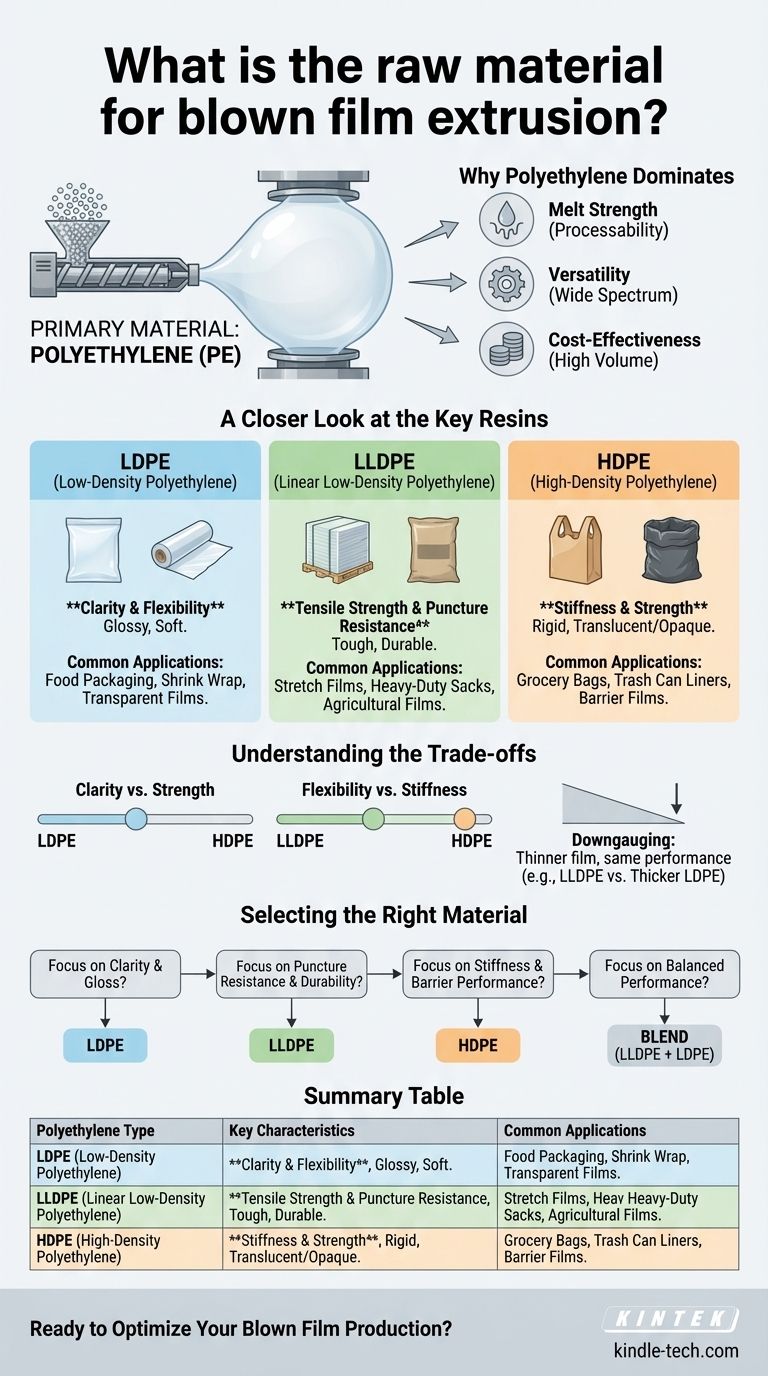
The primary raw material for blown film extrusion is polyethylene. This versatile polymer resin serves as the foundation for the process, with specific grades being selected or blended to achieve the desired physical properties in the final film. The most common resins used are Low-Density Polyethylene (LDPE), Linear Low-Density Polyethylene (LLDPE), and High-Density Polyethylene (HDPE).
The core principle is simple: while polyethylene is the universal raw material, the specific type of polyethylene you choose directly dictates the film's final characteristics, such as its clarity, strength, and flexibility.
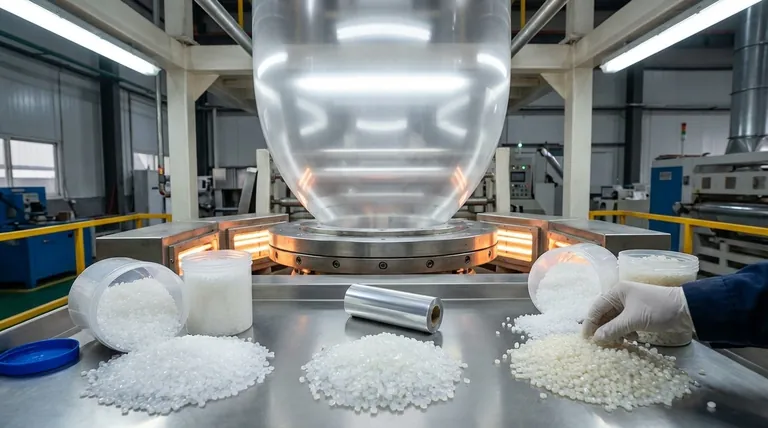

Why Polyethylene Dominates Blown Film Extrusion
Polyethylene is not the only polymer that can be used, but its molecular structure and cost-effectiveness make it the ideal choice for the vast majority of blown film applications.
Inherent Processability
Polyethylene possesses excellent melt strength. This means that when it is melted and extruded, it has enough integrity to be pulled and expanded into a large, stable "bubble" without tearing, which is the central mechanism of this process.
Versatility in Properties
The polyethylene family offers a wide spectrum of performance characteristics. By selecting a specific grade or blending different types, manufacturers can engineer films for vastly different purposes.
Cost-Effectiveness
As a high-volume commodity polymer, polyethylene provides a reliable and economical raw material source, which is critical for the cost-sensitive industries that rely on film products, such as packaging and agriculture.
A Closer Look at the Key Resins
Understanding the differences between the main polyethylene types is crucial for selecting the right material for a specific end-use.
Low-Density Polyethylene (LDPE)
LDPE is known for its exceptional clarity and flexibility. It produces a glossy film that is soft to the touch.
Its primary advantage is optical quality, making it a common choice for food packaging, shrink wrap, and other applications where high transparency is essential.
Linear Low-Density Polyethylene (LLDPE)
LLDPE is the modern workhorse of the industry, offering superior tensile strength and puncture resistance compared to LDPE.
While not as clear as LDPE, its toughness makes it the standard for applications requiring durability, such as stretch films, heavy-duty sacks, and agricultural films. It is frequently blended with LDPE to improve strength.
High-Density Polyethylene (HDPE)
HDPE is characterized by its stiffness and strength. It creates a stronger, more rigid film that is often translucent or opaque and has a characteristic "crinkle."
Its high strength-to-density ratio makes it ideal for applications like grocery bags, trash can liners, and barrier films where structural integrity and chemical resistance are more important than clarity.
Understanding the Trade-offs
Selecting a material is always a matter of balancing competing properties. No single resin can maximize every desirable characteristic.
Clarity vs. Strength
There is a direct trade-off between the optical clarity of a film and its ultimate strength. LDPE provides the best clarity but is the weakest, while HDPE is the strongest but is typically hazy or opaque.
Flexibility vs. Stiffness
LLDPE provides excellent flexibility and resistance to tearing. In contrast, HDPE provides high stiffness and rigidity but is more prone to splitting if a tear is initiated.
Material Cost vs. Downgauging
A key advantage of stronger resins like LLDPE is downgauging. Because it is stronger, manufacturers can produce a thinner film that has the same performance as a thicker LDPE film, potentially saving on raw material costs.
Selecting the Right Material for Your Application
Your choice of raw material should be driven entirely by the performance requirements of your final product.
- If your primary focus is clarity and gloss (e.g., retail packaging, bread bags): LDPE is the ideal choice for its excellent optical properties.
- If your primary focus is puncture resistance and durability (e.g., heavy-duty sacks, stretch wrap): LLDPE provides the necessary toughness and tensile strength for demanding applications.
- If your primary focus is stiffness and barrier performance (e.g., grocery bags, chemical liners): HDPE delivers the rigidity and strength required for structural films.
- If your primary focus is a balanced performance: Blending LLDPE with LDPE is a common industry practice to create a film with good strength and acceptable clarity.
Ultimately, understanding the distinct properties of each polyethylene resin is the key to engineering a film that meets your exact performance and cost requirements.
Summary Table:
| Polyethylene Type | Key Characteristics | Common Applications |
|---|---|---|
| LDPE | Excellent clarity, high gloss, flexibility | Food packaging, shrink wrap |
| LLDPE | Superior toughness, puncture resistance | Stretch film, heavy-duty sacks |
| HDPE | High stiffness, strength, chemical resistance | Grocery bags, trash liners |
Ready to Optimize Your Blown Film Production?
Choosing the right polyethylene resin is critical to achieving the perfect balance of clarity, strength, and cost for your film. KINTEK specializes in supplying high-quality laboratory equipment and consumables to support your material testing and R&D efforts, ensuring your formulations meet performance targets.
Let our experts help you select the ideal materials for your application. Contact KINTEK today to discuss your specific needs and enhance your film production process.
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Aluminum-Plastic Flexible Packaging Film for Lithium Battery Packaging
- Custom PTFE Teflon Parts Manufacturer for Hollow Etching Flower Basket ITO FTO Developing Glue Removal
- Custom PTFE Teflon Parts Manufacturer for Culture Dish and Evaporation Dish
- Vacuum Hot Press Furnace Machine for Lamination and Heating
- RF PECVD System Radio Frequency Plasma-Enhanced Chemical Vapor Deposition RF PECVD
People Also Ask
- What are the properties of Aluminium (Al) relevant to its use in coatings? High Reflectivity & Conductivity Explored
- What materials are used in thin film optical coating? Key Materials for Precise Light Control
- What does a layered film mean? Unpacking the Depths of Cinematic Storytelling
- What is the blown film technique? A Guide to High-Strength Plastic Film Production
- How is plastic waste different from other types of waste? The Hidden Threat of Microplastics



















