In a laboratory, an evaporator is a device used to efficiently and gently remove a liquid solvent from a solution to leave behind a concentrated or solid sample. The most common type, a rotary evaporator or "rotovap," achieves this by reducing the pressure, which lowers the solvent's boiling point, allowing for rapid evaporation at a low temperature that will not damage the compound of interest.
The core challenge in many chemical processes is separating a solvent from a solute quickly without destroying the solute with high heat. An evaporator solves this by using a vacuum to lower the solvent's boiling point, enabling rapid and safe separation at temperatures gentle enough for even sensitive biological molecules.

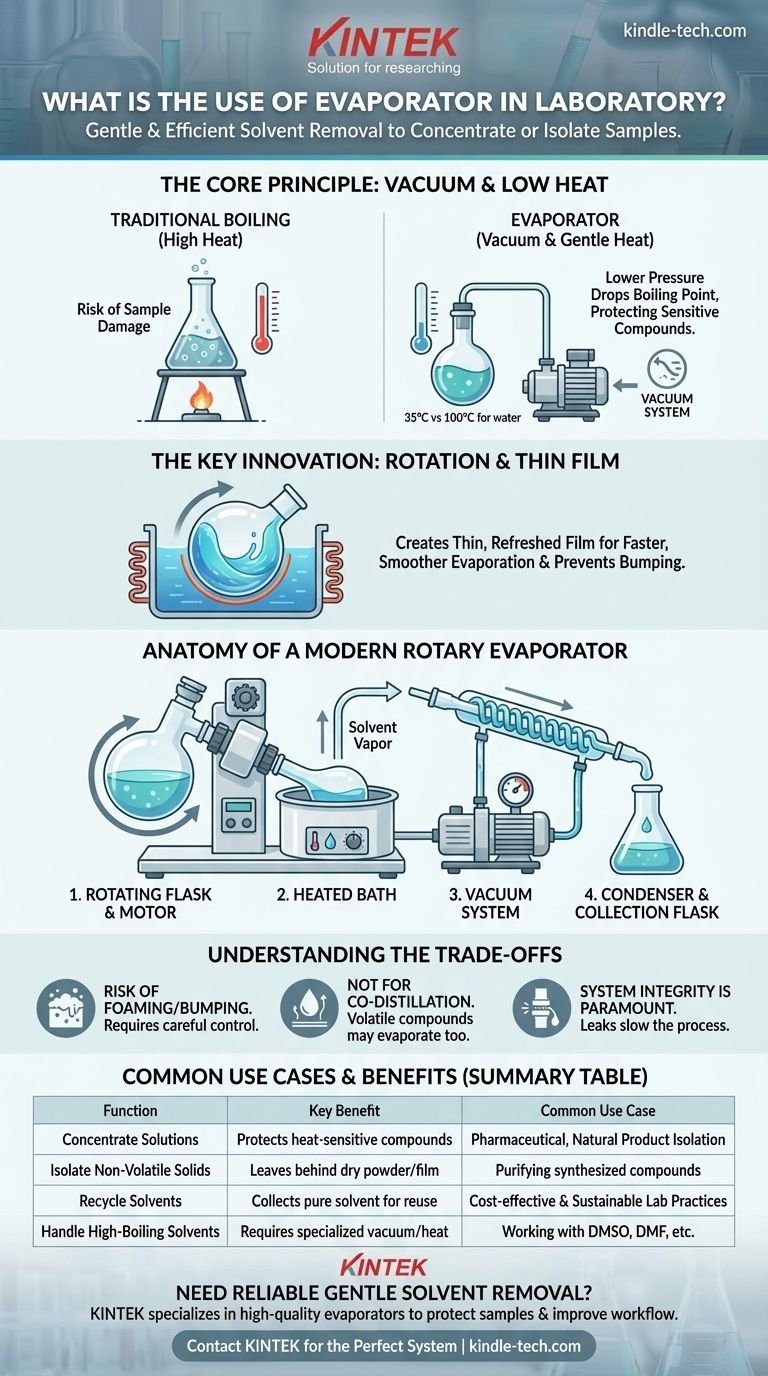
The Principle: How Evaporation Beats Simple Boiling
In nearly every chemical synthesis or extraction, the final step involves isolating your desired product from the solvent it's dissolved in. An evaporator is the standard tool for this task.
The Problem with High Heat
Simply boiling away a solvent at atmospheric pressure is often a poor choice. Many organic compounds, pharmaceuticals, and natural products are thermally sensitive and will decompose or degrade at their solvent's normal boiling point.
This high-heat approach can destroy the very product you've worked hard to create.
The Solution: Lowering the Boiling Point
The boiling point of a liquid is not a fixed number; it is entirely dependent on the pressure above it. By attaching a vacuum pump, an evaporator reduces the pressure inside the system.
This dramatic pressure drop significantly lowers the solvent's boiling point. For example, water boils at 100°C (212°F) at sea level but will boil at just 35°C (95°F) under a moderate vacuum. This allows you to remove the solvent at or near room temperature.
Why Rotation is the Key Innovation
A rotary evaporator adds a crucial element: rotation. The sample flask is spun continuously in a heated water or oil bath.
This rotation spreads the solution into a thin, constantly refreshed film on the inner surface of the flask. This vastly increases the surface area for evaporation and ensures even heating, preventing violent "bumping" and leading to a much faster and smoother process.
Anatomy of a Modern Rotary Evaporator
A rotary evaporator is a system of interconnected components, each with a critical role.
The Rotating Flask and Drive Motor
This is the heart of the system. The flask contains your solution, and the motor spins it to create the thin film necessary for efficient evaporation.
The Heated Bath
This water or oil bath provides a gentle and controlled source of energy (latent heat of vaporization) needed to convert the liquid solvent into a gas. The temperature is set low enough to protect the sample.
The Vacuum System
A vacuum pump removes air and solvent vapor from the system, maintaining the low pressure required to keep the boiling point down. A pressure controller allows for precise settings.
The Condenser and Collection Flask
As the solvent evaporates, its vapor travels into a chilled glass coil called a condenser. Here, the vapor is cooled and re-liquefies, dripping down into a separate collection flask. This allows the removed solvent to be collected for disposal or recycling.
Understanding the Trade-offs
While indispensable, evaporators are not without their operational considerations.
Risk of Foaming or Bumping
Some solutions, particularly those containing soaps or fine particulates, have a tendency to foam or "bump" violently, even with rotation. This can cause your sample to be carried over into the condenser, resulting in product loss. Careful control of the vacuum and rotation speed is required to manage this.
Not for Co-distillation
If your desired compound is also volatile (has a low boiling point), it may evaporate along with the solvent. In these cases, a rotovap may not be suitable, and a different purification technique like chromatography is needed.
System Integrity is Paramount
The entire process relies on maintaining a good vacuum seal. Worn-out gaskets or improperly greased glass joints can cause leaks, which prevent the system from reaching the target pressure and dramatically slow down evaporation.
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
Using an evaporator effectively means matching its function to your specific objective.
- If your primary focus is isolating a non-volatile solid: Use a rotovap to remove all the solvent until a dry powder or film remains in the flask.
- If your primary focus is concentrating a thermally sensitive compound: A rotovap is the industry standard. Gently remove solvent until your desired concentration is reached, protecting your sample from heat damage.
- If your primary focus is purifying or recycling a solvent: The rotovap is ideal, as the evaporated solvent is cleanly collected in the receiving flask for reuse.
- If you are working with very high-boiling solvents (like DMSO or DMF): You will need a more powerful vacuum pump and potentially an oil bath for higher temperatures to effectively remove them.
Mastering the principles of vacuum evaporation empowers you to control chemical separations with precision, protecting your valuable samples and ensuring high-purity results.
Summary Table:
| Function | Key Benefit | Common Use Case |
|---|---|---|
| Concentrate Solutions | Protects heat-sensitive compounds | Pharmaceutical, natural product isolation |
| Isolate Non-Volatile Solids | Leaves behind dry powder or film | Purifying synthesized compounds |
| Recycle Solvents | Collects pure solvent for reuse | Cost-effective and sustainable lab practices |
| Handle High-Boiling Solvents | Requires specialized vacuum/heat | Working with DMSO, DMF, etc. |
Need a reliable solution for gentle solvent removal? KINTEK specializes in high-quality laboratory evaporators and rotovaps designed to protect your sensitive samples and improve your workflow efficiency. Our experts can help you select the perfect system for concentrating, isolating, or purifying your valuable compounds. Contact KINTEK today to find the right evaporator for your lab's needs!
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Laboratory Benchtop Water Circulating Vacuum Pump for Lab Use
- Circulating Water Vacuum Pump for Laboratory and Industrial Use
- Oil Free Diaphragm Vacuum Pump for Laboratory and Industrial Use
- 30T 40T Split Automatic Heated Hydraulic Press Machine with Heated Plates for Laboratory Hot Press
- Electric Heated Hydraulic Vacuum Heat Press for Lab
People Also Ask
- What are the failures in a hydraulic system? Prevent Costly Downtime with Expert Diagnosis
- Why must a laboratory vacuum pump be used to evacuate a PM-HIP capsule before it is sealed? Ensure Material Integrity
- What determines the vacuum degree achievable by a water circulating vacuum pump? Unlock the Physics of Its Limits
- What are the preventive maintenance of hydraulic systems? Extend Equipment Life and Maximize Uptime
- Why is a high-precision vacuum pump system essential for iCVD? Achieve Superior Film Purity and Uniformity



















