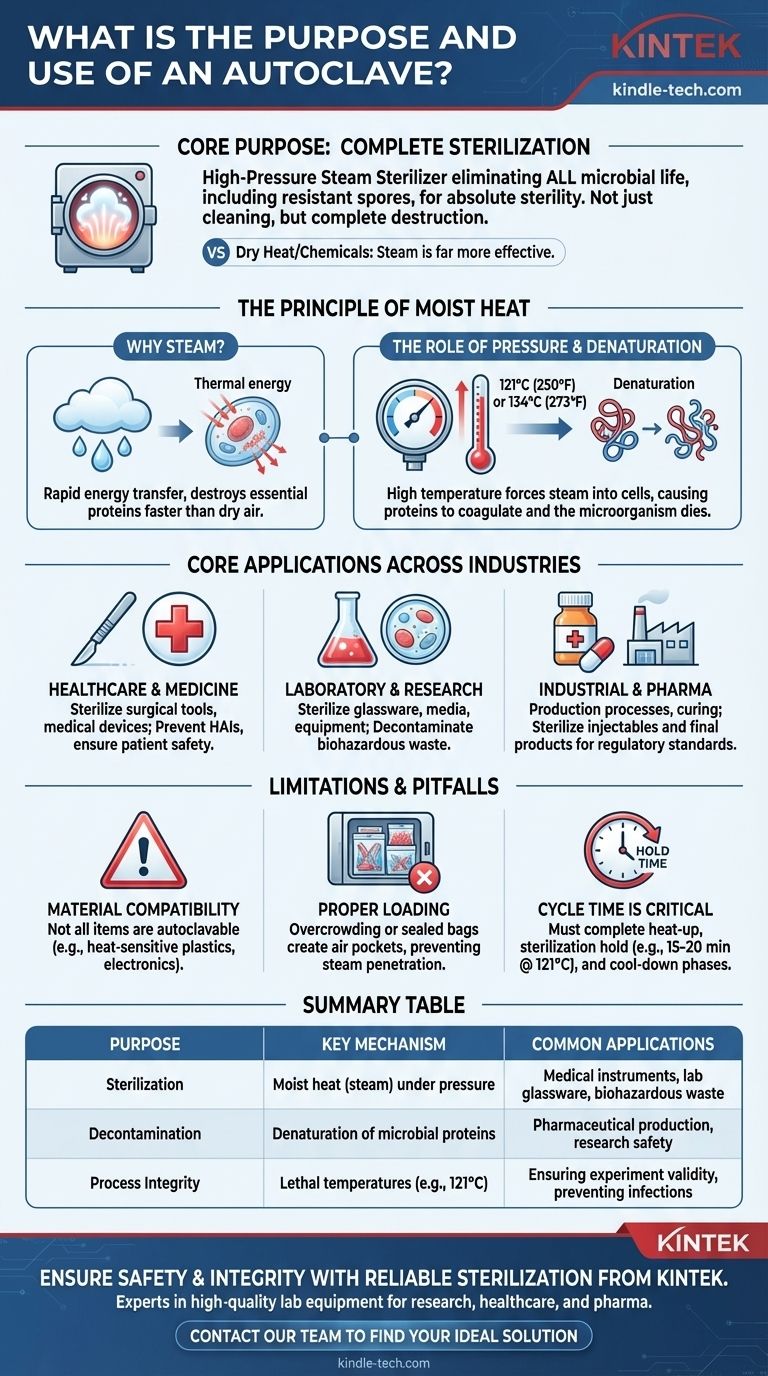
At its core, an autoclave is a high-pressure steam sterilizer. Its fundamental purpose is to use a combination of elevated temperature and pressure to eliminate all forms of microbial life—including bacteria, viruses, fungi, and highly resistant spores—from objects placed inside it. This process makes it an indispensable tool in any environment where absolute sterility is required.
While simple cleaning removes visible dirt, it leaves behind a world of invisible microbes. An autoclave's purpose is not just to clean, but to achieve complete sterilization by using pressurized steam, a method far more effective at killing resilient organisms than dry heat or chemical disinfectants alone.

The Principle of Moist Heat Sterilization
The effectiveness of an autoclave is not based on just heat or pressure, but on the specific interaction between them. The process is formally known as moist heat sterilization.
Why Steam is the Key Ingredient
Dry heat, like in a conventional oven, is an inefficient way to transfer energy. Air is a poor conductor of heat.
Moist heat, in the form of steam, is dramatically more effective. The moisture in the steam rapidly transfers thermal energy to any item it contacts, penetrating microbial cells and destroying their essential proteins much faster than dry air at the same temperature.
The Role of Pressure
Under normal atmospheric conditions, water boils at 100°C (212°F). This temperature is not sufficient to reliably kill heat-resistant bacterial spores.
By increasing the pressure inside the autoclave's sealed chamber, we can raise the boiling point of water. This allows the creation of steam at much higher temperatures, typically 121°C (250°F) or 134°C (273°F), which are lethal to all known microorganisms.
How Sterilization Actually Occurs
The combination of high-temperature steam and moisture is lethal to microbes. This energy forces its way into the cells and causes denaturation, a process where vital proteins and enzymes coagulate and lose their structure, similar to how an egg white solidifies when cooked.
Once its critical proteins are denatured, the microorganism cannot perform its life functions and dies.
Core Applications Across Industries
The reliability of steam sterilization makes the autoclave a cornerstone of safety and quality control in numerous fields.
In Healthcare and Medicine
In hospitals and clinics, autoclaves are used to sterilize surgical instruments, medical devices, and other reusable materials. This is a critical step in preventing healthcare-associated infections (HAIs) and ensuring patient safety.
In Laboratory and Research Settings
For scientists, an autoclave serves two main purposes. First, it sterilizes glassware, growth media, and equipment to prevent unwanted microbial contamination from ruining experiments and invalidating data.
Second, it is used to decontaminate biohazardous waste (like used petri dishes or live cultures) before disposal, ensuring the safety of lab personnel and the environment.
In Industrial and Pharmaceutical Production
Many industrial processes rely on autoclaves for more than just sterilization, using the high heat and pressure for chemical reactions or curing composite materials. In pharmaceuticals, they are essential for sterilizing injectable solutions, equipment, and final product containers to meet stringent regulatory standards.
Understanding the Limitations and Pitfalls
While highly effective, autoclaving is not a universal solution. Understanding its limitations is crucial for proper use and avoiding costly mistakes.
Not All Materials are Autoclavable
The intense heat and pressure will damage or destroy certain items. Heat-sensitive materials like many plastics, volatile chemicals, and delicate electronics cannot be autoclaved. It is critical to confirm a material's compatibility before processing it.
Proper Loading is Non-Negotiable
Steam must be able to circulate freely and contact every surface of the items being sterilized. Overcrowding the chamber or packing items in sealed, non-permeable bags can create air pockets that prevent steam penetration.
These air pockets act as an insulating barrier, leaving the items inside unsterilized and creating a significant safety risk. This is one of the most common causes of sterilization failure.
Sterilization is Not Instantaneous
An autoclave cycle has multiple phases: a heat-up phase, a sterilization "hold" time, and a cool-down phase. The hold time at the target temperature (e.g., 15-20 minutes at 121°C) is the critical window where killing occurs. Shortening this time to save a few minutes will compromise the entire process.
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
Effective autoclaving depends on aligning the process with your specific objective. A validated cycle for decontaminating waste is different from one used for preparing sterile surgical tools.
- If your primary focus is patient safety (Healthcare): Your priority is rigorous adherence to validated cycles and using biological indicators (spore tests) to prove that every instrument is sterile.
- If your primary focus is data integrity (Research): Your priority is ensuring that all media, buffers, and glassware are completely free of contaminants that could interfere with your results.
- If your primary focus is biosafety (Waste Decontamination): Your priority is using a cycle with sufficient time and steam penetration to ensure all biohazardous agents are neutralized before the waste leaves the lab.
Ultimately, the autoclave is a foundational tool of modern science and medicine, providing a reliable guarantee of sterility that underpins safety and integrity across technical fields.
Summary Table:
| Purpose | Key Mechanism | Common Applications |
|---|---|---|
| Sterilization | Moist heat (steam) under pressure | Medical instruments, lab glassware, biohazardous waste |
| Decontamination | Denaturation of microbial proteins | Pharmaceutical production, research safety |
| Process Integrity | Lethal temperatures (e.g., 121°C) | Ensuring experiment validity, preventing infections |
Ensure the safety and integrity of your work with reliable sterilization from KINTEK.
Whether you are preparing sterile media for critical research, decontaminating biohazardous waste, or sterilizing surgical tools, the right autoclave is fundamental to your success. KINTEK specializes in high-quality lab equipment, including autoclaves designed to meet the rigorous demands of laboratories, healthcare facilities, and pharmaceutical production.
Our experts can help you select the perfect autoclave to achieve complete sterilization, protect your personnel, and maintain the integrity of your processes. Contact our team today to discuss your specific needs and find the ideal solution for your laboratory.
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Laboratory Sterilizer Lab Autoclave Herbal Powder Sterilization Machine for Plant
- Laboratory High Pressure Steam Sterilizer Vertical Autoclave for Lab Department
- Desktop Fast Laboratory Autoclave Sterilizer 35L 50L 90L for Lab Use
- Desktop Fast Laboratory Autoclave Sterilizer 20L 24L for Lab Use
- Portable Digital Display Automatic Laboratory Sterilizer Lab Autoclave for Sterilization Pressure
People Also Ask
- What is the primary purpose of an autoclave in the preparation of media for the biological leaching of uranium?
- How should solid materials in bags be prepared for decontamination? Master Steam Penetration for Safe Sterilization
- How does an autoclave ensure the reliability of experimental results? Achieving a Sterile Baseline for Lab Research
- What is the necessity of using a steam autoclave for dental alloys? Ensure Pure Bacterial Adhesion Data
- What role does an autoclave play in remediation experiments? Ensure Precision by Eliminating Biological Noise



















