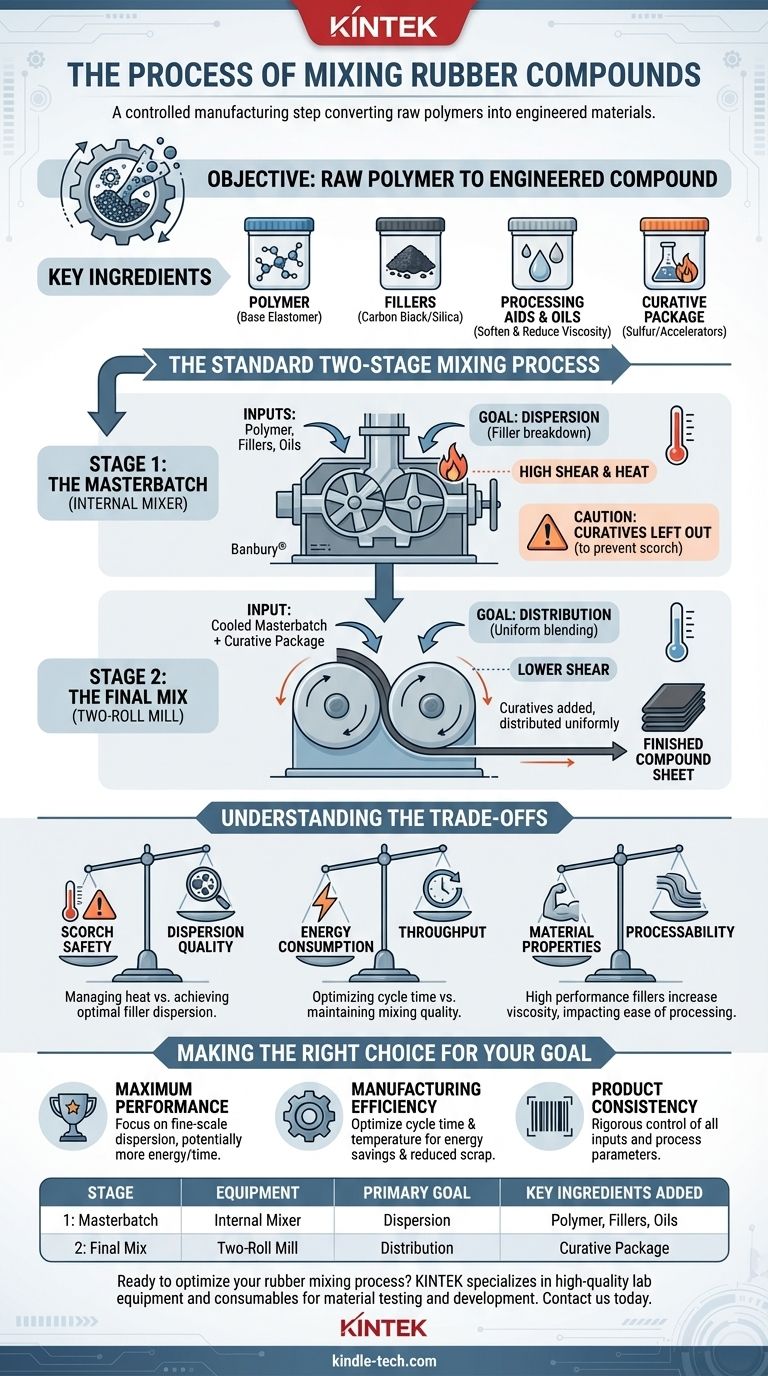
The process of mixing rubber compounds is a highly controlled manufacturing step that transforms raw polymers and additives into a uniform, processable material with specific engineered properties. It relies on intense mechanical energy to break down, blend, soften, and homogenize all ingredients, creating a compound ready for shaping and curing.
At its core, rubber mixing is not simply blending ingredients. It is a thermomechanical process designed to achieve two critical goals: first, the physical breakdown and dispersion of additives into a raw polymer matrix, and second, the uniform distribution of a heat-sensitive curing package without activating it prematurely.

The Objective: From Raw Polymer to Engineered Compound
A raw rubber polymer, like natural rubber or a synthetic equivalent, rarely has the properties required for a finished product. The mixing process is where value is added by incorporating a precise recipe of ingredients to achieve desired characteristics like strength, durability, color, and elasticity.
The Key Ingredients
A typical rubber compound formula consists of several key components:
- The Polymer: This is the base elastomer (e.g., Natural Rubber, SBR, EPDM) that forms the backbone of the compound.
- Fillers: Materials like carbon black or silica are added to reinforce the polymer, improving strength, tear resistance, and abrasion resistance.
- Processing Aids & Oils: These are used to soften the compound, reduce its viscosity, and make it easier to process in subsequent steps.
- The Curative Package: This includes sulfur, accelerators, and activators. These chemicals create cross-links between polymer chains during the final curing (vulcanization) stage, which gives the rubber its final elastic properties.
The Standard Two-Stage Mixing Process
To properly incorporate all ingredients while managing heat, the industry standard is a two-stage process involving an internal mixer followed by a two-roll mill.
Stage 1: The Masterbatch in an Internal Mixer
The first and most energy-intensive stage occurs in a powerful internal mixer, such as a Banbury® mixer. The primary goal here is dispersion—breaking down clumps of fillers and forcing them into the polymer matrix.
This stage involves adding the polymer, fillers, and oils in a specific sequence. The mixer's rotors apply immense mechanical shear forces, which physically tear apart the ingredients and generate significant heat. This combination of shear and heat is essential for achieving a homogenous blend known as the "masterbatch."
Crucially, the temperature-sensitive curative package is left out of this stage. The heat generated would cause premature vulcanization, a condition known as scorch, rendering the batch unusable.
Stage 2: The Final Mix on a Two-Roll Mill
After the masterbatch is discharged and cooled, it moves to the second stage, typically on an open two-roll mill. The primary goal here is distribution.
The cooled masterbatch is passed through the gap (or "nip") between the two rolls repeatedly. The temperature-sensitive curative package is added at this point. The shear forces are much lower than in the internal mixer, allowing the curatives to be distributed uniformly throughout the batch without generating excessive, scorch-inducing heat.
Once mixing is complete, the final compound is taken off the mill in continuous sheets and cooled, ready for shaping processes like extrusion or molding.
Understanding the Trade-offs
Successfully mixing rubber is a balancing act between competing factors. Understanding these trade-offs is critical for process control and quality.
Scorch Safety vs. Dispersion Quality
This is the fundamental challenge. Achieving the best possible dispersion of fillers requires high energy and long mixing times, both of which increase compound temperature. However, exceeding the activation temperature of the curatives will ruin the batch. The entire two-stage process is designed to manage this risk.
Energy Consumption vs. Throughput
Rubber mixing is an extremely energy-intensive process. Optimizing the cycle time to maximize throughput is a constant operational goal, but it cannot come at the expense of proper dispersion. Rushing the masterbatch stage can lead to poorly dispersed fillers and a final product that fails to meet performance specifications.
Material Properties vs. Processability
Adding high levels of reinforcing fillers dramatically improves the physical properties of the final product but also increases the compound's viscosity. This makes it much harder to mix and process. The formulation must be balanced to ensure the compound can be manufactured efficiently while still meeting end-use requirements.
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
The focus of the mixing process can be adjusted depending on the final objective.
- If your primary focus is maximum material performance: The key is achieving excellent, fine-scale dispersion of fillers during the masterbatch stage, even if it requires more energy and time.
- If your primary focus is manufacturing efficiency: The key is optimizing the mixing cycle time and temperature profile to minimize energy use and prevent scrap without compromising essential quality standards.
- If your primary focus is product consistency: The key is rigorous control over all inputs—raw material quality, ingredient weights, mixing times, and temperature—to ensure every batch is identical.
Mastering the principles of rubber mixing is fundamental to transforming simple raw materials into high-performance, reliable engineered products.
Summary Table:
| Stage | Equipment | Primary Goal | Key Ingredients Added |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1: Masterbatch | Internal Mixer (e.g., Banbury®) | Dispersion (filler breakdown) | Polymer, Fillers, Oils |
| 2: Final Mix | Two-Roll Mill | Distribution (uniform blending) | Curative Package (Sulfur, Accelerators) |
Ready to optimize your rubber mixing process for superior product performance and manufacturing efficiency?
KINTEK specializes in high-quality lab equipment and consumables for material testing and development. Whether you're focused on achieving maximum material performance, improving manufacturing efficiency, or ensuring product consistency, our solutions can help.
Contact us today to discuss how we can support your laboratory's specific rubber compounding needs!
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Lab Internal Rubber Mixer Rubber Kneader Machine for Mixing and Kneading
- Laboratory Vortex Mixer Orbital Shaker Multifunctional Rotation Oscillation Mixer
- Laboratory Disc Rotary Mixer for Efficient Sample Mixing and Homogenization
- Laboratory Oscillating Orbital Shaker
- High Shear Homogenizer for Pharmaceutical and Cosmetic Applications
People Also Ask
- What is the internal structure of a mixer? A Guide to Core Components and Operation
- What is a rubber mixing mill used for? Transforming Raw Rubber into High-Performance Compounds
- What are the three 3 basic types of mixers? Find Your Perfect Match for Baking & Production
- What finishes are done using calendering technique? Achieve High Gloss, Embossing, and More
- What machine makes molding? Injection Molding Machines for Mass Production
- What is an internal screw mixer? A Guide to Gentle, Efficient Powder Blending
- How many types of rolling mills are there? A Guide to Roll Configurations & Capabilities
- What is the manufacturing process of rubber? From Raw Material to Durable End Product


















