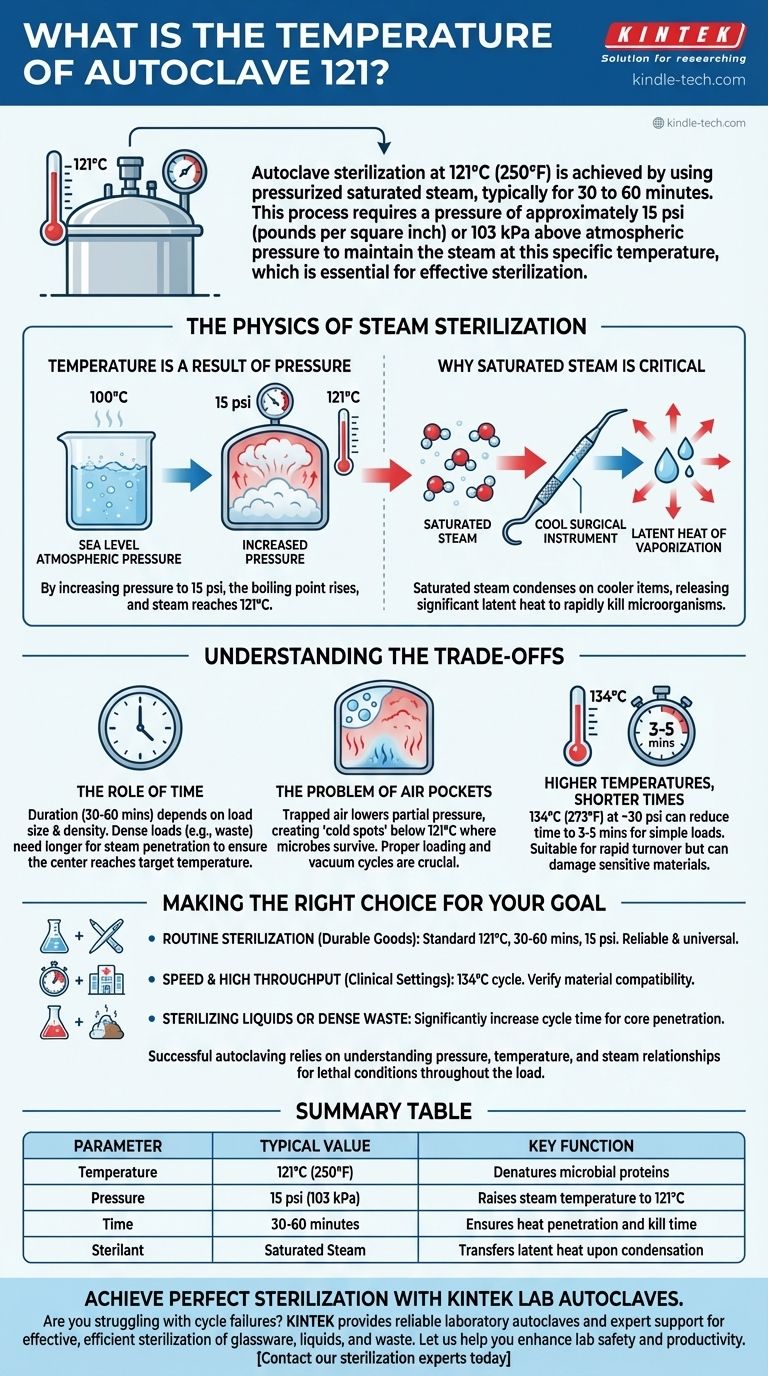
Autoclave sterilization at 121°C is achieved by using pressurized saturated steam, typically for 30 to 60 minutes. This process requires a pressure of approximately 15 psi (pounds per square inch) or 103 kPa above atmospheric pressure to maintain the steam at this specific temperature, which is essential for effective sterilization.
The question isn't just about temperature, but about how that temperature is achieved and why it matters. The true mechanism for sterilization is the combination of high temperature, direct steam contact, and sufficient time, which together irreversibly denature the proteins in microorganisms.
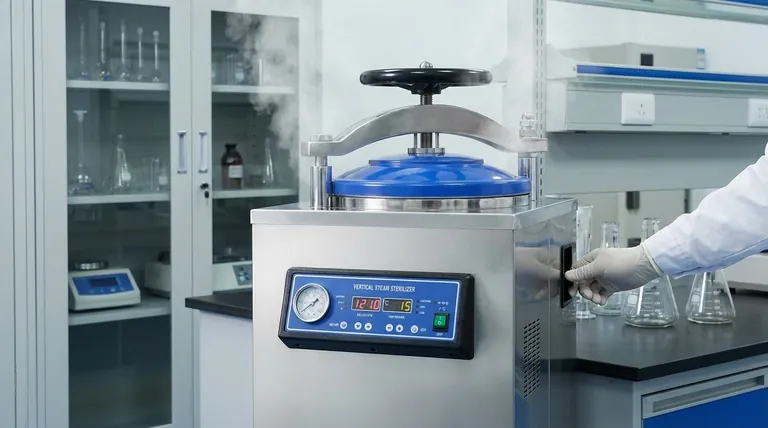

The Physics of Steam Sterilization
At the heart of autoclaving is a fundamental principle of physics: the temperature of boiling water and steam increases as pressure increases.
Temperature is a Result of Pressure
At normal sea-level atmospheric pressure, water boils at 100°C (212°F). You can never get liquid water or steam hotter than this without raising the pressure.
By increasing the pressure inside the autoclave chamber to 15 psi above atmospheric pressure, we can raise the boiling point of water and the temperature of the resulting steam to 121°C (250°F).
Why Saturated Steam is Critical
The autoclave uses saturated steam, which is steam at the precise temperature it needs to be to remain a gas at a given pressure.
This state is crucial because as the steam makes contact with cooler items in the load (like glassware or surgical tools), it immediately condenses back into water.
This condensation releases a large amount of energy, known as latent heat of vaporization, directly onto the surface of the item. This rapid heat transfer is what actually kills microorganisms, not just the ambient heat of the chamber.
Understanding the Trade-offs
Simply setting an autoclave to 121°C is not enough. Effective sterilization depends on a balance between temperature, pressure, and time, and understanding their interplay is key to avoiding failures.
The Role of Time
The standard duration for a 121°C cycle is often cited as 30-60 minutes. The specific time depends entirely on the size and density of the load.
A large, dense load (like a bag of laboratory waste) takes longer for steam to penetrate than a simple tray of surgical instruments. If the cycle is too short, the center of the load may never reach the target temperature, leading to incomplete sterilization.
The Problem of Air Pockets
The most common cause of autoclave failure is trapped air. If air pockets are present in the chamber or within the load, the total pressure might be correct, but the partial pressure of the steam is too low.
This means the actual temperature in that air pocket will be significantly lower than 121°C, creating a "cold spot" where microbes can survive. This is why proper loading and, in some autoclaves, a vacuum cycle are so important.
Higher Temperatures, Shorter Times
Some protocols use 134°C (273°F). This requires a higher pressure (around 30 psi) but can reduce sterilization time to as little as 3-5 minutes for simple loads.
This is a common trade-off in hospital settings where rapid turnover of instruments is necessary. However, the higher temperature can be damaging to more sensitive materials like certain plastics.
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
The correct parameters depend entirely on what you are trying to sterilize.
- If your primary focus is routine sterilization of durable goods (glassware, metal instruments): A standard cycle of 121°C for 30-60 minutes at 15 psi is the reliable and universally accepted method.
- If your primary focus is speed and high throughput (clinical settings): A 134°C cycle may be more appropriate, but you must verify that your materials can withstand the higher temperature.
- If your primary focus is sterilizing liquids or dense waste: You must increase the cycle time significantly to ensure the core of the load reaches the target temperature for the required duration.
Ultimately, successful autoclaving relies on understanding the relationship between pressure, temperature, and steam to ensure lethal conditions are met throughout the entire load.
Summary Table:
| Parameter | Typical Value | Key Function |
|---|---|---|
| Temperature | 121°C (250°F) | Denatures microbial proteins |
| Pressure | 15 psi (103 kPa) | Raises steam temperature to 121°C |
| Time | 30-60 minutes | Ensures heat penetration and kill time |
| Sterilant | Saturated Steam | Transfers latent heat upon condensation |
Achieve Perfect Sterilization with KINTEK Lab Autoclaves
Are you struggling with autoclave cycle failures or inconsistent results? KINTEK specializes in providing reliable laboratory autoclaves and expert support to ensure your sterilization processes are effective and efficient every time. Whether you are processing durable glassware, sensitive liquids, or dense waste, our equipment is designed to deliver precise temperature and pressure control for complete microbial elimination.
Let us help you enhance your lab's safety and productivity. Contact our sterilization experts today to discuss your specific application needs!
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Laboratory High Pressure Steam Sterilizer Vertical Autoclave for Lab Department
- Portable Digital Display Automatic Laboratory Sterilizer Lab Autoclave for Sterilization Pressure
- Desktop Fast Laboratory Autoclave Sterilizer 35L 50L 90L for Lab Use
- Desktop Fast Laboratory Autoclave Sterilizer 20L 24L for Lab Use
- Portable High Pressure Laboratory Autoclave Steam Sterilizer for Lab Use
People Also Ask
- What is the primary function and principle of autoclaving? Master Lab Sterilization with High-Pressure Steam
- What critical environmental conditions does a laboratory autoclave provide for evaluating wear resistance? - KINTEK
- What is the life expectancy of an autoclave machine? Maximize Your Investment with Proper Care
- What is the necessity of using an autoclave for pre-treating culture media? Ensure Accurate Ag2O/TiO2 Testing
- Why is the standard autoclave temperature set to 121? The Science of Effective Sterilization



















