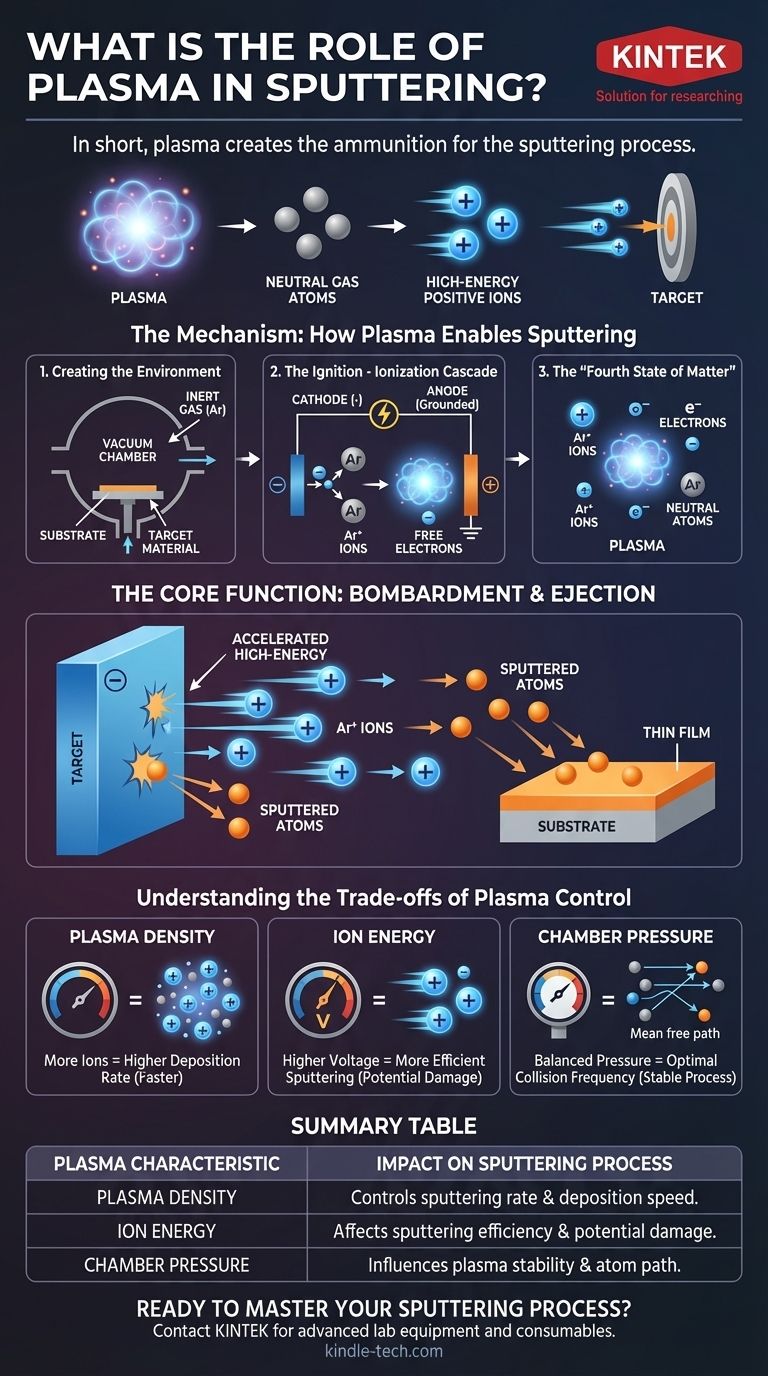
In short, the role of plasma in sputtering is to create the ammunition. The plasma acts as a medium to generate a large quantity of high-energy positive ions, which are then accelerated into a target material, physically knocking atoms off its surface to be deposited as a thin film.
The core function of plasma is to transform a neutral, inert gas into a controlled cloud of ionic projectiles. Without plasma, there are no ions to accelerate, and the entire sputtering deposition process cannot occur.
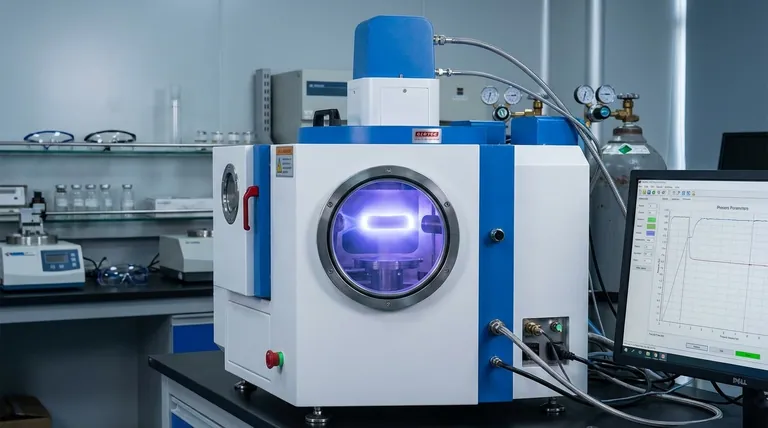

The Mechanism: How Plasma Enables Sputtering
To understand sputtering, you must first understand how the plasma is created and what it does. The process is a carefully controlled chain reaction within a vacuum chamber.
Step 1: Creating the Environment
Before plasma can exist, a specific environment must be established. This involves placing a substrate and a target material into a chamber, pumping it down to a high vacuum, and then backfilling it with a small amount of an inert gas, most commonly argon (Ar).
Step 2: The Ignition - Ionization Cascade
A high voltage is applied between two electrodes: the cathode (which holds the target material and is given a negative charge) and the anode (often the chamber walls, which are grounded).
This strong electric field accelerates the few free electrons already present in the gas. These high-speed electrons collide with neutral argon atoms, knocking an electron off the atom.
The result of this collision is one positive argon ion (Ar+) and two free electrons. These newly freed electrons are also accelerated by the electric field, leading to more collisions and creating a self-sustaining cascade that rapidly ignites the plasma.
Step 3: The "Fourth State of Matter"
This process creates plasma, a dynamic and energized state often called the "fourth state of matter." It is a near-balanced soup of positive ions, free electrons, and remaining neutral gas atoms.
This state is inherently unstable and requires a constant energy source (like a DC or RF power supply) to prevent the ions and electrons from simply recombining back into neutral atoms.
The Core Function: Bombardment and Ejection
Once the plasma is stable, its primary role begins. The same electric field that created the plasma now directs it.
The Acceleration of Ions
Because the target material is seated on the negatively charged cathode, the newly created positive argon ions (Ar+) are powerfully accelerated directly toward it.
The Sputtering Event
These Ar+ ions slam into the target surface with significant kinetic energy. The impact is a purely physical momentum transfer, acting like a subatomic sandblaster.
This bombardment has enough force to dislodge, or "sputter," individual atoms from the target material.
Deposition onto the Substrate
These sputtered atoms are ejected from the target and travel through the low-pressure chamber until they land on the substrate, gradually building up a thin, uniform film.
Understanding the Trade-offs of Plasma Control
The characteristics of the plasma directly dictate the outcome of your deposition. Controlling the plasma is controlling the quality, speed, and properties of your final film.
Plasma Density vs. Deposition Rate
A denser plasma contains more ions. More ions hitting the target per second results in a higher sputtering rate and faster film deposition. However, managing this density is key, as overly dense or unstable plasma can lead to non-uniform films or arcing.
Ion Energy vs. Film Damage
The voltage applied directly influences the kinetic energy of the ions. Higher energy leads to more efficient sputtering, but it can also cause damage to the substrate or implant argon atoms into the growing film, which is often undesirable.
Chamber Pressure vs. Collision Frequency
The gas pressure inside the chamber affects the "mean free path"—the average distance an atom or ion can travel before colliding with something else.
- Too high pressure: Sputtered atoms may collide with gas atoms too frequently, losing energy and never reaching the substrate.
- Too low pressure: It may be difficult to sustain a stable plasma, leading to an inefficient process.
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
Controlling the plasma is the primary lever you have to tune the sputtering process for a specific outcome.
- If your primary focus is a high deposition rate: Your goal is to generate a very dense, stable plasma, often achieved with techniques like magnetron sputtering that use magnetic fields to confine electrons and increase ionization efficiency.
- If your primary focus is coating a delicate substrate: You must use lower ion energies by reducing the cathode voltage, which requires careful balancing of pressure and power to maintain a stable, low-energy plasma.
- If your primary focus is a highly uniform film: You need to ensure the plasma density is uniform across the entire face of the target to guarantee an even rate of sputtering and deposition.
Ultimately, mastering sputtering is mastering the creation and control of plasma.
Summary Table:
| Plasma Characteristic | Impact on Sputtering Process |
|---|---|
| Plasma Density | Controls the sputtering rate and deposition speed. |
| Ion Energy | Affects sputtering efficiency and potential substrate/film damage. |
| Chamber Pressure | Influences the stability of the plasma and the path of sputtered atoms. |
Ready to master your sputtering process? The precise control of plasma is critical for achieving high-quality, uniform thin films. KINTEK specializes in advanced lab equipment and consumables for all your deposition needs. Our experts can help you select the right sputtering system to optimize plasma density, ion energy, and pressure for your specific application—whether you need high deposition rates or delicate substrate coating.
Contact our team today via our Contact Form to discuss how KINTEK's solutions can enhance your laboratory's capabilities and ensure reliable, repeatable results.
Visual Guide
Related Products
- RF PECVD System Radio Frequency Plasma-Enhanced Chemical Vapor Deposition RF PECVD
- Chemical Vapor Deposition CVD Equipment System Chamber Slide PECVD Tube Furnace with Liquid Gasifier PECVD Machine
- Evaporation Boat for Organic Matter
- Electron Beam Evaporation Coating Oxygen-Free Copper Crucible and Evaporation Boat
- Hemispherical Bottom Tungsten Molybdenum Evaporation Boat
People Also Ask
- What are the advantages of plasma enhanced CVD? Enable Low-Temperature, High-Quality Thin Film Deposition
- How does RF power create plasma? Achieve Stable, High-Density Plasma for Your Applications
- What is the principle of plasma enhanced chemical vapor deposition? Achieve Low-Temperature Thin Film Deposition
- Why does PECVD commonly use RF power input? For Precise Low-Temperature Thin Film Deposition
- What is the difference between PECVD and sputter? Choose the Right Thin-Film Deposition Method


















