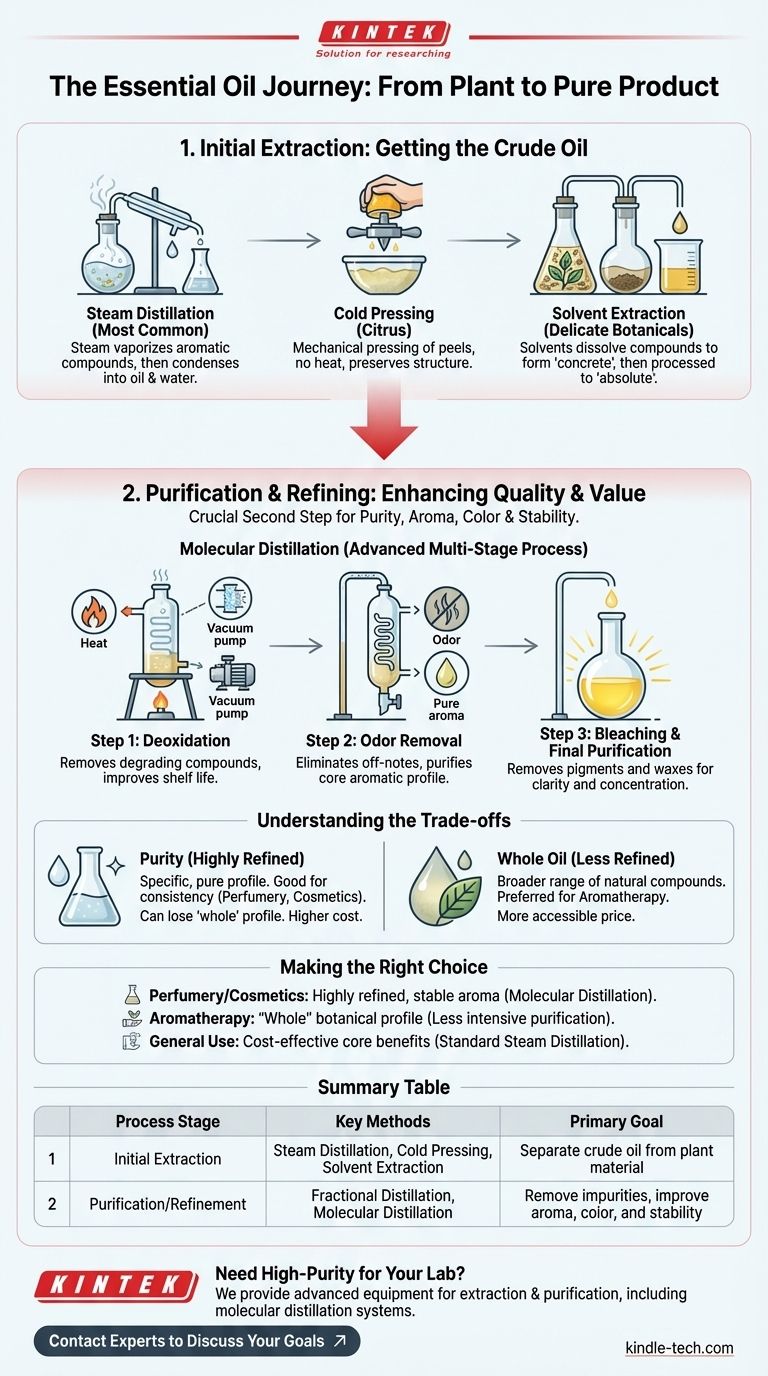
In short, essential oils are extracted through methods like steam distillation and cold pressing, but the process doesn't stop there. The initial "crude" oil then undergoes advanced refining and purification, such as molecular distillation, to achieve the final product's desired purity, aroma, and color. It is this second stage of refinement that often defines the quality and value of the oil you ultimately use.
The key distinction to understand is between extraction, which gets the raw oil out of the plant material, and purification, which refines that raw oil into a high-quality, stable, and valuable final product.

The Initial Extraction: Getting the Oil from the Plant
Before any refinement can occur, the essential oil must first be separated from its source botanical material. This initial step produces what is known as a "crude" essential oil.
Steam Distillation
This is the most common method. Steam is passed through the plant material, causing the aromatic compounds to vaporize. This vapor is then cooled, which condenses it back into a liquid mixture of water and essential oil, which are then easily separated.
Cold Pressing
Used almost exclusively for citrus peels like lemon, orange, and bergamot, this mechanical process involves puncturing and pressing the peels to release the oil. No heat is used, which helps preserve the oil's delicate chemical structure.
Solvent Extraction
For delicate botanicals that cannot withstand the heat of steam distillation, solvents are used to dissolve the aromatic compounds from the plant. This creates a waxy substance called a "concrete," which is then further processed to yield an "absolute."
The Crucial Second Step: Refining the Crude Oil
The crude oil from initial extraction often contains undesirable elements like unpleasant smells, deep colors, or high wax content. Purification is necessary to remove these impurities and enhance the oil's quality and value.
Why Refinement is Necessary
Crude oils, like rose oil, can have issues that make them less appealing or useful. Refining addresses these problems, turning a raw extract into a polished product suitable for high-end applications like perfumery or therapeutics.
Key Refining Methods
The two primary methods for purifying crude essential oils are fractional distillation (also called rectification) and the more advanced molecular distillation. These techniques selectively separate components of the oil to achieve a purer result.
A Closer Look at Molecular Distillation
Molecular distillation is a highly effective, multi-stage process used to significantly improve the quality of an essential oil. It operates under a high vacuum, which allows for distillation at lower temperatures, protecting the oil's delicate compounds.
Step 1: Deoxidation
The first stage is designed to remove compounds that can cause the oil to degrade or spoil over time, improving its shelf life and stability.
Step 2: Odor Removal
In the second stage, the process targets and removes any off-notes or unpleasant smells from the crude oil, purifying and clarifying its core aromatic profile.
Step 3: Bleaching and Final Purification
The final stage is focused on improving the oil's appearance. It removes pigments to lighten the color and gets rid of any remaining waxes, resulting in a clean, clear final product with a higher concentration of desired aromatic molecules.
Understanding the Trade-offs
While purification creates a cleaner, more consistent product, it's important to recognize the implications of these advanced processes.
Purity vs. "Whole" Oil
Heavy refinement creates an oil with a very specific, pure aromatic profile. However, this process can also remove some of the heavier, more complex molecules present in the original plant, which some users may prefer for a more "full-spectrum" or "whole" oil.
Cost and Complexity
Multi-stage processes like molecular distillation require specialized equipment and expertise. This adds complexity and cost to the final product, which is why highly purified oils are often more expensive.
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
Understanding the journey from plant to bottle empowers you to choose the right oil for your specific needs.
- If your primary focus is a pure, stable aroma for perfumery or cosmetics: A highly refined oil that has undergone molecular distillation is often the best choice for its clarity and consistency.
- If your primary focus is a "whole" botanical profile for aromatherapy: You may prefer an oil that has undergone less intensive purification to retain a broader range of the plant's natural compounds.
- If your primary focus is cost-effectiveness for general use: A standard steam-distilled oil without extensive secondary refinement will provide the core benefits at a more accessible price point.
Ultimately, knowing the difference between extraction and purification allows you to select an essential oil based on its processing, not just its name.
Summary Table:
| Process Stage | Key Methods | Primary Goal |
|---|---|---|
| Initial Extraction | Steam Distillation, Cold Pressing, Solvent Extraction | Separate crude oil from plant material |
| Purification/Refinement | Fractional Distillation, Molecular Distillation | Remove impurities, improve aroma, color, and stability |
Need High-Purity Essential Oils for Your Laboratory or Production?
The journey from raw plant material to a high-quality essential oil requires precise control and reliable equipment. At KINTEK, we specialize in providing the advanced laboratory equipment and consumables necessary for both extraction and purification processes, including systems for molecular distillation.
Whether you are in R&D, quality control, or manufacturing, our solutions help you achieve the purity, stability, and consistency your products demand.
Contact our experts today to discuss how we can support your essential oil production goals.
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Laboratory Sterilizer Lab Autoclave Herbal Powder Sterilization Machine for Plant
- Single Punch Electric Tablet Press Machine TDP Tablet Punching Machine
- Single Punch Electric Tablet Press Machine Laboratory Powder Tablet Punching TDP Tablet Press
- Automatic Heated Hydraulic Press Machine with Heated Plates for Laboratory Hot Press 25T 30T 50T
- Desktop Fast Laboratory Autoclave Sterilizer 35L 50L 90L for Lab Use
People Also Ask
- What role does an autoclave play in remediation experiments? Ensure Precision by Eliminating Biological Noise
- Why is a 24-hour hydrothermal treatment in an autoclave necessary for BMO nanosheets? Unlock Superior Photocatalysis
- How does an autoclave ensure the reliability of experimental results? Achieving a Sterile Baseline for Lab Research
- What is the primary purpose of an autoclave in the preparation of media for the biological leaching of uranium?
- What are the standard operating parameters for an autoclave? Master Temperature, Pressure, and Time for Sterilization



















