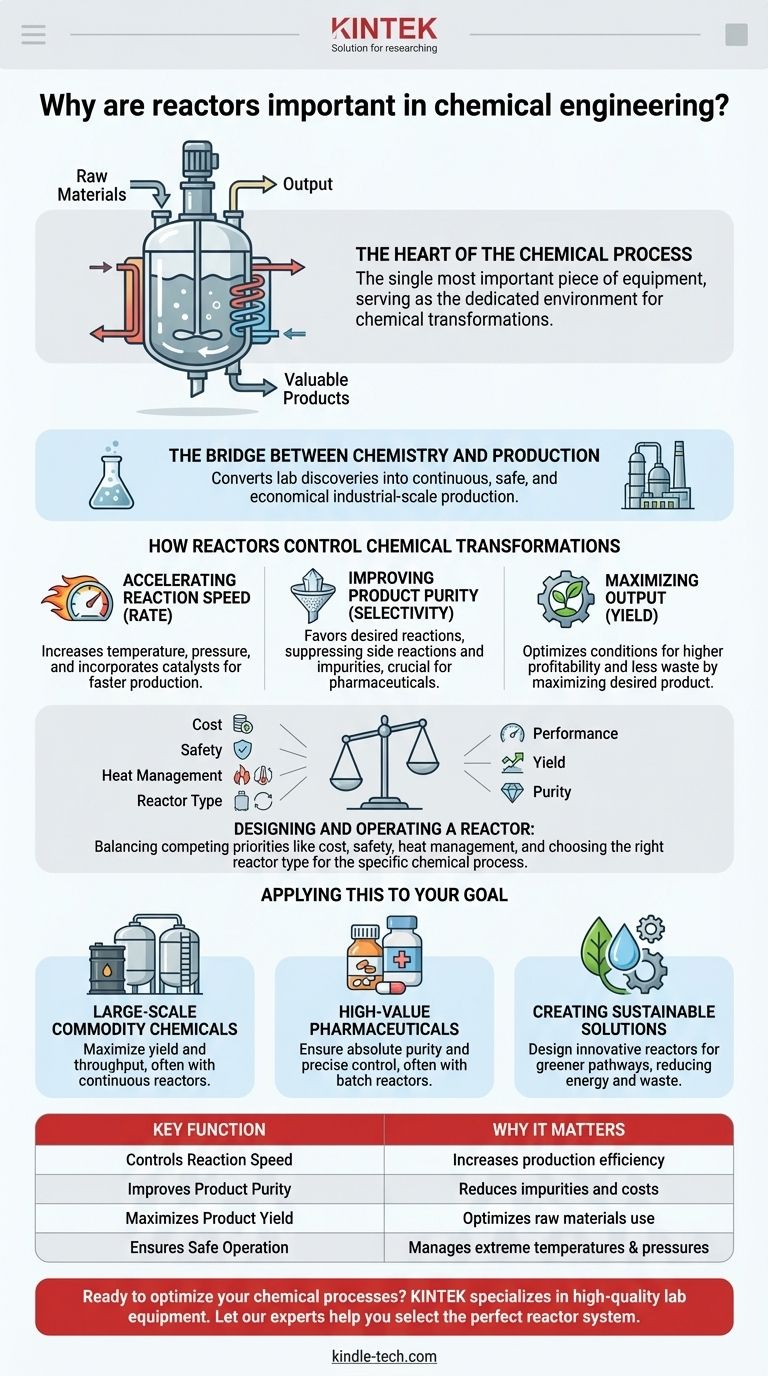
In essence, chemical reactors are the single most important piece of equipment in chemical engineering. They are the core of any chemical plant, serving as the dedicated environment where raw materials undergo chemical transformations to become valuable, finished products. Without the reactor, a chemical process is merely a concept; with it, it becomes a reality.
A chemical reactor is far more than a simple container. It is a highly engineered system designed to precisely control the conditions of a chemical reaction—such as temperature, pressure, and mixing—to maximize product yield, ensure purity, and maintain safe operation at an industrial scale.

The Reactor as the Heart of the Process
A chemical plant can be visualized as a system with inputs and outputs. The reactor is the heart of that system, performing the fundamental conversion that justifies the entire operation.
From Raw Materials to Value
At its most basic level, a reactor takes in reactants (raw materials) and facilitates their conversion into products. This is where the actual "chemistry" of chemical engineering happens. All other equipment in the plant, such as pumps, heaters, and separators, exists to support the reactor's function.
The Bridge Between Chemistry and Production
A chemist may discover a new reaction in a lab beaker, but a chemical engineer designs a reactor to perform that same reaction continuously, safely, and economically at a scale thousands or millions of times larger. The reactor is the critical bridge between laboratory discovery and industrial production.
How Reactors Control Chemical Transformations
The importance of a reactor lies in its ability to manipulate the environment to favor a desired chemical outcome. This control is typically focused on three key performance indicators.
Accelerating Reaction Speed (Rate)
Most chemical reactions are sensitive to their conditions. By increasing temperature and pressure, reactors can significantly speed up the rate at which reactants are converted to products. As noted in high-pressure applications, this acceleration is a primary driver for economic efficiency.
Furthermore, many reactors are designed to incorporate catalysts, which are substances that speed up a reaction without being consumed. The reactor's design ensures maximum contact between the reactants and the catalyst.
Improving Product Purity (Selectivity)
Few chemical processes produce only one product. Often, undesirable side reactions occur, creating impurities that must be removed later.
A well-designed reactor creates conditions that favor the desired reaction while suppressing others. This focus on selectivity is crucial, as it reduces waste and minimizes the cost and complexity of downstream purification steps. This is especially vital in industries like pharmaceuticals, where purity is paramount.
Maximizing Output (Yield)
Yield is the measure of how much desired product is created from a given amount of raw material. It is a direct function of both reaction rate and selectivity.
By optimizing conditions to make the reaction faster (high rate) and more precise (high selectivity), reactors maximize the overall yield. This directly translates to higher profitability and less wasted material, a key component of creating more sustainable chemical solutions.
Understanding the Trade-offs and Design Challenges
While essential, designing and operating a reactor involves balancing competing priorities. The "perfect" reactor does not exist; instead, it is always an engineered compromise.
The Balance of Cost, Safety, and Performance
A reactor that can operate at extreme pressures and temperatures can achieve incredible performance, but it is expensive to build and requires complex safety systems. The choice of materials and the thickness of the reactor walls are critical design decisions driven by the need to contain the reaction safely.
The Challenge of Heat Management
Chemical reactions either release heat (exothermic) or absorb heat (endothermic). A reactor must be designed with heating or cooling systems to manage this thermal load. For highly exothermic reactions, failure to remove heat quickly can lead to a dangerous "runaway" condition where temperature and pressure increase uncontrollably.
Choosing the Right Reactor Type
There is no single reactor for all purposes. Engineers must choose from various types, such as batch reactors (where ingredients are loaded at once) or continuous reactors (where reactants flow in and products flow out constantly), based on the scale of production, reaction chemistry, and economic goals.
Applying This to Your Goal
The design and operational philosophy for a reactor is dictated entirely by the final objective of the chemical process.
- If your primary focus is large-scale commodity chemicals: The key is maximizing yield and throughput to minimize cost, often using large, continuous reactors.
- If your primary focus is high-value pharmaceuticals: The key is ensuring absolute purity and precise control (selectivity), often using smaller, highly controlled batch reactors.
- If your primary focus is creating sustainable solutions: The key is designing innovative reactors that can handle new catalysts or operate under conditions that enable greener chemical pathways, reducing energy use and waste.
Ultimately, chemical reactors are the engines that power the modern material world, from fuels and plastics to medicines and fertilizers.
Summary Table:
| Key Function | Why It Matters |
|---|---|
| Controls Reaction Speed | Increases production efficiency and economic output. |
| Improves Product Purity | Reduces impurities and downstream purification costs. |
| Maximizes Product Yield | Optimizes use of raw materials for higher profitability. |
| Ensures Safe Operation | Manages extreme temperatures and pressures at scale. |
Ready to optimize your chemical processes? The right reactor is critical for achieving your goals in yield, purity, and safety. KINTEK specializes in high-quality lab equipment and consumables, serving laboratory needs from R&D to production scaling. Let our experts help you select the perfect reactor system for your application. Contact us today to discuss your project and enhance your lab's capabilities!
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Customizable High Pressure Reactors for Advanced Scientific and Industrial Applications
- Mini SS High Pressure Autoclave Reactor for Laboratory Use
- Stainless High Pressure Autoclave Reactor Laboratory Pressure Reactor
- High Pressure Laboratory Autoclave Reactor for Hydrothermal Synthesis
- Laboratory Hydraulic Press Split Electric Lab Pellet Press
People Also Ask
- What is the function of a constant temperature hydrothermal reactor? Master Coal Fly Ash Activation
- What is the purpose of using high-purity argon gas in a high-pressure reactor? Ensure Precise Corrosion Test Data
- What role does an autoclave play in simulating PWR conditions? Advanced Material Validation for Nuclear Safety
- What is the contribution of a hydrothermal reactor to graded pore construction? Precision Templates for TAS
- What is the role of high-pressure reactors in the study of alloy oxidation? Essential Tools for Supercritical Research



















