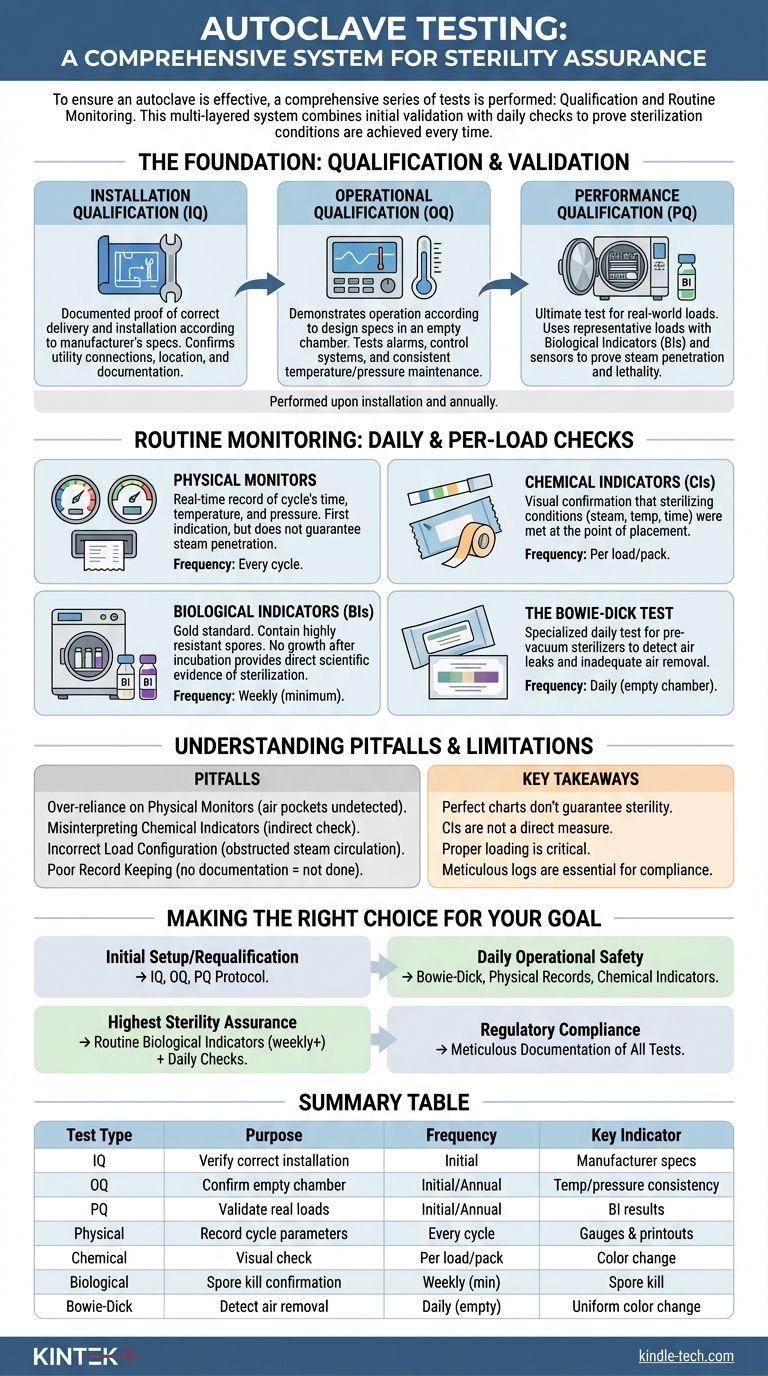
To ensure an autoclave is effective, a comprehensive series of tests is performed, divided into two main categories. First are the qualification tests—Installation Qualification (IQ), Operational Qualification (OQ), and Performance Qualification (PQ)—which are performed upon installation and annually. Second are the routine monitoring tests, including physical, chemical, and biological indicators, which are used on a daily or per-load basis to verify performance.
Autoclave testing is not a single event but a multi-layered system. It combines initial validation with daily checks to create a verifiable process that proves the conditions required for sterilization are achieved, every single time.
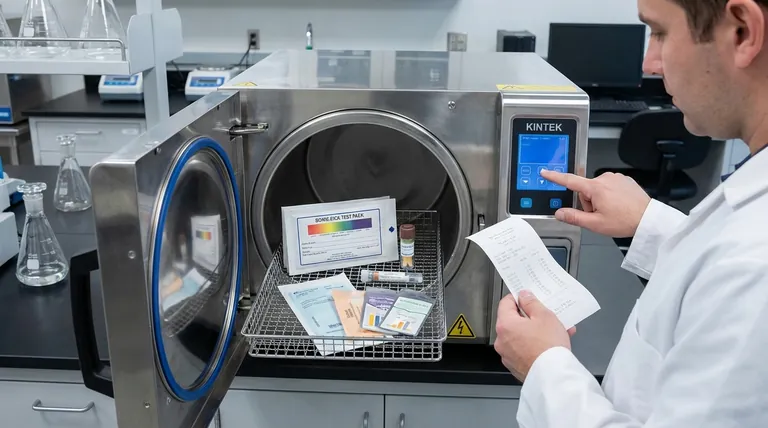

The Foundation: Qualification and Validation
Before an autoclave is ever used for sterilizing instruments, it must be formally validated. This process establishes documented evidence that the equipment is installed correctly, operates as expected, and effectively sterilizes its intended loads.
Installation Qualification (IQ)
This is the first step. IQ is documented proof that the autoclave and its auxiliary systems have been delivered and installed in accordance with the manufacturer's specifications.
It confirms details like correct utility connections (steam, water, electricity), proper location with adequate clearance, and verification that all documentation and manuals are present.
Operational Qualification (OQ)
Once installed correctly, OQ demonstrates that the autoclave operates according to its design specifications in an empty chamber.
This phase involves testing alarms, control systems, and displays. It includes running empty cycles to verify that the chamber consistently reaches and maintains the programmed temperatures and pressures for the required time.
Performance Qualification (PQ)
PQ is the ultimate test: does the autoclave effectively sterilize real-world loads? This is the most critical phase of validation.
Using a representative load (or the most challenging load), technicians place biological indicators (BIs) and temperature sensors throughout the chamber. The goal is to prove that steam penetrates the entire load and kills highly resistant microorganisms, confirming the cycle is lethal and effective.
Routine Monitoring: Daily and Per-Load Checks
After initial validation, routine monitoring ensures the autoclave continues to perform correctly on a day-to-day basis.
Physical Monitors
These are the gauges, printouts, and digital readouts on the autoclave itself. They provide a real-time record of the cycle's time, temperature, and pressure.
A correct printout is the first indication of a successful cycle, but it does not guarantee steam penetration within the packs.
Chemical Indicators (CIs)
CIs are paper strips or tapes that change color when exposed to specific sterilization parameters (e.g., steam, temperature, and time).
They provide instant visual confirmation that sterilizing conditions were met at the point of placement. A Class 5 integrating indicator, for example, is designed to react to all critical parameters and is placed inside each pack.
Biological Indicators (BIs)
BIs are the gold standard for sterility assurance. They contain a known population of highly resistant bacterial spores, typically Geobacillus stearothermophilus.
After a cycle, the BI is incubated. If the spores are killed and show no growth, it provides direct scientific evidence that the sterilization process was successful. They are typically used at least weekly and for all implantable loads.
The Bowie-Dick Test
This is a specialized daily test performed only on pre-vacuum steam sterilizers. Its sole purpose is to detect air leaks and inadequate air removal from the chamber.
A Bowie-Dick test pack is placed in an empty, pre-warmed chamber. A uniform color change on the indicator sheet confirms proper steam penetration, while a non-uniform change indicates an air removal failure.
Understanding the Pitfalls and Limitations
A robust testing program relies on understanding the limitations of each component and avoiding common errors.
Over-reliance on Physical Monitors
A perfect chart printout does not guarantee sterility. An air pocket trapped within a dense pack can prevent steam contact, leading to a localized failure that the chamber's sensors would never detect.
Misinterpreting Chemical Indicators
A chemical indicator's color change confirms that specific conditions were met, but it is not a direct measure of sterility. It is an indirect process variable check, unlike a biological indicator which directly challenges the cycle's lethality.
Incorrect Load Configuration
Improperly loading an autoclave is a primary cause of sterilization failure. Overloading the chamber or placing packs too tightly together can obstruct steam circulation and prevent it from penetrating to the center of the load.
Poor Record Keeping
For regulatory and quality purposes, a test that is not documented is a test that was not done. Meticulous logs of all qualification, maintenance, and routine monitoring results are essential for troubleshooting and proving compliance.
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
Your specific testing strategy depends on your immediate objective, but all elements are necessary for a complete assurance program.
- If your primary focus is initial setup or requalification: Your priority is the full IQ, OQ, and PQ protocol to establish a documented, validated state for the equipment.
- If your primary focus is daily operational safety: Implement a routine of Bowie-Dick tests (for pre-vacuum units), physical record checks, and chemical indicators placed within every pack.
- If your primary focus is the highest level of sterility assurance: You must incorporate routine (at least weekly) biological indicator tests in addition to all other daily physical and chemical checks.
- If your primary focus is regulatory compliance: Ensure meticulous and organized documentation of all qualification and routine monitoring tests, as this is your non-negotiable proof of performance.
A systematic testing protocol transforms an autoclave from a machine into a reliable and verifiable sterilization system.
Summary Table:
| Test Type | Purpose | Frequency | Key Indicator |
|---|---|---|---|
| Installation Qualification (IQ) | Verify correct installation and setup | Initial installation | Manufacturer specs |
| Operational Qualification (OQ) | Confirm empty chamber performance | Initial and annual | Temperature/pressure consistency |
| Performance Qualification (PQ) | Validate sterilization of real loads | Initial and annual | Biological indicator (BI) results |
| Physical Monitors | Record cycle parameters (time, temp, pressure) | Every cycle | Gauges and printouts |
| Chemical Indicators (CIs) | Visual check of sterilizing conditions | Per load/pack | Color change |
| Biological Indicators (BIs) | Gold standard for sterility assurance | Weekly (minimum) | Spore kill confirmation |
| Bowie-Dick Test | Detect air removal failures (pre-vacuum units) | Daily (empty chamber) | Uniform color change |
Ensure your autoclave operates with uncompromising sterility assurance. KINTEK specializes in laboratory equipment and consumables, providing the reliable autoclaves, biological indicators, chemical integrators, and validation services your lab needs for complete compliance and patient safety. Contact our sterilization experts today to discuss your specific requirements and build a robust testing protocol.
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Desktop Fast Laboratory Autoclave Sterilizer 20L 24L for Lab Use
- Desktop Fast Laboratory Autoclave Sterilizer 35L 50L 90L for Lab Use
- Laboratory Sterilizer Lab Autoclave Herbal Powder Sterilization Machine for Plant
- Laboratory High Pressure Steam Sterilizer Vertical Autoclave for Lab Department
- Laboratory Horizontal Autoclave Steam Sterilizer Lab Microcomputer Sterilizer
People Also Ask
- What precautions should be taken during autoclave in laboratory? A Complete Safety Guide to Prevent Burns and Explosions
- What is the life expectancy of an autoclave machine? Maximize Your Investment with Proper Care
- What is the primary function and principle of autoclaving? Master Lab Sterilization with High-Pressure Steam
- What critical environmental conditions does a laboratory autoclave provide for evaluating wear resistance? - KINTEK
- What types of items and materials can be processed in a laboratory autoclave? Essential Guide for Lab Safety



















