To safely remove flammable solvents, you must use an evaporation method that systematically eliminates ignition sources while controlling temperature and pressure. The standard and most trusted piece of equipment for this task is an explosion-proof rotary evaporator, often referred to as a "rotovap," which is specifically designed with non-sparking components and operates under vacuum to lower the solvent's boiling point.
The core challenge with flammable solvents isn't just removing them, but doing so without creating an explosive mixture of vapor and air. The solution lies in using a system, like a rotary evaporator, that reduces the heat required for evaporation and is engineered from the ground up to prevent sparks.

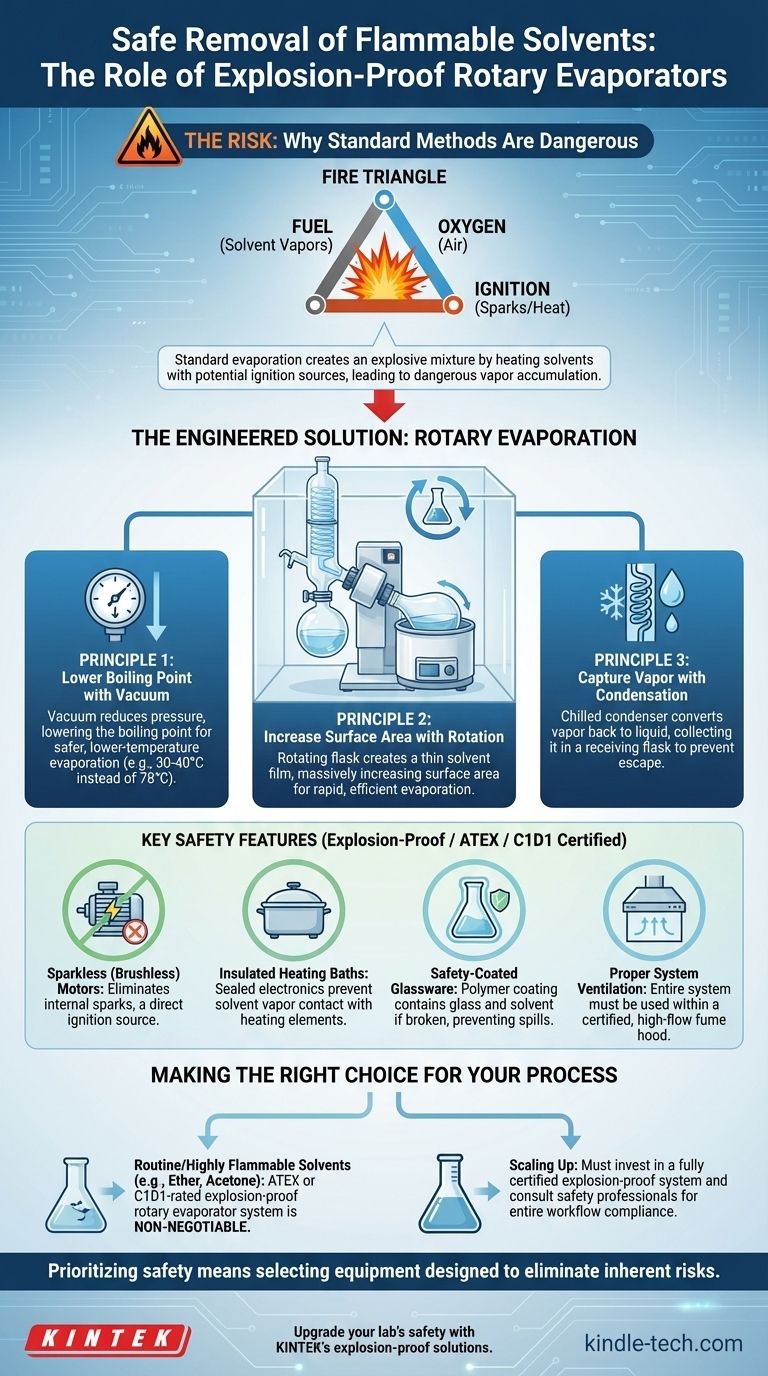
Why Standard Evaporation is a Critical Risk
Evaporating a flammable solvent with simple heating methods, like a hot plate, creates a dangerous situation by combining the three elements of the "fire triangle": fuel, oxygen, and an ignition source.
The Fuel: Solvent Vapors
Flammable solvents have low flash points, meaning they produce ignitable vapors at low temperatures. As you heat the solvent, the concentration of this vapor (the fuel) in the air increases dramatically.
The Ignition Source: Hidden Dangers
Standard laboratory equipment is full of potential ignition sources. The most common are electric sparks from brushed motors (in stirrers or pumps), arcs from thermostats and power switches, and static electricity.
The Unseen Hazard: Vapor Accumulation
Most solvent vapors are heavier than air. Without proper containment and ventilation, these vapors can flow off a benchtop, accumulate in low-lying areas, and travel a surprising distance to an ignition source.
The Engineered Solution: Rotary Evaporation
A rotary evaporator is a system designed to mitigate these risks through several core principles. It is the industry standard for safely and efficiently removing volatile solvents.
Principle 1: Lowering the Boiling Point with Vacuum
The defining feature of a rotovap is its use of a vacuum pump. By reducing the pressure inside the system, the solvent's boiling point is significantly lowered. This means you can evaporate solvents like acetone or ethanol at a much lower, safer temperature (e.g., 30-40°C instead of 78°C).
Principle 2: Increasing Surface Area with Rotation
The rotating flask constantly coats the inner surface with a thin film of the solvent. This massively increases the surface area available for evaporation, making the process far more rapid and efficient than simply boiling a static pool of liquid.
Principle 3: Capturing Vapor with Condensation
The evaporated solvent vapor is immediately channeled over a chilled condenser coil. The vapor turns back into a liquid and is collected in a receiving flask, preventing it from escaping into the laboratory atmosphere and keeping the process contained.
Key Features for Flammable Solvent Safety
For flammable solvents, a standard rotary evaporator is a good start, but a truly safe setup requires specific explosion-proof features. These are often certified under standards like ATEX or Class I, Division 1 (C1D1).
Sparkless (Brushless) Motors
Standard DC motors use carbon brushes that create small sparks during operation—a direct ignition source. Explosion-proof rotovaps use brushless DC motors that are electronically commutated and produce no sparks.
Insulated Heating Baths
The heating bath must be designed to prevent solvent vapors from contacting the heating elements. High-quality systems use sealed electronics and allow for precise temperature control to stay well below the solvent's autoignition temperature.
Safety-Coated Glassware
Using plastic or polymer-coated glassware is a critical secondary safety measure. If the rotating flask were to break under vacuum, the coating contains the glass shards and the flammable solvent, preventing a dangerous spill.
Proper System Ventilation
Even with a sealed system, the entire rotary evaporator setup, including the vacuum pump, must be placed inside a certified, high-flow fume hood. This ensures that any fugitive emissions or leaks are safely vented away.
Understanding the Trade-offs
While rotary evaporation is the correct method, it's essential to recognize the associated factors.
Higher Initial Cost
Certified explosion-proof rotary evaporators and vacuum pumps are significantly more expensive than standard laboratory equipment. This cost, however, is an investment in fundamental safety.
System Complexity
A rotovap is not a standalone device. It requires a compatible vacuum pump to lower the pressure and a chiller or cold trap to cool the condenser effectively. Proper setup and ensuring all seals are tight is essential for performance and safety.
Requires Operator Knowledge
Safe operation depends on the user understanding the properties of the solvent. You must know the target boiling point at your desired vacuum level to set the heating bath and chiller temperatures correctly.
Making the Right Choice for Your Process
Your approach should be dictated by the scale of your work and the specific solvent you are handling.
- If your primary focus is small-scale research with less volatile solvents: A standard rotary evaporator placed within a high-performance fume hood may be acceptable, but a thorough risk assessment is mandatory.
- If your primary focus is routine evaporation of highly flammable solvents (like ether, pentane, or acetone): An ATEX or C1D1-rated explosion-proof rotary evaporator system is non-negotiable.
- If your primary focus is scaling up a process: You must invest in a fully certified explosion-proof system and consult with safety professionals to ensure your entire workflow, including storage and transfer, is compliant.
Ultimately, prioritizing safety means selecting equipment designed to eliminate the inherent risks of your materials.
Summary Table:
| Safety Feature | Purpose | Key Benefit |
|---|---|---|
| Vacuum System | Lowers boiling point | Reduces required heat, preventing ignition |
| Brushless Motor | Eliminates sparks | Prevents ignition of solvent vapors |
| Sealed Heating Bath | Contains heat source | Avoids contact between vapors and heating elements |
| Safety-Coated Glassware | Contains breakages | Prevents spills and exposure if glass fails |
| Condenser System | Captures vapor | Converts vapor back to liquid for safe collection |
Upgrade your lab's safety and efficiency with KINTEK's explosion-proof rotary evaporators.
Handling flammable solvents requires precision-engineered equipment to mitigate risks and ensure operator safety. KINTEK specializes in robust, ATEX-certified rotary evaporators designed with sparkless motors, sealed heating baths, and safety-coated glassware to protect your lab and processes.
Our solutions are ideal for laboratories routinely working with volatile solvents like acetone, ethanol, or ether, providing reliable performance and compliance with safety standards.
Ready to enhance your solvent removal process? Contact our experts today to find the perfect system for your needs.
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Molybdenum Tungsten Tantalum Evaporation Boat for High Temperature Applications
- Ceramic Evaporation Boat Set Alumina Crucible for Laboratory Use
- Laboratory Benchtop Water Circulating Vacuum Pump for Lab Use
- Hemispherical Bottom Tungsten Molybdenum Evaporation Boat
- Evaporation Crucible for Organic Matter
People Also Ask
- What is the meaning of thermal evaporation? A Guide to Simple, Cost-Effective Thin Film Coating
- What is thermal evaporation used to deposit? A Guide to Metals, Compounds, and Key Applications
- What are the drawbacks of thermal evaporation? Understanding the Limitations for High-Performance Applications
- What is the evaporation process in semiconductors? A Guide to Thin Film Deposition
- What is thermal evaporation technique thin film deposition? A Guide to Simple, Cost-Effective PVD


















