While a common benchmark is 15-20 minutes, the "standard" time for sterilization is not a single, universal number. True sterilization time is critically dependent on the method used, the temperature and pressure achieved, and the specific items being processed. For the most common method, steam autoclaving, a typical cycle runs for a minimum of 15 minutes at 121°C (250°F) once the chamber has reached temperature.
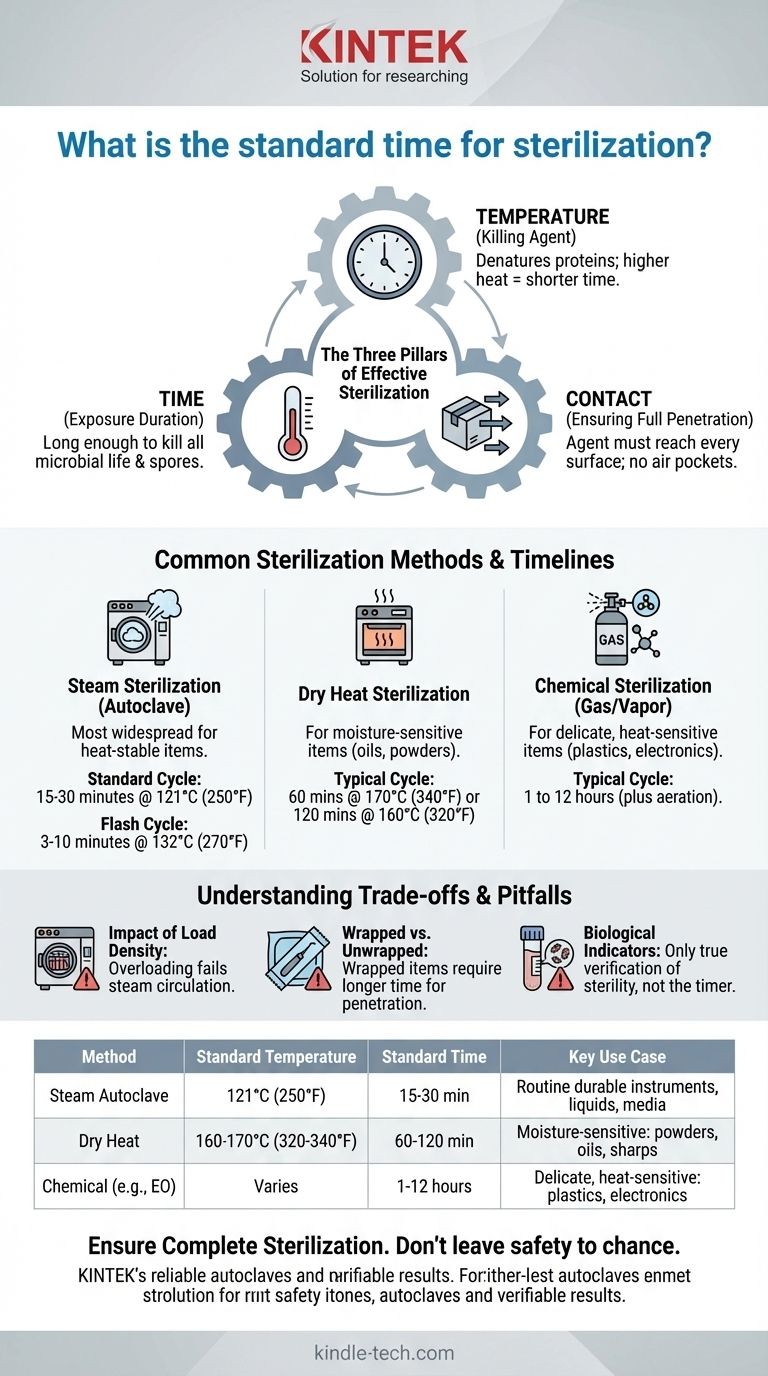
The true standard for sterilization is not a fixed duration, but the successful achievement of conditions lethal to microorganisms. Time is just one of three critical variables—alongside temperature and direct contact—that must be correctly balanced for the specific load and method used.
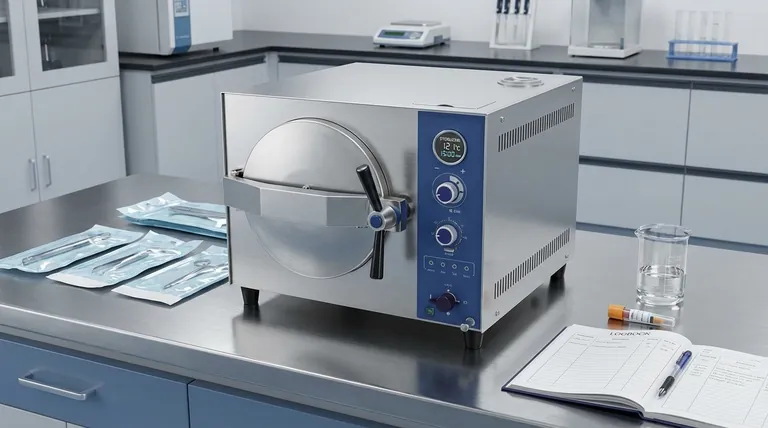

The Three Pillars of Effective Sterilization
Thinking about sterilization purely in terms of time is a common oversimplification. A successful and verifiable process relies on the interplay of three distinct factors.
Time: The Required Exposure Duration
Time is the duration that the item is exposed to the lethal agent (e.g., high-temperature steam). This duration must be long enough to kill all forms of microbial life, including the most resilient bacterial spores, which are used as a benchmark for efficacy.
Temperature: The Killing Agent
For thermal methods like steam or dry heat, temperature is the primary killing factor. High temperatures denature the essential proteins and enzymes that microorganisms need to survive. Higher temperatures can often achieve sterilization in a shorter amount of time.
Contact: Ensuring Full Penetration
This is the most frequently overlooked pillar. The sterilizing agent—whether it's steam, dry heat, or a chemical gas—must make direct contact with every surface of the item. If air is trapped in a package or a lumen, or if an item is wrapped improperly, sterilization will fail regardless of the time or temperature.
Common Sterilization Methods and Their Timelines
The required time varies dramatically based on the sterilization method you choose, as each operates on a different principle.
Steam Sterilization (Autoclave)
This is the most widespread method for heat-stable items. It uses pressurized steam to rapidly transfer thermal energy.
- Standard Cycle: 15 to 30 minutes at 121°C (250°F). This is the workhorse cycle for many labs and clinics, used for liquids, media, and instruments. The timer begins only after the chamber reaches the target temperature.
- Flash Cycle: 3 to 10 minutes at 132°C (270°F). This high-temperature cycle is designed for the emergency sterilization of unwrapped instruments that are needed for immediate use.
Dry Heat Sterilization
This method is used for items that cannot tolerate moisture, such as powders, oils, or certain sharp instruments prone to dulling. Because dry air is less efficient at transferring heat than steam, it requires significantly longer times and higher temperatures.
- Typical Cycle: 60 minutes at 170°C (340°F) or 120 minutes at 160°C (320°F).
Chemical Sterilization (Gas/Vapor)
Used for delicate items that cannot withstand high temperatures, such as plastics or complex electronics. Cycle times are highly variable and depend on the specific system and concentration of the chemical agent (e.g., Ethylene Oxide, Hydrogen Peroxide).
- Typical Cycle: 1 to 12 hours of exposure, often followed by a lengthy aeration period to remove residual toxic gases.
Understanding the Trade-offs and Pitfalls
Simply setting a timer is not enough and can lead to a false sense of security. Several factors can render a standard cycle ineffective.
The Impact of Load Density
A densely packed autoclave will fail. Steam must be able to circulate freely to displace all the air and contact all surfaces. Overloading the chamber creates cool air pockets where sterilization cannot occur.
Wrapped vs. Unwrapped Items
Items wrapped in sterilization pouches or drapes require longer cycle times. The steam must first penetrate the wrapper before it can begin to act on the item's surface, adding to the total time needed.
The Role of Biological Indicators
The timer on a machine only confirms the cycle ran for a set duration. It does not confirm that sterilization was achieved. The only true verification comes from using biological indicators—vials containing highly resistant spores. If the spores are killed, you can be confident the load is sterile.
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
To ensure safety and efficacy, select your sterilization parameters based on the material and your specific need.
- If your primary focus is routine sterilization of durable lab or medical instruments: Use a standard steam autoclave cycle of at least 15 minutes at 121°C, ensuring loads are not overly dense.
- If you are sterilizing moisture-sensitive items like oils or powders: You must use a dry heat oven, requiring a much longer cycle such as 60 minutes at 170°C.
- If you absolutely must verify the efficacy of your process: Rely on biological spore tests, not just the equipment's timer, as the definitive proof of sterility.
Ultimately, effective sterilization is the result of a validated process, not just a set time.
Summary Table:
| Method | Standard Temperature | Standard Time | Key Use Case |
|---|---|---|---|
| Steam Autoclave | 121°C (250°F) | 15-30 minutes | Routine sterilization of durable instruments, liquids, and media |
| Dry Heat | 160°C - 170°C (320°F - 340°F) | 60 - 120 minutes | Moisture-sensitive items like powders, oils, and sharp instruments |
| Chemical (e.g., EO Gas) | Varies | 1 - 12 hours | Delicate, heat-sensitive items like plastics and electronics |
Ensure Complete Sterilization in Your Lab
Don't leave safety to chance. The right equipment is critical for achieving the perfect balance of time, temperature, and contact for your specific loads.
KINTEK specializes in providing reliable autoclaves and lab equipment designed to deliver consistent, verifiable sterilization results. Our solutions help you avoid the pitfalls of overloading and improper cycles, ensuring your instruments and materials are truly sterile.
Contact us today to find the perfect sterilization system for your laboratory's needs and achieve peace of mind with every cycle.
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Laboratory Sterilizer Lab Autoclave Pulsating Vacuum Desktop Steam Sterilizer
- Desktop Fast Laboratory Autoclave Sterilizer 20L 24L for Lab Use
- Laboratory High Pressure Steam Sterilizer Vertical Autoclave for Lab Department
- Portable High Pressure Laboratory Autoclave Steam Sterilizer for Lab Use
- Laboratory High Pressure Horizontal Autoclave Steam Sterilizer for Lab Use
People Also Ask
- What is the minimum temperature and time for autoclave? Achieve Guaranteed Sterilization Every Time
- How is an autoclave checked and maintained? A Guide to Guaranteed Sterilization
- Why are high-pressure autoclaves required for Zirconium alloy testing? Essential for Nuclear Environment Validation
- What is the function of thermocouples or temperature loggers in autoclave validation? Ensure Sterilization Success
- What are the most important parameters for autoclave validation? Master Time, Temperature, and Pressure
- What is the primary function and principle of autoclaving? Master Lab Sterilization with High-Pressure Steam
- Why is the standard autoclave temperature set to 121? The Science of Effective Sterilization
- Are there any specific types of contamination that an autoclave cannot remove? Understanding the Limits of Steam



















