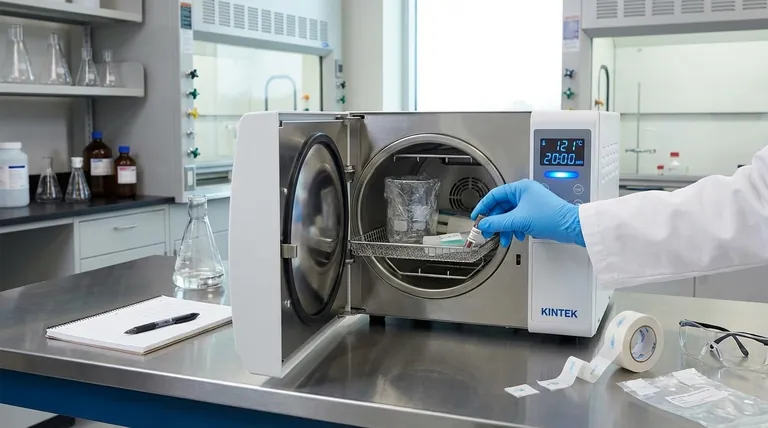
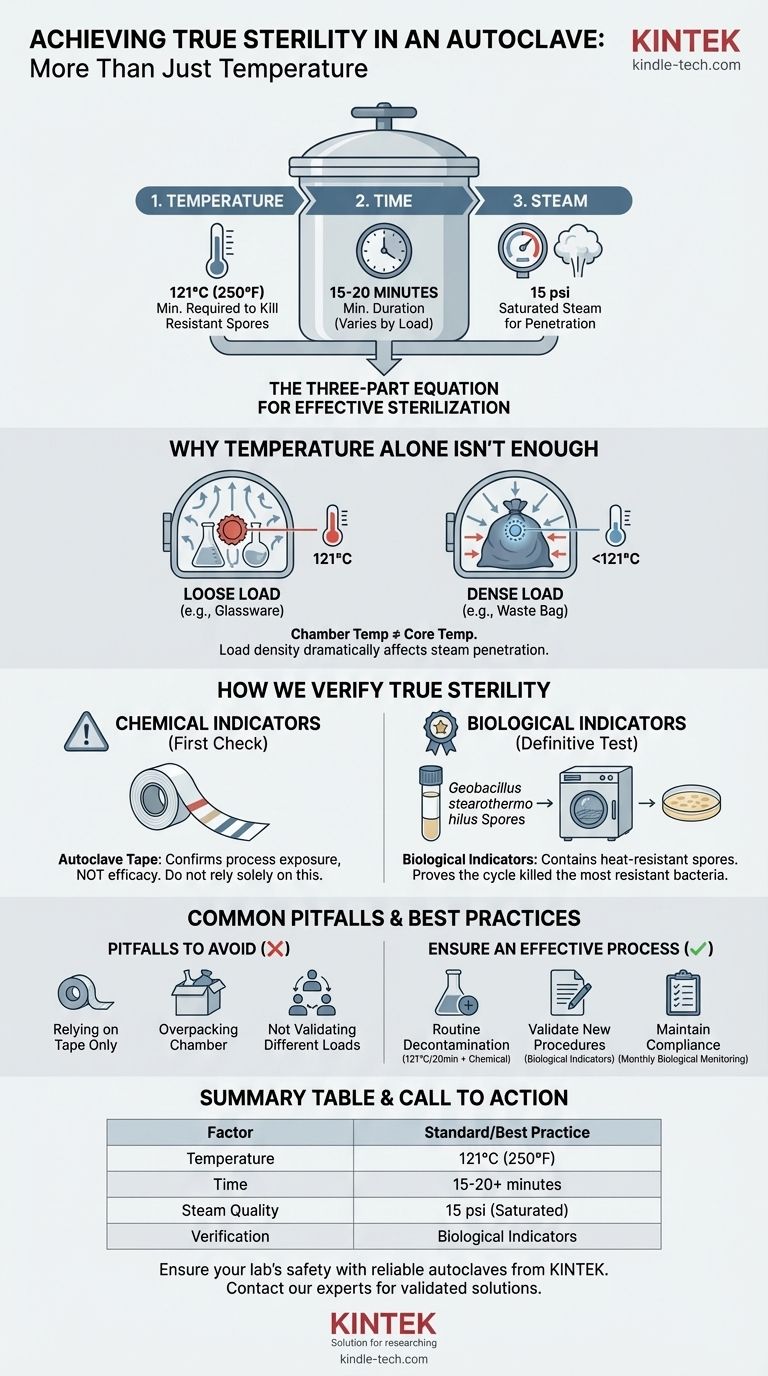
The standard temperature for achieving sterility in an autoclave is 121°C (250°F). However, this temperature must be held for a minimum duration, typically 15-20 minutes, under a pressure of 15 psi to ensure saturated steam can effectively penetrate the entire load. Temperature is only one part of a three-part equation for effective sterilization.
Effective sterilization is not a single setting but a validated process. True sterility depends on a precise interplay of time, temperature, and steam penetration, which must be rigorously verified with biological indicators, not just assumed.

Why Temperature Alone Isn't the Whole Story
Relying solely on the autoclave's temperature gauge is a common but critical mistake. The reading on the display indicates the temperature of the autoclave's chamber, not necessarily the temperature at the core of the items you are trying to sterilize.
The Three Pillars of Sterilization
Effective steam sterilization relies on three interdependent variables: temperature, time, and steam. The standard of 121°C is the minimum temperature required to reliably kill the most heat-resistant microorganisms and their spores.
This temperature must be maintained for a sufficient time to ensure the entire load reaches it. The steam itself is the vehicle for heat transfer, which is far more efficient than dry heat.
The Critical Role of Saturated Steam
An autoclave works by using pressurized, saturated steam. This steam condenses on cooler surfaces, rapidly transferring a massive amount of thermal energy and lethally denaturing the proteins within microorganisms.
Without proper steam penetration, you can have cold spots within your load that never reach the target temperature, even if the chamber itself is at 121°C.
The Impact of Load and Density
The nature of your load dramatically affects the time required for sterilization. A dense bag of waste or a large flask of liquid will take significantly longer for steam to penetrate and heat than loosely packed glassware.
This is why sterilization cycles are not one-size-fits-all; the time must be adjusted based on the specific contents.
How We Verify True Sterility
Because we cannot physically measure the temperature inside every item, we use indicators to confirm that the conditions for sterility were met throughout the entire load.
Chemical Indicators: The First Check
Chemical indicators, such as autoclave tape, change color when exposed to a specific temperature. They provide a quick visual confirmation that a load has been through a heat cycle.
However, they are not a reliable measure of efficacy. They confirm that the autoclave got hot, but not that it stayed hot for the required duration or that steam penetrated properly.
Biological Indicators: The Gold Standard
The definitive test for sterility relies on biological indicators. These contain spores from a highly heat-resistant bacterium, Geobacillus stearothermophilus.
These specific spores are chosen as a benchmark because they are harder to kill than the common pathogens you aim to eliminate. If your cycle kills these spores, you can be confident that it has achieved sterility.
The Validation Process
The reference Geobacillus spores are known to be killed at 121°C (250°F) after 13 minutes of exposure. By placing vials or strips of these spores in the most challenging parts of a load (e.g., the center of a dense pack), you directly test the autoclave's performance.
After the cycle, the indicator is incubated. If the spores were not killed, they will germinate and grow, causing a color change that signals a failed sterilization cycle.
Common Pitfalls to Avoid
Achieving consistent sterility requires avoiding common process errors that can compromise an otherwise effective cycle.
Relying Solely on Autoclave Tape
The most frequent misconception is that a color change on autoclave tape equals a sterile load. This is false. It is only an indicator that the item has been processed, not that the process was successful.
Improper Loading
Overpacking the autoclave chamber is a primary cause of sterilization failure. When items are packed too tightly, it creates air pockets and prevents steam from circulating and penetrating the load, leaving cold spots untouched by the sterilizing heat.
Not Validating for Different Loads
A cycle validated for glassware may be completely inadequate for sterilizing liquid media or biohazard waste. Each type of load, container, and fluid volume must be separately validated using biological indicators to establish the correct cycle time.
How to Ensure an Effective Process
Your approach to sterilization should be guided by the level of assurance you require for your specific application.
- If your primary focus is routine decontamination: Always use the standard 121°C cycle for at least 20 minutes and place a chemical indicator on every load to confirm it was processed.
- If your primary focus is validating a new procedure or container: You must use biological indicators placed at the hardest-to-reach points within the load to prove your chosen cycle time is effective.
- If your primary focus is maintaining compliance and safety: Implement a routine monitoring schedule, using biological indicators at least monthly and keeping meticulous records of all sterilization cycles and validation tests.
Ultimately, true sterility is achieved not by a setting on a dial, but by a consistent, validated, and meticulously monitored process.
Summary Table:
| Factor | Key Consideration | Standard/Best Practice |
|---|---|---|
| Temperature | Minimum required to kill resistant spores. | 121°C (250°F) |
| Time | Duration to ensure entire load reaches temperature. | 15-20 minutes minimum (varies by load). |
| Steam Quality | Saturated steam is critical for heat transfer. | 15 psi pressure for proper steam penetration. |
| Verification | Confirms the process was effective. | Biological indicators (Geobacillus stearothermophilus). |
Ensure your lab's safety and compliance with reliable autoclaves from KINTEK.
Sterilization is a precise science, and the right equipment is fundamental to a validated process. KINTEK specializes in high-performance lab equipment, including autoclaves designed for consistent, verifiable results. Whether you're decontaminating waste, sterilizing glassware, or validating a new procedure, our solutions are built to meet the rigorous demands of your laboratory.
Don't leave sterility to chance. Contact our experts today to discuss your specific needs and find the perfect autoclave solution for your lab.
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Desktop Fast Laboratory Autoclave Sterilizer 35L 50L 90L for Lab Use
- Laboratory High Pressure Steam Sterilizer Vertical Autoclave for Lab Department
- Desktop Fast Laboratory Autoclave Sterilizer 20L 24L for Lab Use
- Laboratory Sterilizer Lab Autoclave Vertical Pressure Steam Sterilizer for Liquid Crystal Display Automatic Type
- Portable Digital Display Automatic Laboratory Sterilizer Lab Autoclave for Sterilization Pressure
People Also Ask
- Why is it important to use the autoclave to sterilize laboratory tools? Ensure Complete Sterility for Reliable Results
- What is the pressure of autoclave at 121 C? The Key to Effective Steam Sterilization
- What precautions should be taken when using an autoclave in the laboratory? A Guide to Safe Sterilization
- How is an autoclave used to sterilize various requirement in the laboratory? A Guide to Effective Steam Sterilization
- How do you sterilize glassware by autoclave? Master the 3-Step Process for Reliable Sterility



















