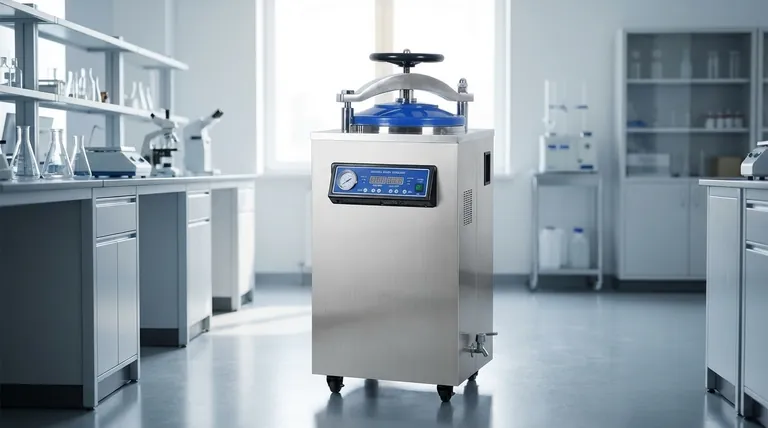
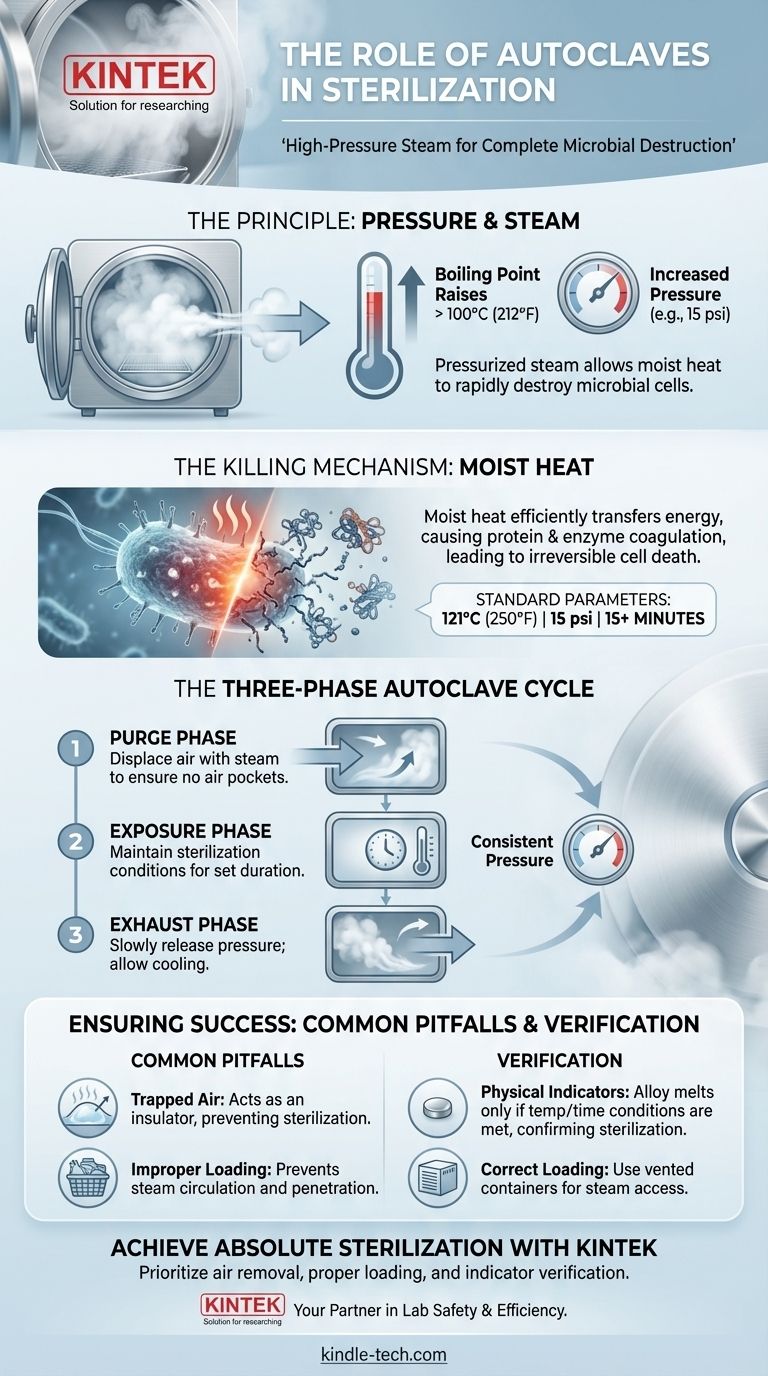
The primary role of an autoclave is to achieve absolute sterilization through the use of high-pressure steam. Unlike simple boiling, this method generates temperatures high enough to destroy all forms of microbial life, including the most resilient bacterial spores, ensuring that medical instruments, lab equipment, and other materials are completely free of contaminants.
An autoclave's effectiveness lies not just in its heat, but in its use of pressurized steam. By increasing pressure, an autoclave raises the boiling point of water far beyond 100°C (212°F), allowing the penetrating power of moist heat to rapidly and irreversibly destroy microbial cells.

How an Autoclave Achieves Sterilization
To understand the autoclave's role, we must first look at the principles that make it so effective. It’s a precise combination of physics and biology.
The Principle: Pressure and Temperature
The core concept is based on the relationship between pressure and the boiling point of water. At normal atmospheric pressure, water boils at 100°C (212°F).
By sealing a chamber and pumping steam into it, an autoclave increases the internal pressure. This forces the boiling point of water to rise.
The Killing Mechanism: Moist Heat
The high temperature is delivered via steam, a form of moist heat. This is far more effective at sterilization than dry heat.
The moisture in the steam efficiently transfers thermal energy and penetrates microbial cells. This process rapidly coagulates and denatures essential proteins and enzymes, causing irreversible damage and cell death.
Standard Sterilization Parameters
While settings can vary, a widely accepted standard for sterilization is maintaining a temperature of 121°C (250°F) at a pressure of 15 pounds per square inch (psi) for at least 15 minutes. These conditions are sufficient to kill even heat-resistant endospores.
The Three Phases of an Autoclave Cycle
A typical sterilization cycle isn't instantaneous. It follows a controlled, three-phase process to ensure safety and effectiveness.
Phase 1: The Purge Phase
The cycle begins by displacing the cooler, less effective air from the chamber with steam. As steam enters, the chamber's temperature and pressure begin to ramp up toward their target levels. This phase is critical for ensuring no air pockets remain.
Phase 2: The Exposure (Sterilization) Phase
Once all air is purged, the exhaust valves close, and the chamber reaches the desired sterilization temperature and pressure. The control system maintains these conditions for a set duration, known as the exposure time. This is when the actual killing of microorganisms occurs.
Phase 3: The Exhaust Phase
After the exposure time is complete, the exhaust valve opens to slowly release pressure from the chamber, returning it to ambient levels. The contents inside remain extremely hot and must cool before being handled.
Common Pitfalls and Ensuring Success
Simply running an autoclave cycle does not guarantee sterilization. The process is sensitive to operator error, and understanding potential failures is key to ensuring its success.
The Danger of Trapped Air
The most common reason for sterilization failure is the presence of trapped air. Air acts as an insulator, preventing steam from making direct contact with the surfaces of the items being sterilized. An area shielded by an air pocket will not reach the required temperature, and microbes will survive. This is why the purge phase is so important.
The Importance of Proper Loading
Items must be loaded into the autoclave to allow for free circulation of steam. Overpacking the chamber or using sealed containers without vents prevents steam from penetrating the load effectively. Specialized sterilization boxes with vents are often used to facilitate this process.
Verifying Success with Indicators
You cannot see sterilization happen, so you must verify it. Physical indicators are often used for this purpose. These consist of a small alloy pellet designed to melt only after being exposed to a specific temperature for the required amount of time. If the alloy has melted, it provides a visual confirmation that sterilization conditions were met.
How to Apply This to Your Goal
Understanding the autoclave's function allows you to use it with precision and confidence. Your primary goal will dictate your main point of focus.
- If your primary focus is ensuring complete sterilization: Prioritize the removal of all air by ensuring a proper purge cycle and by loading items correctly to allow for full steam penetration. Always use indicators to verify the cycle's success.
- If your primary focus is process efficiency: Understand the three phases to optimize cycle times based on the load's size and density, without compromising the required exposure time for safe and effective sterilization.
Ultimately, mastering the use of an autoclave transforms it from a simple machine into a reliable tool for guaranteeing microbial safety.
Summary Table:
| Key Aspect | Role in Sterilization |
|---|---|
| Core Principle | Uses pressurized steam to raise water's boiling point beyond 100°C (212°F) |
| Killing Mechanism | Moist heat coagulates and denatures microbial proteins, causing irreversible cell death |
| Standard Parameters | 121°C (250°F) at 15 psi for at least 15 minutes |
| Critical for Success | Proper air removal, correct loading, and verification with physical indicators |
Ensure Absolute Sterilization in Your Lab with KINTEK Autoclaves
Are you looking for reliable, high-performance sterilization solutions for your laboratory? KINTEK specializes in advanced autoclaves designed to deliver precise temperature and pressure control, ensuring complete destruction of all microbial life—including resilient bacterial spores.
Our autoclaves are engineered for:
- Guaranteed Sterilization: Achieve and verify absolute sterility for medical instruments, lab equipment, and consumables.
- User-Friendly Operation: Optimize your workflow with intuitive controls and efficient cycle management.
- Durability and Safety: Built to the highest standards for long-lasting, safe performance in demanding environments.
Contact us today to find the perfect autoclave for your laboratory's needs and enhance your sterilization protocols. Let KINTEK be your trusted partner in laboratory safety and efficiency.
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Laboratory High Pressure Steam Sterilizer Vertical Autoclave for Lab Department
- Laboratory Sterilizer Lab Autoclave Herbal Powder Sterilization Machine for Plant
- Desktop Fast Laboratory Autoclave Sterilizer 35L 50L 90L for Lab Use
- Desktop Fast Laboratory Autoclave Sterilizer 20L 24L for Lab Use
- Portable Digital Display Automatic Laboratory Sterilizer Lab Autoclave for Sterilization Pressure
People Also Ask
- How are autoclaves used to sterilize surgical instruments? Master the Key Steps for Patient Safety
- What is the most efficient method of sterilization? Match the Right Method to Your Materials
- Why is a PTFE-lined hydrothermal autoclave required for the preparation of Pt/Nb-TiO2 electrocatalysts?
- What are the advantages of autoclave for sterilization? Achieve Unmatched Sterility with Steam and Pressure
- Why are high-temperature and high-pressure reactors (autoclaves) essential for friction and wear tests? Get Real Data
- What is the maximum temperature range for an autoclave? Achieve Guaranteed Sterilization
- Why are autoclave parameters 121°C for 15 minutes? The Science of Sterilizing Bacterial Spores
- Why are hydrothermal autoclaves lined with PTFE selected for MCC-1 static leaching? Ensure Chemical Integrity



















