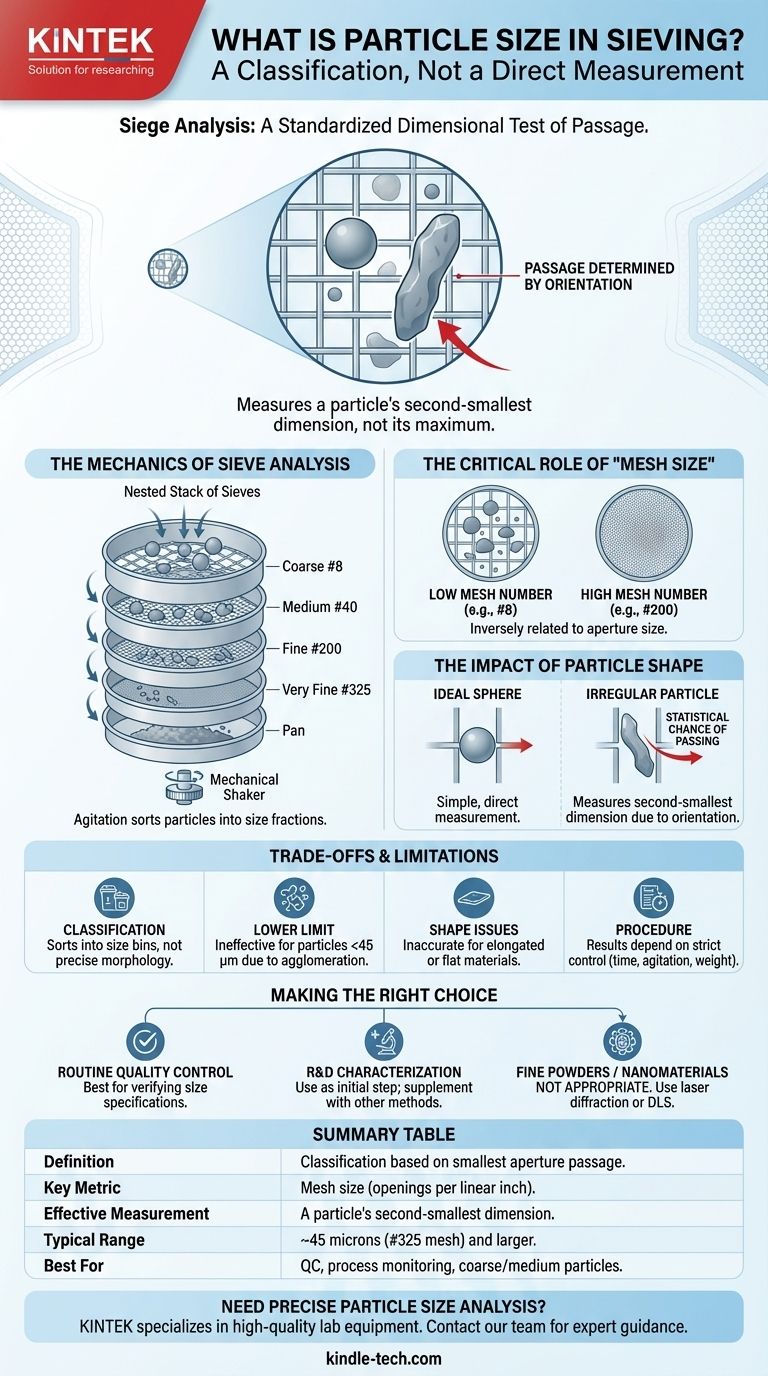
In sieving, particle size is not a direct measurement of a particle's length or width, but rather a classification based on the minimum square aperture it is able to pass through. This means a particle's reported size is defined by the standardized mesh screen that either retains it or allows it to fall through. It is fundamentally a dimensional test of passage.
Sieving classifies particles into size ranges, not absolute dimensions. The result is heavily influenced by a particle's shape, as it determines the orientation required to pass through the mesh, meaning sieving effectively measures a particle's second-smallest dimension.

The Mechanics of Sieve Analysis
To understand what a sieve analysis tells you, you must first understand the tool itself and the process. The result is a distribution, not a single number.
What is a Sieve?
A test sieve is a precision instrument consisting of a screen, typically made of woven wire cloth, with openings of a uniform and specific size. These screens are mounted in a rigid circular frame.
The Critical Role of "Mesh Size"
The term mesh size refers to the number of openings in the wire screen per linear inch. This is an inverse relationship: a high mesh number corresponds to many small openings, while a low mesh number means fewer, larger openings.
For example, a U.S. Standard #8 sieve has eight openings per inch and an aperture of 2.36 mm, suitable for coarse sand. In contrast, a #200 sieve has 200 openings per inch and a tiny aperture of 75 micrometers (µm), used for fine silts and powders.
The Sieving Process
Sieve analysis uses a nested stack of sieves with progressively smaller mesh sizes from top to bottom. A pre-weighed sample of the material is placed in the top sieve.
The entire stack is then agitated by a mechanical shaker. This motion gives each particle the opportunity to pass through the apertures until it reaches a sieve it cannot get through.
How Particle Size is Reported
After shaking, the material retained on each sieve is weighed. The "particle size" is then reported as a size fraction or range.
For instance, particles that passed through a #40 sieve (425 µm) but were retained on a #60 sieve (250 µm) are classified as being in the size range of -425 µm to +250 µm. The results are typically presented as a weight percentage for each size fraction.
Why Particle Shape is the Deciding Factor
The most misunderstood aspect of sieving is the profound impact of particle shape. The method assumes particles are spherical, which is rarely the case in the real world.
The Ideal Sphere
If you were sieving perfect spheres, the sieve aperture would directly correspond to the sphere's diameter. The measurement would be simple and unambiguous.
The Reality of Irregular Particles
Most materials—from sand and gravel to powders and grains—consist of irregular, elongated, or flattened particles. These shapes do not have a single "diameter."
The "Statistical Chance" of Passing
An elongated, needle-like particle can pass through a mesh opening much smaller than its total length. It simply needs to orient itself vertically during agitation to fall through end-first.
Therefore, sieving does not measure a particle's maximum dimension. With sufficient agitation time, it effectively measures a particle's second-smallest dimension, as this is what ultimately governs its ability to pass through the square aperture.
Understanding the Trade-offs and Limitations
Sieving is a foundational and cost-effective technique, but it's crucial to be aware of its limitations to interpret results correctly.
It's a Classification, Not a Precise Measurement
Sieve analysis sorts particles into size bins. It cannot provide the detailed information on particle morphology (shape, sphericity, surface texture) that methods like digital image analysis or microscopy can.
The Lower Limit of Practicality
For very fine particles, typically below about 45 microns (#325 mesh), sieving becomes ineffective. Van der Waals forces cause fine particles to agglomerate (clump together), preventing them from passing through the mesh individually.
Inaccurate Results for Certain Shapes
Highly elongated or flat materials (e.g., mica flakes, certain fibers) can produce misleading results. A long fiber might be classified in a very fine fraction because its narrow width allows it to pass through small openings, misrepresenting its overall scale.
The Need for Standardized Procedure
Results are only repeatable if the procedure is strictly controlled. Factors like the duration of shaking, the amplitude of agitation, and the initial sample weight can all significantly impact the final distribution.
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
Sieve analysis remains an indispensable tool when used for the correct application. Your specific goal determines whether it's the right choice.
- If your primary focus is routine quality control or process monitoring: Sieving is an excellent, reliable, and inexpensive method for verifying that a material consistently meets a defined size specification.
- If your primary focus is comprehensive particle characterization for R&D: Use sieving for initial classification, but supplement it with other methods like laser diffraction or image analysis to get a complete picture of size and shape.
- If your primary focus is analyzing fine powders or nanomaterials: Sieving is not the appropriate tool. You should use advanced methods like laser diffraction, dynamic light scattering (DLS), or electron microscopy.
Ultimately, sieve analysis provides a standardized, practical framework for classifying the physical world by size.
Summary Table:
| Aspect | Description |
|---|---|
| Definition | Classification based on the smallest square aperture a particle can pass through. |
| Key Metric | Mesh size (number of openings per linear inch). |
| Effective Measurement | A particle's second-smallest dimension. |
| Typical Range | ~45 microns (#325 mesh) and larger. |
| Best For | Quality control, process monitoring, and coarse to medium-sized particles. |
Need precise particle size analysis for your lab?
KINTEK specializes in high-quality lab equipment and consumables for all your sieving and particle analysis needs. Whether you require standard test sieves, mechanical shakers, or guidance on the best method for your specific materials, our experts are here to help you achieve accurate and repeatable results.
Contact our team today to discuss your application and discover how KINTEK can enhance your laboratory's efficiency and data quality.
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Laboratory Test Sieves and Sieving Machines
- Laboratory Vibratory Sieve Shaker Machine Slap Vibrating Sieve
- Laboratory Single Horizontal Jar Mill
- High Energy Vibratory Laboratory Ball Mill Grinding Mill Single Tank Type
- High Energy Planetary Ball Mill Machine for Laboratory Horizontal Tank Type
People Also Ask
- What is the primary purpose of using standard sieves? Master Particle Uniformity for High-Quality Catalyst Preparation
- What is the primary function of a mechanical sieve shaker for biomass analysis? Optimize Particle Size Distribution
- What are the specifications for test sieves? A Guide to ASTM & ISO Standards for Accurate Particle Analysis
- What is the role of standard sieves in gold scrap leaching kinetic studies? Ensure Precision in Particle Classification
- How is a vibratory sieve shaker used in the particle size analysis of mechanically alloyed powders? Expert Guide



















