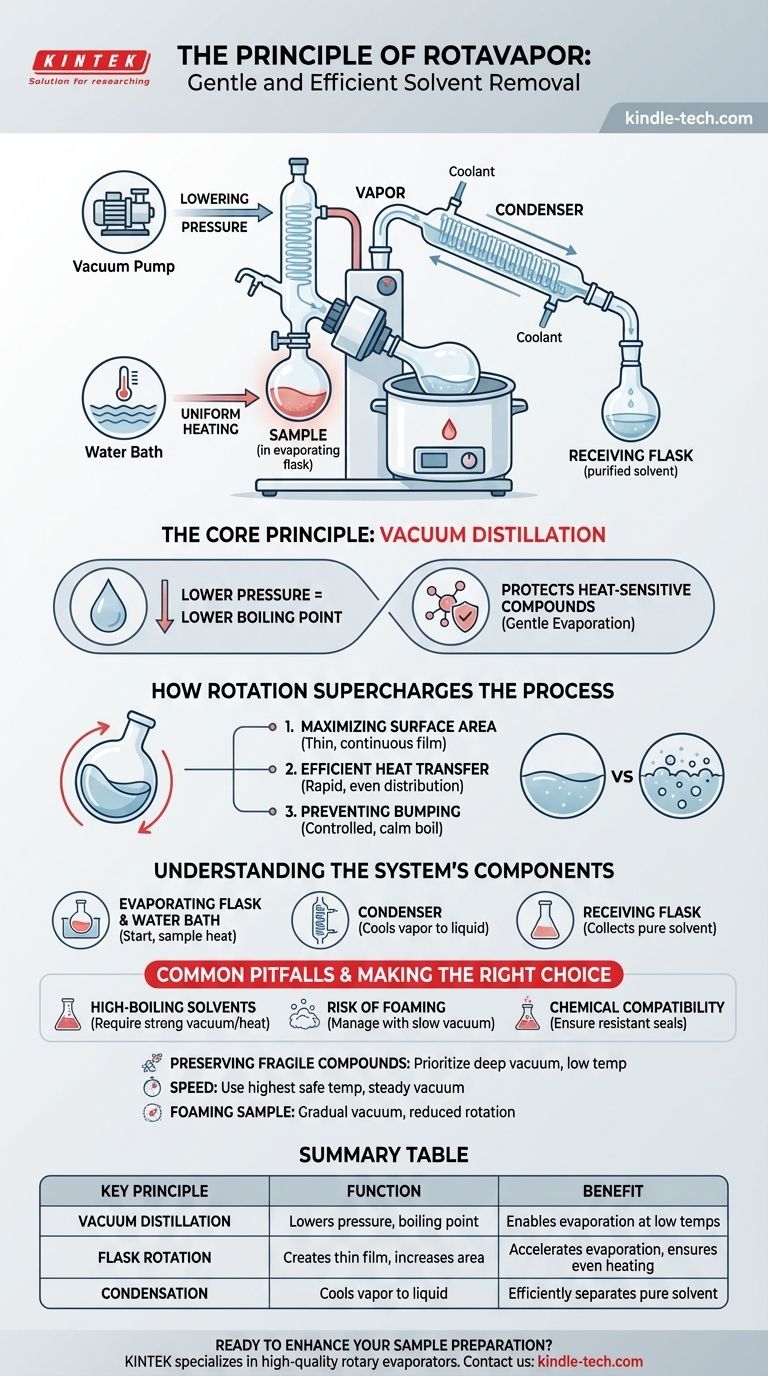
At its core, a rotary evaporator (or rotovap) is a device for gently and efficiently removing volatile solvents from a sample. It operates on the principle of vacuum distillation, where reducing the system's pressure lowers the solvent's boiling point. This process is accelerated by rotating a flask to increase the liquid's surface area and ensure uniform heating in a warm water bath.
The rotovap's primary advantage is not simply its speed, but its gentleness. By enabling evaporation at a low temperature, it protects heat-sensitive compounds in the sample that would otherwise be degraded or destroyed by conventional high-temperature distillation.

The Core Principle: Lowering the Boiling Point
The fundamental physics behind the rotovap is the direct relationship between a liquid's boiling point and the pressure exerted upon it.
The Critical Role of the Vacuum
A vacuum pump is attached to the rotovap to systematically remove air from the sealed apparatus. As the pressure inside the system drops, the temperature required to make the solvent boil also drops significantly.
For example, water boils at 100°C (212°F) at standard atmospheric pressure. Under a strong vacuum, it can be made to boil at room temperature or even lower.
Why a Lower Boiling Point Matters
This ability to evaporate solvents at a low temperature is the rotovap's key feature. It allows a chemist to remove a solvent like ethanol or ethyl acetate without applying high heat, thus preserving the chemical integrity of the desired compound dissolved within it.
How Rotation Supercharges the Process
The constant rotation of the sample flask is not just for show; it serves three distinct and crucial purposes that dramatically increase the efficiency of the evaporation.
Maximizing Surface Area
Rotation spreads the sample liquid into a thin, continuous film across the entire inner surface of the flask. This vastly increases the surface area exposed to the vacuum, allowing for a much faster rate of evaporation than would occur with a static pool of liquid.
Ensuring Efficient Heat Transfer
The flask is partially submerged in a temperature-controlled water bath. As it rotates, the thin film of liquid is constantly renewed and warmed, ensuring rapid and even heat distribution throughout the entire sample. This prevents localized overheating.
Preventing Bumping
Heating a liquid under vacuum without agitation can lead to violent, uncontrolled boiling known as "bumping," which can cause sample loss. The smooth, constant agitation from the rotation ensures a calm and controlled boil, making the process safe and predictable.
Understanding the System's Components
A complete understanding requires seeing how the individual parts work together to achieve the final goal.
The Evaporating Flask & Water Bath
This is where the process begins. The sample (solute dissolved in a solvent) is placed in a round-bottom flask, which is then attached to the rotovap and heated gently by the water bath.
The Condenser
After the solvent evaporates into a gas, it travels up into a chilled condenser coil. Coolant (typically cold tap water or a recirculating chiller) flows through the outside of this coil.
The cold surface of the condenser causes the solvent vapor to instantly turn back into a liquid, just as water droplets form on the outside of a cold glass.
The Receiving Flask
This condensed, purified solvent then drips down from the condenser and is collected in a separate receiving flask. This effectively separates the solvent from your now-concentrated sample, which remains in the original evaporating flask.
Common Pitfalls to Avoid
While powerful, the rotovap requires proper technique to be used effectively and safely.
Working with High-Boiling Solvents
Solvents with very high boiling points, such as DMSO or water, can be challenging to remove completely. They may require a combination of higher bath temperatures and a very strong vacuum, which increases the risk to heat-sensitive samples.
The Risk of Foaming
Some samples have a tendency to foam or bubble excessively under vacuum. This foam can travel up into the condenser, causing contamination and sample loss. This is managed by applying the vacuum slowly or using a larger evaporating flask.
Chemical Compatibility
The seals and gaskets of a rotovap are critical for maintaining a vacuum. You must ensure they are made of a material (e.g., Viton, FFKM) that is chemically resistant to the solvents you are using to prevent degradation and vacuum leaks.
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
Applying these principles allows you to tailor the process to your specific objective.
- If your primary focus is preserving a fragile compound: Prioritize achieving a deep vacuum to enable evaporation at the lowest possible temperature, even if it takes longer.
- If your primary focus is speed: Use the highest bath temperature your compound can safely tolerate and apply just enough vacuum to achieve a steady, controlled boil without bumping.
- If you are working with a foaming sample: Apply the vacuum very gradually and consider reducing the rotation speed to minimize agitation until the bulk of the solvent is removed.
Mastering these principles transforms the rotovap from a simple machine into a precision tool for sample preparation.
Summary Table:
| Key Principle | Function | Benefit |
|---|---|---|
| Vacuum Distillation | Lowers pressure to reduce solvent boiling point. | Enables evaporation at low temperatures. |
| Flask Rotation | Creates a thin film, increasing surface area. | Accelerates evaporation and ensures even heating. |
| Condensation | Cools vapor back into liquid in a separate flask. | Efficiently separates and collects the pure solvent. |
Ready to enhance your sample preparation with precision and care?
KINTEK specializes in high-quality laboratory equipment, including rotary evaporators designed for efficient and gentle solvent removal. Our rotovaps are ideal for chemists and researchers working with heat-sensitive compounds, ensuring your valuable samples are protected.
Contact us today to find the perfect solution for your lab's needs and discover how our expertise can support your research goals.
Get in touch with our experts now!
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Circulating Water Vacuum Pump for Laboratory and Industrial Use
- Evaporation Crucible for Organic Matter
- Ceramic Evaporation Boat Set Alumina Crucible for Laboratory Use
- Hemispherical Bottom Tungsten Molybdenum Evaporation Boat
- Oil Free Diaphragm Vacuum Pump for Laboratory and Industrial Use
People Also Ask
- What is the purpose of the compression chamber in a vacuum pump? The Heart of Vacuum Generation
- What determines the vacuum degree achievable by a water circulating vacuum pump? Unlock the Physics of Its Limits
- Why is a water circulating vacuum pump suitable for handling flammable or explosive gases? Inherent Safety Through Isothermal Compression
- What can I use a vacuum pump for? Powering Industrial Processes from Packaging to Automation
- How is a circulating water vacuum pump utilized for hydrogen production residues? Optimize Your Solid-Liquid Separation



















