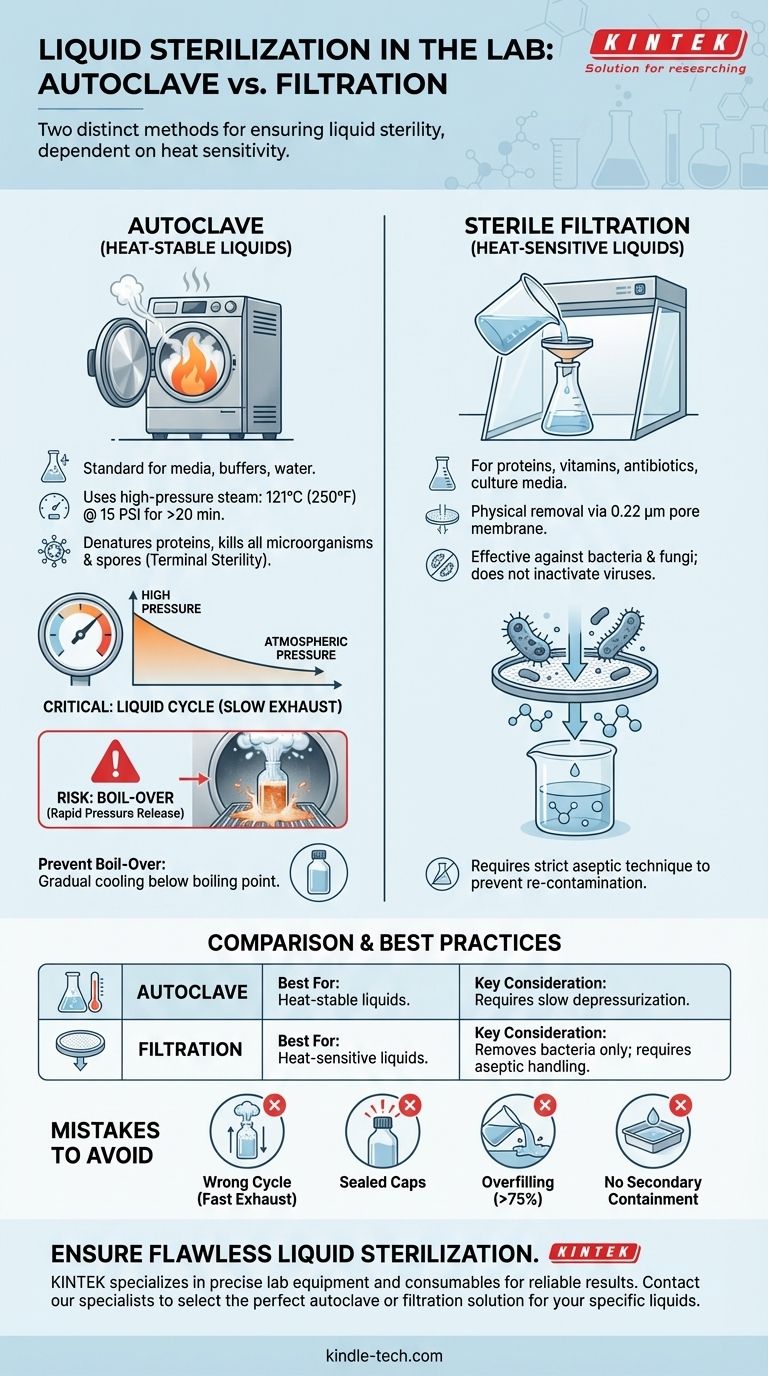
For sterilizing most liquids, the standard instrument is an autoclave using a specific "liquid cycle." This process uses high-pressure saturated steam at 121°C (250°F) to achieve sterilization. However, for liquids that are heat-sensitive, a completely different method called sterile filtration is required.
The core challenge in liquid sterilization isn't just achieving the required temperature, but managing the cool-down process. Rapid pressure changes can cause violent boiling, known as boil-over, which compromises the liquid and creates significant safety hazards.

The Autoclave: The Standard for Liquid Sterilization
An autoclave is essentially a highly sophisticated pressure cooker. It's the gold standard for sterilizing laboratory media, water, saline solutions, and other heat-stable liquids.
How an Autoclave Works
An autoclave injects high-pressure steam into a sealed chamber, displacing the air. This steam dramatically increases both the temperature and pressure inside, which denatures proteins and other essential biomolecules, killing all microorganisms, including resilient bacterial spores.
The Critical "Liquid Cycle"
You cannot sterilize liquids using the same cycle as solid instruments. A liquid cycle (also called a "slow exhaust" cycle) is essential.
After the sterilization time is complete, this cycle releases pressure very slowly and gradually. This slow depressurization allows the superheated liquid to cool below its boiling point before the chamber returns to normal atmospheric pressure, preventing boil-over.
Key Parameters for Success
The standard for liquid autoclaving is maintaining a temperature of 121°C at 15 PSI for a minimum of 20 minutes. However, this duration is for the liquid itself to reach temperature, not just the chamber. Larger volumes of liquid require significantly longer cycle times to ensure the core of the liquid is properly sterilized.
Understanding the Primary Challenge: Boil-Over
The most significant risk when autoclaving liquids is boil-over. This phenomenon occurs when pressure is released too quickly from the autoclave chamber.
The Physics of Boil-Over
Inside the autoclave, the liquid is heated well above its normal boiling point of 100°C because it is under high pressure. If that pressure is released suddenly, the boiling point of the liquid instantly drops, causing the entire volume to flash into steam violently. It's analogous to shaking a can of soda and opening it abruptly.
The Consequences
Boil-over is not a minor inconvenience. It leads to:
- Loss of Volume: Your carefully measured solution is now inaccurate.
- Altered Concentration: The loss of water vapor changes the concentration of solutes.
- Contamination Risk: Liquid can foam out of its container and contact non-sterile surfaces.
- Safety Hazard: Can cause glassware to shatter and creates a severe burn risk from scalding steam and liquid.
When an Autoclave Isn't the Answer: Heat-Sensitive Liquids
Many biological solutions, such as protein solutions, cell culture media with supplements, vitamins, or certain antibiotics, are destroyed by high heat. For these, autoclaving is not an option.
Introducing Sterile Filtration
The solution for heat-labile liquids is sterile filtration. This is a physical removal method, not a killing method.
The liquid is passed through a membrane filter with a pore size that is too small for microorganisms to pass through. The standard pore size for sterilization is 0.22 micrometers (µm), which effectively removes all bacteria and fungi.
The Process of Filtration
Filtration is typically done inside a laminar flow hood to maintain sterility. The liquid is forced through the filter using a vacuum pump, a syringe, or positive pressure into a pre-sterilized collection vessel.
Understanding the Trade-offs
Choosing between autoclaving and filtration depends entirely on the nature of your liquid and your goal.
Autoclaving vs. Sterile Filtration
An autoclave provides terminal sterility—it kills virtually all life forms within the container. However, it can only be used for liquids that are stable at high temperatures and pressures.
Sterile filtration removes bacteria but does not inactivate viruses or endotoxins (toxic substances released from dead bacteria). The process preserves the integrity of heat-sensitive components but requires strict aseptic technique to prevent re-contamination.
Common Mistakes in Liquid Autoclaving
- Using the Wrong Cycle: Using a fast-exhaust "gravity" or "wrapped goods" cycle is the most common cause of boil-over.
- Sealing Containers: Caps must be loosened or vented. A completely sealed container will explode under pressure.
- Overfilling Bottles: Never fill a container more than 75% full to leave adequate headspace for liquid expansion.
- Forgetting Secondary Containment: Always place liquid containers inside a shallow, autoclavable plastic or stainless steel tray to contain any potential spills or boil-over.
Making the Right Choice for Your Liquid
To select the correct method, you must first define the properties of your solution.
- If your primary focus is terminally sterilizing heat-stable media, buffers, or water: Use an autoclave with a dedicated slow-exhaust liquid cycle.
- If your primary focus is sterilizing solutions with heat-sensitive components like proteins or vitamins: Use sterile filtration with a 0.22 µm membrane filter under aseptic conditions.
- If your primary focus is safety and reproducibility: Always use secondary containment trays, never overfill your bottles, and ensure caps are loosened before every autoclave cycle.
Mastering liquid sterilization comes from understanding that you are managing temperature and pressure, not just heat.
Summary Table:
| Method | Best For | Key Consideration |
|---|---|---|
| Autoclave (Liquid Cycle) | Heat-stable liquids (media, buffers, water) | Requires slow depressurization to prevent boil-over |
| Sterile Filtration (0.22 µm) | Heat-sensitive liquids (proteins, antibiotics) | Removes bacteria but not viruses; requires aseptic technique |
Ensure flawless liquid sterilization in your lab.
Choosing the wrong sterilization method can lead to ruined experiments, contaminated samples, and significant safety risks. KINTEK specializes in providing the precise lab equipment and consumables you need for reliable results.
Whether you require a dependable autoclave with specialized liquid cycles or sterile filtration supplies, our experts can help you select the perfect solution for your specific liquids and protocols.
Contact our sterilization specialists today to discuss your laboratory's needs and discover how KINTEK can enhance your workflow's safety and efficiency.
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Laboratory Sterilizer Lab Autoclave Vertical Pressure Steam Sterilizer for Liquid Crystal Display Automatic Type
- Laboratory Sterilizer Lab Autoclave Pulse Vacuum Lifting Sterilizer
- Portable Digital Display Automatic Laboratory Sterilizer Lab Autoclave for Sterilization Pressure
- Laboratory Sterilizer Lab Autoclave Pulsating Vacuum Desktop Steam Sterilizer
- Desktop Fast Laboratory Autoclave Sterilizer 35L 50L 90L for Lab Use
People Also Ask
- What is the primary function of a laboratory autoclave in the pre-treatment of medical plastic waste for liquid fuel?
- What is the necessity of using an autoclave for pre-treating culture media? Ensure Accurate Ag2O/TiO2 Testing
- What role does an autoclave play in the acid treatment for microalgae disruption? Unlock High-Yield Cell Pretreatment
- What is the function of laboratory autoclaves in SCWR research? Predict Material Compatibility and Corrosion Kinetics
- What critical environmental conditions does a laboratory autoclave provide for evaluating wear resistance? - KINTEK



















