Ultimately, the "best" method for removing a solid from a liquid depends entirely on the physical properties of your specific mixture. There is no single universal answer, but the most common and effective techniques are filtration, decantation, evaporation, and centrifugation, each suited for a different type of solid-liquid combination.
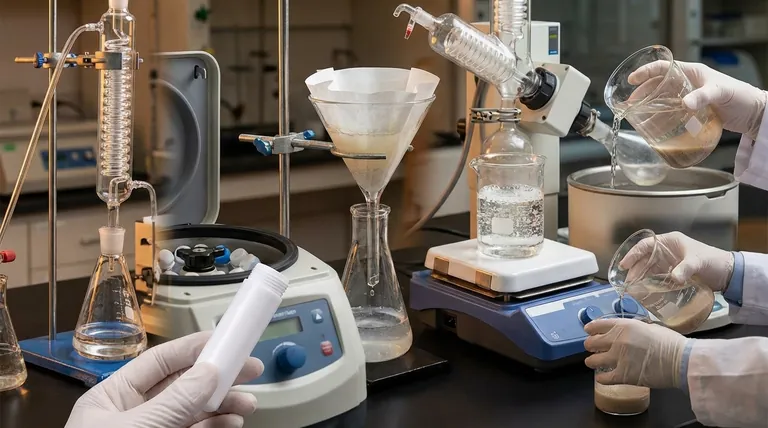
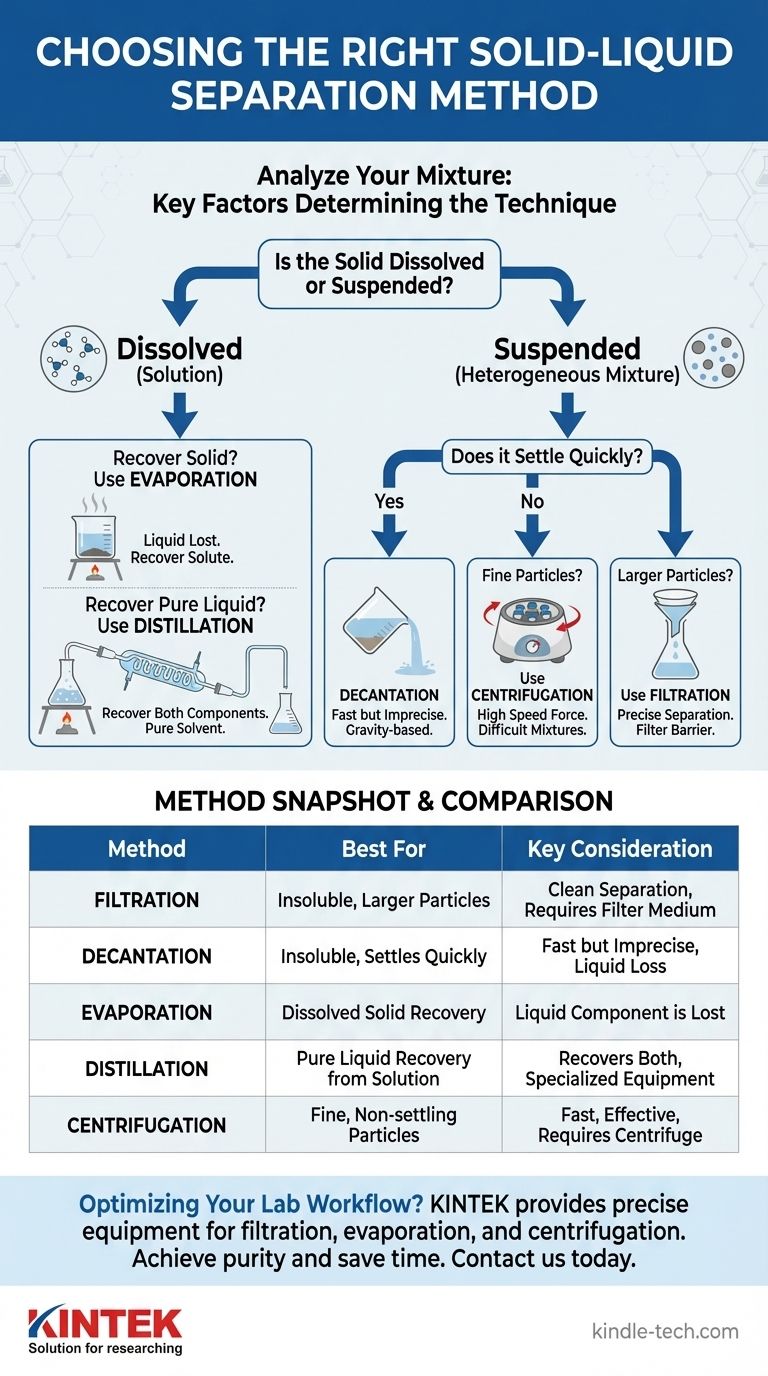
The optimal separation technique is not determined by a simple preference, but by a clear diagnosis of your mixture. The critical questions are whether the solid is dissolved or suspended, the size of its particles, and the density difference between the solid and the liquid.

Analyzing Your Mixture: The Key to Choosing a Method
Before you can select a tool, you must understand the job. The characteristics of your mixture will point directly to the most efficient separation method.
Is the Solid Dissolved or Suspended?
This is the most important question. A dissolved solid (solute) is one that has broken down into individual molecules and dispersed evenly within the liquid (solvent), forming a solution. You cannot see the individual particles.
A suspended solid consists of larger, undissolved particles distributed throughout the liquid, forming a heterogeneous mixture. These particles are often visible to the naked eye.
What is the Size of the Solid Particles?
For suspended solids, particle size is a critical factor. Large, heavy particles like sand will behave very differently from fine, lightweight particles like silt or clay.
Methods like simple filtration work well for larger particles, while techniques designed to handle extremely fine particles may be necessary for others.
Is There a Density Difference?
Most solids are denser than the liquids they are in, causing them to sink over time due to gravity. This process is called sedimentation.
The greater the density difference and the larger the particle size, the faster the solid will settle, making certain gravity-based methods more effective.
A Guide to Common Separation Techniques
Once you have analyzed your mixture, you can confidently choose from the following standard techniques.
Filtration: For Insoluble Solids with Larger Particles
Filtration is the process of passing a mixture through a barrier, or filter medium, that allows the liquid (the filtrate) to pass through but blocks the solid particles.
Think of a coffee filter: it lets the liquid coffee pass into the pot while trapping the solid coffee grounds. This is the go-to method for separating a non-dissolved solid from a liquid, such as sand from water.
Decantation: For Insoluble Solids that Settle Quickly
Decantation is a faster but less precise method that relies on gravity. After the denser, insoluble solid has settled at the bottom of the container, the liquid is carefully poured off.
This is often used for separating a clear liquid from a small amount of coarse sediment. However, it is difficult to perform without leaving some liquid behind or accidentally pouring off some of the solid.
Evaporation: For Soluble Solids (Recovering the Solid)
When a solid is fully dissolved, filtration won't work because the solid particles are small enough to pass through any filter. Evaporation separates a dissolved solid from a solvent by heating the solution.
The liquid turns into a gas and evaporates away, leaving the solid behind. This is the classic method for recovering salt from saltwater. The key drawback is that the liquid component is lost to the atmosphere.
Distillation: For Soluble Solids (Recovering the Liquid)
Distillation is a variation of evaporation that allows you to collect the liquid component. The solution is heated until the liquid evaporates, but the vapor is then captured and cooled in a condenser.
This cooled vapor turns back into a pure liquid and is collected in a separate container, leaving the solid behind in the original flask. Use distillation when your goal is to obtain a pure liquid from a solution.
Centrifugation: For Fine, Suspended Particles
Sometimes, suspended particles are so small and light that they won't settle out on their own, or would take far too long. Centrifugation is a technique that speeds up this process dramatically.
The mixture is spun at very high speeds, creating a powerful centrifugal force that drives the denser solid particles to the bottom of the container much more quickly and compactly than gravity alone. This is essential for separating blood cells from plasma or fine sediments from water.
Understanding the Trade-offs
Choosing a method often involves balancing competing priorities like speed, purity, and complexity.
Speed vs. Purity
Decantation is very fast but often results in an impure separation. Careful filtration is slower but yields a much cleaner separation of the solid and liquid components. The "best" choice depends on how much cross-contamination you can tolerate.
Equipment and Complexity
Pouring off a liquid (decantation) requires nothing more than a steady hand. Filtration requires a funnel and filter paper. Distillation and centrifugation, however, require specialized and more expensive laboratory equipment.
Recovering Both Components
Consider which parts of the mixture you need to keep. Evaporation is excellent for recovering a dissolved solid, but the liquid is lost. If you need to recover both the solid and the liquid, you must use a method like distillation or filtration.
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
Base your decision on a clear-eyed assessment of your mixture and your objective.
- If your solid is insoluble and visible (like sand in water): Filtration is your most reliable and precise choice.
- If your solid has dissolved completely (like salt in water): Use evaporation to recover the solid or distillation to recover the pure liquid.
- If your solid is insoluble but settles out on its own: Decantation is a quick but imprecise option; for better results, use filtration.
- If your solid is made of very fine, suspended particles that won't settle: Centrifugation is the most effective and often necessary method.
By first understanding the properties of your mixture, you can confidently select the most effective separation technique for your specific needs.
Summary Table:
| Method | Best For | Key Consideration |
|---|---|---|
| Filtration | Insoluble solids with larger particles (e.g., sand from water) | Provides a clean separation; requires filter paper/funnel |
| Decantation | Insoluble solids that settle quickly | Fast but imprecise; can leave liquid behind |
| Evaporation | Recovering a dissolved solid (e.g., salt from water) | Liquid is lost; only the solid is recovered |
| Distillation | Recovering pure liquid from a solution | Recovers both components but requires specialized equipment |
| Centrifugation | Fine, suspended particles that won't settle (e.g., blood cells) | Fast and effective for difficult mixtures; requires a centrifuge |
Struggling to choose the right separation method for your lab work? KINTEK specializes in providing the precise lab equipment and consumables you need for efficient solid-liquid separation. Whether your process requires reliable filtration setups, robust evaporation systems, or high-performance centrifuges, our experts can help you select the ideal tools to achieve purity and save time. Contact our team today to optimize your separation workflow and get the results you need.
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Custom PTFE Teflon Parts Manufacturer for Centrifuge Tubes
- Laboratory Disc Rotary Mixer for Efficient Sample Mixing and Homogenization
- Automatic Laboratory Heat Press Machine
- Heated Hydraulic Press Machine with Heated Plates Split Manual Laboratory Hot Press
- Double Plate Heating Press Mold for Lab
People Also Ask
- What is the binder in XRF? The Key to Creating Stable, Accurate Sample Pellets
- What are some common applications of ultra-low temperature freezers? Essential for Biomedical, Pharma, and Clinical Storage
- Is it fitting the mould or mold? A Guide to Correct Spelling by Region
- What is a pyrolysis fluidized bed reactor? Maximize Bio-Oil Yield with Superior Heat Transfer
- How do metal oxides like Cerium Oxide (CeO2) or Zinc Oxide (ZnO) function in solar thermochemical cycles?
- How much does biomass cost per kWh? Understanding the True Price of Renewable Power
- What are the effects of pyrolysis on biomass? A Tunable Process for Biochar, Bio-oil, and Syngas
- What are the four steps to the heat treating process? Master the 3 Core Stages for Superior Results



















