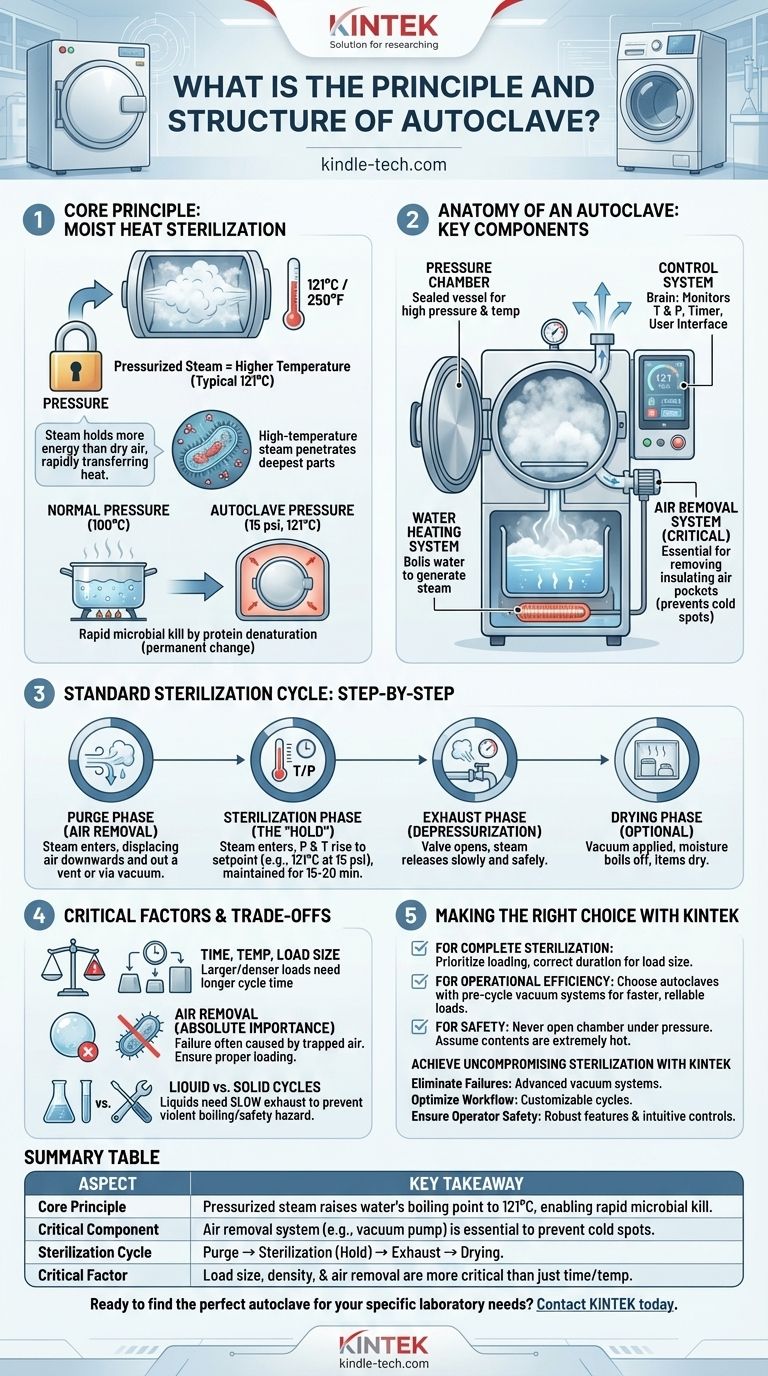
At its core, an autoclave is a machine that uses high-pressure steam to achieve sterilization. It operates on the principle that increasing pressure raises the boiling point of water, allowing the steam to reach temperatures (typically 121°C or 250°F) that can rapidly kill all forms of microbial life, including heat-resistant spores, by irreversibly damaging their essential proteins.
The fundamental insight is this: an autoclave doesn't just use hot steam; it uses pressurized steam. This pressure is the key that unlocks temperatures well above water's normal boiling point, enabling fast and complete penetration of heat into the items being sterilized.
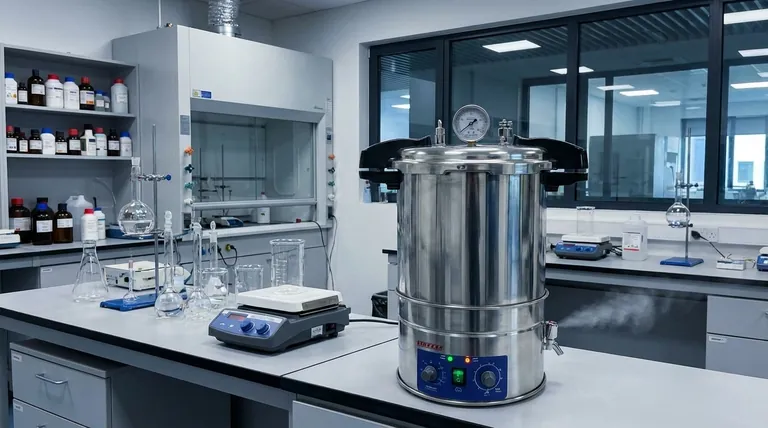

The Core Principle: Moist Heat Sterilization
The effectiveness of an autoclave is rooted in a simple law of physics combined with a key biological vulnerability.
Why Steam is More Effective Than Dry Heat
Moist heat, in the form of saturated steam, is a far more efficient agent for heat transfer than dry air.
Steam can hold significantly more energy than hot air at the same temperature. When it condenses on a cooler surface, it rapidly transfers this energy, quickly heating the item.
The Critical Role of Pressure
Under normal atmospheric pressure, water boils at 100°C (212°F). This temperature is not sufficient to reliably destroy hardy bacterial spores.
By sealing the chamber and increasing the pressure (typically to 15 psi above atmospheric pressure), an autoclave prevents water from boiling until it reaches 121°C (250°F).
How Sterilization Occurs at a Molecular Level
This high-temperature steam forces its way into the deepest parts of the equipment or media being sterilized.
The intense heat causes essential microbial proteins and enzymes to coagulate and denature. This is a permanent structural change, much like cooking an egg, which effectively and irreversibly kills the microorganism.
Anatomy of an Autoclave: Key Components
An autoclave is more than just a pressure cooker; it's a precision instrument with several critical components working in concert.
The Pressure Chamber
This is the central vessel, a robust container with a locking, sealed door. It is built to safely withstand the high pressures and temperatures required for sterilization.
The Water Heating System
Typically located at the bottom of the chamber, an electric heating element boils a reservoir of water to generate the necessary steam.
The Air Removal System
This is arguably one of the most critical parts for effective sterilization. Air is a poor conductor of heat, and any trapped air pockets will prevent steam from reaching the items, creating cold spots and leading to sterilization failure. Modern autoclaves use a vacuum pump to actively remove all air before the cycle begins.
The Control System
This is the brain of the autoclave. It consists of sensors for monitoring temperature and pressure, a timer, and a user interface (often a touchscreen) to select and customize sterilization programs.
The Standard Sterilization Cycle: A Step-by-Step Process
A typical autoclave cycle consists of several distinct phases to ensure safety and effectiveness.
1. Purge Phase (Air Removal)
The cycle begins by removing the insulating air from the chamber. Steam is injected to displace the cooler air downwards and out a vent, or a vacuum pump actively evacuates the chamber.
2. Sterilization Phase (The "Hold")
Once all air is removed, the exhaust vents close. Steam continues to enter the chamber, causing pressure and temperature to rise to the target setpoint (e.g., 121°C at 15 psi). The controller holds these conditions for the specified duration, typically 15-20 minutes.
3. Exhaust Phase (Depressurization)
After the hold time is complete, a valve opens to slowly and safely release the steam and pressure from the chamber. This must be done gradually, especially for liquid loads, to prevent them from boiling over.
4. Drying Phase (Optional)
Many autoclaves include a final drying phase. A vacuum may be applied to the heated chamber, causing any remaining moisture on the load to boil away, leaving the instruments or glassware completely dry.
Understanding the Trade-offs and Critical Factors
Proper autoclave use requires understanding the variables that can impact the outcome.
Time, Temperature, and Load Size
The standard 121°C for 15 minutes is a guideline. A larger, denser load requires a longer cycle time to ensure the steam fully penetrates to the center of the items.
The Absolute Importance of Air Removal
Sterilization failure is most often caused by trapped air. Items must be loaded in a way that allows for easy air removal and steam penetration. Never pack the chamber so tightly that steam flow is obstructed.
Liquid vs. Solid Cycles
Sterilizing liquids requires a much slower exhaust phase. Depressurizing too quickly will cause superheated liquids to boil violently, which can lead to loss of media and create a significant safety hazard.
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
By understanding these principles, you can ensure your sterilization processes are both effective and safe.
- If your primary focus is ensuring complete sterilization: Prioritize proper loading techniques to eliminate air pockets and always select a cycle duration appropriate for your specific load's size and density.
- If your primary focus is operational efficiency: Recognize that autoclaves with pre-cycle vacuum systems are faster and more reliable for complex loads like wrapped instrument packs or porous materials.
- If your primary focus is safety: Never attempt to open the autoclave door until the chamber pressure has fully returned to zero. Always assume the contents are extremely hot.
Mastering the interplay of steam, pressure, and time is the key to achieving reliable and safe sterilization.
Summary Table:
| Aspect | Key Takeaway |
|---|---|
| Core Principle | Pressurized steam raises water's boiling point to 121°C (250°F), enabling rapid microbial kill. |
| Critical Component | Air removal system (e.g., vacuum pump) is essential to prevent cold spots and ensure sterilization. |
| Sterilization Cycle | Purge (air removal) → Sterilization (hold at 121°C) → Exhaust (depressurization) → Drying (optional). |
| Critical Factor | Load size, density, and proper air removal are more critical than just time and temperature. |
Achieve Uncompromising Sterilization with KINTEK
Understanding the principles of an autoclave is the first step. Implementing them reliably in your laboratory is the next. KINTEK specializes in high-performance lab equipment, including autoclaves designed for safety, efficiency, and precise control.
Let us help you enhance your lab's capabilities:
- Eliminate Sterilization Failures: Our autoclaves feature advanced vacuum systems to ensure complete air removal, preventing cold spots and guaranteeing consistent results.
- Optimize Your Workflow: Choose from models with customizable cycles for solids, liquids, and complex loads to improve your lab's operational efficiency.
- Ensure Operator Safety: Built with robust safety features and intuitive controls, our equipment protects your team and your valuable samples.
Ready to find the perfect autoclave for your specific laboratory needs?
Contact KINTEK today for a personalized consultation. Our experts are ready to discuss your requirements and demonstrate how our solutions bring reliability and value to your sterilization processes.
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Portable Digital Display Automatic Laboratory Sterilizer Lab Autoclave for Sterilization Pressure
- Desktop Fast Laboratory Autoclave Sterilizer 20L 24L for Lab Use
- Portable High Pressure Laboratory Autoclave Steam Sterilizer for Lab Use
- Desktop Fast Laboratory Autoclave Sterilizer 35L 50L 90L for Lab Use
- Laboratory High Pressure Steam Sterilizer Vertical Autoclave for Lab Department
People Also Ask
- What extreme conditions does a laboratory autoclave simulate? Testing Wear Resistance of Nuclear Fuel Cladding
- What are the advantages of using an autoclave equipped with a stirring device for molten salt testing? Dynamic Accuracy
- What are the standard operating parameters for an autoclave? Master Temperature, Pressure, and Time for Sterilization
- Why is a laboratory high-pressure autoclave sterilizer necessary? Ensure Accuracy in Antibacterial Research
- What role does an autoclave play in remediation experiments? Ensure Precision by Eliminating Biological Noise



















