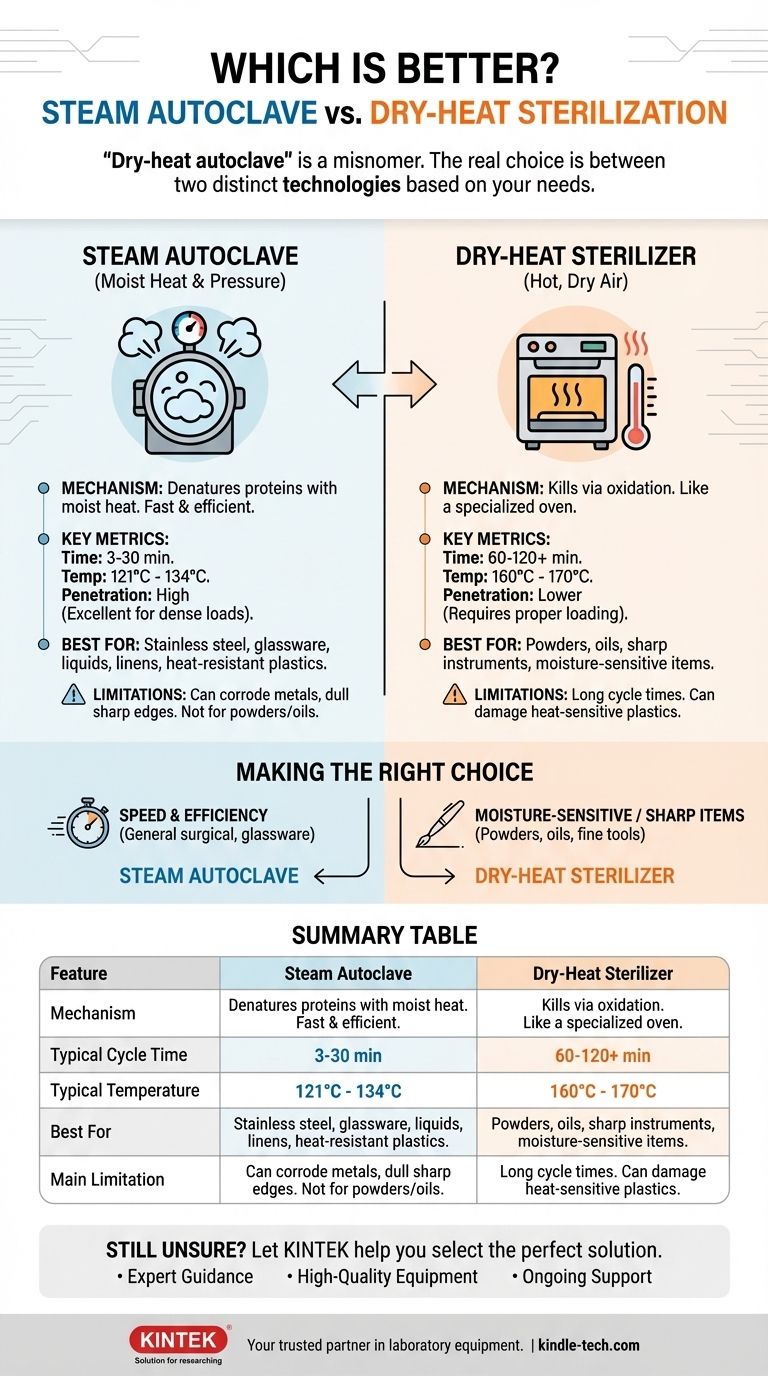
At its core, the term "dry-heat autoclave" is a misnomer. An autoclave, by its very definition, is a machine that uses pressurized steam to sterilize. Therefore, the real question is not about two types of autoclaves, but about two fundamentally different methods of sterilization: steam sterilization (autoclaving) and dry-heat sterilization. Steam is significantly faster and more efficient for most common applications.
The choice isn't between two types of autoclaves, but between two distinct sterilization technologies. Steam autoclaves use moist heat under pressure for rapid sterilization, while dry-heat sterilizers use high-temperature air over a longer period. The "better" method depends entirely on what you need to sterilize.

The Fundamental Difference: How They Sterilize
To make an informed decision, you must first understand the mechanism behind each method. They do not work the same way and are not interchangeable for all items.
Steam Sterilization (Autoclaves)
A steam autoclave introduces saturated steam into a sealed pressure chamber. The sterilization process works through a combination of high temperature (typically 121°C to 134°C), pressure, and the critical presence of moisture.
This moist heat is incredibly effective at denaturing the essential proteins and lipids that make up microorganisms, killing them far more quickly than dry heat can.
Dry-Heat Sterilization
A dry-heat sterilizer is essentially a specialized oven that uses hot, dry air. It kills microorganisms through a process of oxidation, effectively baking them until they are destroyed.
Because dry air is a less efficient conductor of heat than moist steam, this method requires much higher temperatures (often 160°C to 170°C) and significantly longer exposure times to achieve sterility.
Comparing Key Performance Metrics
The differences in their working principles lead to very different performance characteristics. The right choice for you will be determined by these factors.
Time and Temperature
This is the most significant practical difference. A steam autoclave can sterilize a load in as little as 3-4 minutes (for unwrapped instruments in a pre-vacuum cycle at 134°C) to 30 minutes (for wrapped loads at 121°C).
Dry-heat sterilization is drastically slower. A typical cycle runs for 60 to 120 minutes at 160-170°C, not including the time it takes for the chamber to heat up and cool down.
Material Compatibility
Steam is ideal for durable materials like stainless steel surgical instruments, most glassware, and heat-resistant plastics. The moisture makes it highly effective for sterilizing liquids and culture media.
Dry heat is the only option for materials that cannot be exposed to moisture. This includes powders, oils, and certain metal instruments that might corrode in steam. It is also preferred for preserving the sharpness of fine cutting instruments, which can be dulled by the moisture in an autoclave.
Penetration and Efficacy
Steam's ability to condense on cooler surfaces releases latent heat, allowing it to penetrate dense loads and wrapped packs very efficiently. This ensures all surfaces are reached.
Dry heat relies on slow conduction and convection, making it less effective at penetrating complex or densely packed loads. Proper loading is critical to ensure hot air can circulate freely.
Understanding the Trade-offs
Neither method is perfect. Recognizing their limitations is key to avoiding instrument damage or sterilization failure.
The Downside of Steam (Autoclaving)
The primary drawback of steam is its reliance on moisture. It will cause rust and corrosion on carbon steel instruments and cannot be used for any water-sensitive items like powders or oils. It can also dull the edges of sharp instruments over time.
The Downside of Dry Heat
The main disadvantage of dry heat is the extremely long cycle time. The high temperatures required can also damage or melt materials that would otherwise be safe in a lower-temperature autoclave, such as certain rubbers and plastics.
A Note on Autoclave Types
Within the category of steam autoclaves, there are further distinctions. The references you provided highlight two main types:
- Gravity Displacement: Steam is pumped in, displacing the heavier, cooler air which drains out the bottom. These are simpler and less expensive but have longer cycles.
- Pre-vacuum (Prevac): A vacuum pump actively removes air from the chamber before steam is introduced. This allows for faster, more reliable steam penetration and is the standard for most hospital and clinical settings.
Making the Right Choice for Your Sterilization Needs
Your decision should be based entirely on your specific application and the materials you handle.
- If your primary focus is speed and efficiency for general surgical instruments, glassware, or linens: A steam autoclave is the correct choice, with pre-vacuum models (Type B or S) offering the best performance.
- If your primary focus is sterilizing powders, oils, or protecting the integrity of sharp, delicate instruments: Dry-heat sterilization is the necessary method.
- If you run a mixed-use laboratory or clinic: You may need both technologies to properly handle the full range of materials requiring sterilization.
Ultimately, understanding the properties of the items you need to sterilize is the most critical step in selecting the right technology.
Summary Table:
| Feature | Steam Autoclave | Dry-Heat Sterilizer |
|---|---|---|
| Mechanism | Moist heat under pressure | Hot, dry air |
| Typical Cycle Time | 3-30 minutes | 60-120+ minutes |
| Typical Temperature | 121°C - 134°C | 160°C - 170°C |
| Best For | Stainless steel, glassware, liquids, linens | Powders, oils, sharp instruments, moisture-sensitive items |
| Main Limitation | Can corrode metals, dull sharp edges | Long cycle times, can damage heat-sensitive plastics |
Still Unsure Which Sterilization Method is Right for Your Lab?
Choosing the right equipment is critical for effective sterilization and protecting your valuable instruments. KINTEK, your trusted partner in laboratory equipment, specializes in helping labs like yours select the perfect autoclaves and sterilizers.
We provide:
- Expert Guidance: Our specialists will analyze your specific needs—from material types to workflow demands—to recommend the ideal solution.
- High-Quality Equipment: We offer reliable steam autoclaves (including gravity displacement and pre-vacuum models) and durable dry-heat sterilizers to meet any application.
- Ongoing Support: Ensure your lab operates at peak efficiency with our installation, maintenance, and consumables support.
Don't risk instrument damage or inefficient workflows. Let KINTEK provide the reliable sterilization equipment your laboratory deserves.
Contact our experts today for a personalized consultation!
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Desktop Fast Laboratory Autoclave Sterilizer 20L 24L for Lab Use
- Desktop Fast Laboratory Autoclave Sterilizer 35L 50L 90L for Lab Use
- Laboratory High Pressure Horizontal Autoclave Steam Sterilizer for Lab Use
- Laboratory Horizontal Autoclave Steam Sterilizer Lab Microcomputer Sterilizer
- Laboratory Sterilizer Lab Autoclave Pulsating Vacuum Desktop Steam Sterilizer
People Also Ask
- What is the necessity of using an autoclave for pre-treating culture media? Ensure Accurate Ag2O/TiO2 Testing
- How do you use an autoclave in a microbiology lab? Master Sterilization for Lab Safety & Accuracy
- What is the normal temperature of an autoclave? Achieve Sterile Confidence with Precise Control
- What critical environmental conditions does a laboratory autoclave provide for evaluating wear resistance? - KINTEK
- What precautions should be taken during autoclave in laboratory? A Complete Safety Guide to Prevent Burns and Explosions



















