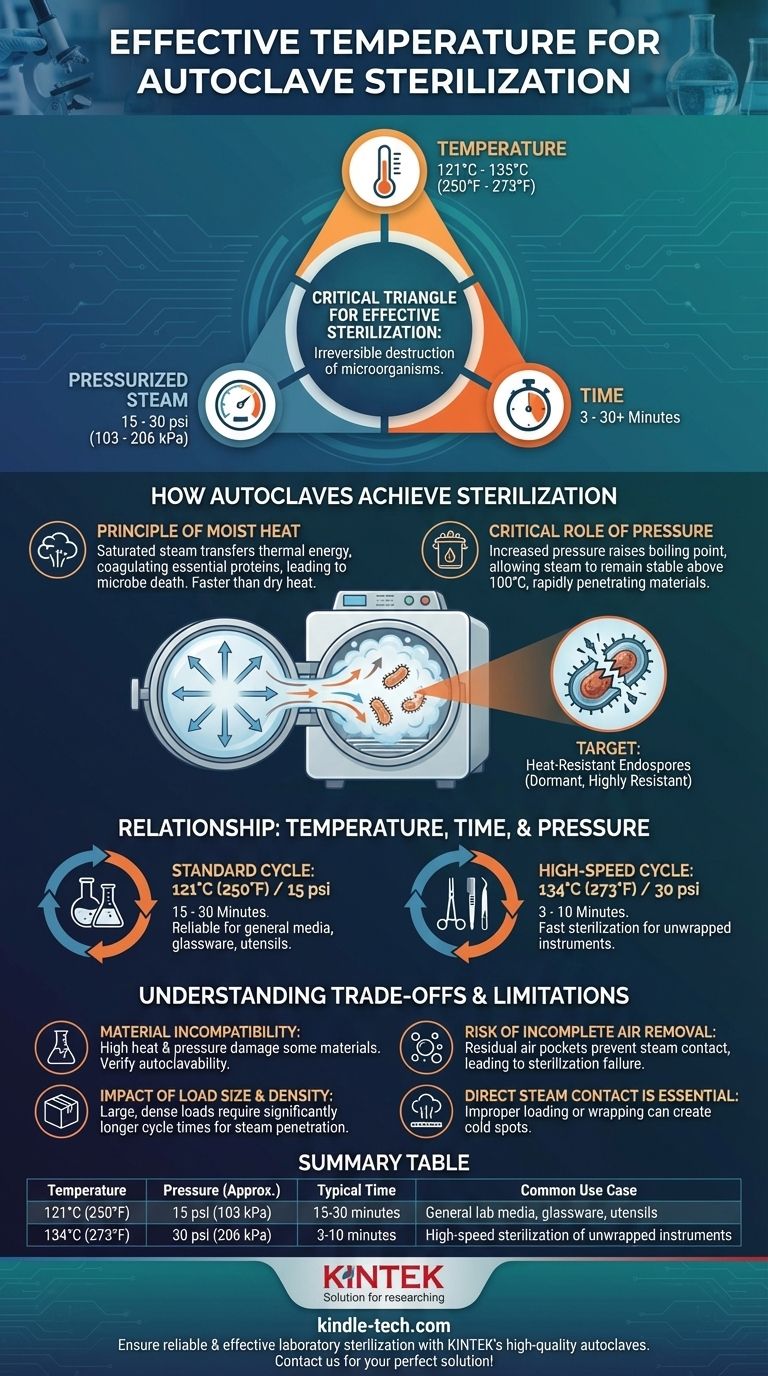
The effective temperature for sterilization in an autoclave typically ranges from 121°C (250°F) to 135°C (273°F). The most common standard is 121°C, which is held for a minimum of 15-20 minutes. This process is effective because the high pressure inside the chamber allows water to exist as steam at temperatures far above its normal boiling point, ensuring the rapid and complete destruction of all microorganisms.
The temperature is only one part of a critical triangle for effective sterilization. True sterilization is achieved by the combination of temperature, pressurized steam, and time, which work together to irreversibly destroy even the most heat-resistant microbes.
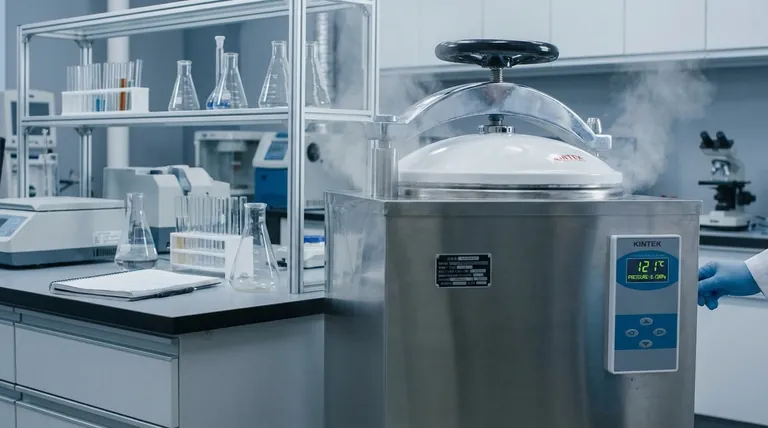

How Autoclaves Achieve Sterilization
An autoclave does not simply heat items. It uses a specific physical process—moist heat sterilization—to guarantee that an object is free of all living microorganisms, including bacterial spores.
The Principle of Moist Heat
The core mechanism is the use of saturated steam under pressure. The moisture in the steam is a highly efficient agent for transferring thermal energy.
This moisture works by coagulating the essential proteins within microbial cells. This process is irreversible, permanently disabling the microbe's cellular functions and leading to its death. Moist heat is significantly faster and more effective at penetrating materials than dry heat.
The Critical Role of Pressure
To reach temperatures above 100°C (212°F), an autoclave must increase its internal pressure. According to physical gas laws, as pressure on a liquid increases, its boiling point also increases.
By pressurizing the chamber, the autoclave creates an environment where steam can remain stable at 121°C or higher. This superheated steam can then rapidly penetrate dense materials and sterilize every exposed surface.
The Target: Killing Heat-Resistant Endospores
The goal of sterilization is not just to kill active bacteria, but to eliminate the toughest life forms: bacterial endospores.
Spores are dormant, highly resistant structures that can survive boiling and many chemical disinfectants. The conditions inside an autoclave are specifically designed to be lethal to these spores, making it the gold standard for sterilization in medical and laboratory settings.
The Relationship Between Temperature, Time, and Pressure
Temperature, time, and pressure are interdependent variables. Understanding their relationship is key to running a successful sterilization cycle. A change in one requires an adjustment in the others.
The Standard Cycle: 121°C
The most widely used sterilization cycle subjects items to 121°C (250°F) at a pressure of approximately 15 psi (103 kPa).
The exposure time at this temperature is typically 15 to 30 minutes, depending on the size and density of the load. This cycle is a reliable workhorse for general laboratory media, glassware, and utensils.
The High-Speed Cycle: 134°C
For applications where speed is essential, such as sterilizing unwrapped surgical instruments between procedures, a higher temperature is used.
At 134°C (273°F), achieved at a pressure of around 30 psi (206 kPa), the required sterilization time can be reduced to as little as 3 to 10 minutes. This demonstrates the inverse relationship: increasing the temperature decreases the required exposure time.
Why Direct Steam Contact is Essential
The temperature reading of the autoclave is meaningless if the steam does not physically touch every surface of the item being sterilized.
Improper loading, airtight wrapping, or trapped air pockets can create cold spots where the temperature never reaches the target. This is a common cause of sterilization failure.
Understanding the Trade-offs and Limitations
While powerful, an autoclave is not a universal solution. Its effectiveness depends on correct use and an awareness of its limitations.
Material Incompatibility
The combination of high heat, steam, and pressure will damage or destroy certain materials. Heat-sensitive plastics may melt, sharp instruments can become dull, and some chemicals may degrade. Always verify that your materials are autoclavable.
Impact of Load Size and Density
A small, loose load will sterilize much faster than a large, dense one. A tightly packed chamber prevents steam from circulating freely, requiring a significantly longer cycle time to ensure the heat penetrates to the center of the load.
The Risk of Incomplete Air Removal
The most critical step at the beginning of a cycle is removing all air from the chamber. If residual air is present, it forms pockets that prevent steam from making contact, leading to incomplete sterilization even if the machine's gauges show the correct temperature and pressure.
Making the Right Choice for Your Application
Selecting the correct cycle parameters is essential for ensuring sterility while protecting your equipment.
- If your primary focus is general-purpose sterilization: Use the standard 121°C cycle for 15-30 minutes, ensuring loads are not packed too densely.
- If your primary focus is speed for robust instruments: The 134°C "flash" or "express" cycle is highly effective, but only for unwrapped, non-porous items.
- If you are sterilizing large, wrapped, or porous loads: Extend the cycle time significantly beyond the minimum and use a biological indicator to validate that sterilization was successful.
Ultimately, successful sterilization relies on understanding that temperature is a tool, not the entire process.
Summary Table:
| Temperature | Pressure (Approx.) | Typical Time | Common Use Case |
|---|---|---|---|
| 121°C (250°F) | 15 psi (103 kPa) | 15-30 minutes | General lab media, glassware, utensils |
| 134°C (273°F) | 30 psi (206 kPa) | 3-10 minutes | High-speed sterilization of unwrapped instruments |
Ensure your laboratory's sterilization process is reliable and effective. KINTEK specializes in providing high-quality autoclaves and lab equipment designed to meet rigorous sterilization standards. Our solutions help you achieve complete microbial destruction, ensuring the safety and integrity of your work. Contact us today to find the perfect autoclave for your specific laboratory needs!
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Laboratory Sterilizer Lab Autoclave Vertical Pressure Steam Sterilizer for Liquid Crystal Display Automatic Type
- Desktop Fast Laboratory Autoclave Sterilizer 35L 50L 90L for Lab Use
- Laboratory High Pressure Steam Sterilizer Vertical Autoclave for Lab Department
- Desktop Fast Laboratory Autoclave Sterilizer 20L 24L for Lab Use
- Laboratory Sterilizer Lab Autoclave Pulse Vacuum Lifting Sterilizer
People Also Ask
- What role do laboratory autoclaves play in pectin extraction? Optimize Prebiotic Yield from Citrus and Apple Biomass
- What is the primary function and principle of autoclaving? Master Lab Sterilization with High-Pressure Steam
- What role does an autoclave play in the acid treatment for microalgae disruption? Unlock High-Yield Cell Pretreatment
- What are the advantages of using an autoclave equipped with a stirring device for molten salt testing? Dynamic Accuracy
- What is the primary function of a laboratory autoclave in the pre-treatment of medical plastic waste for liquid fuel?



















