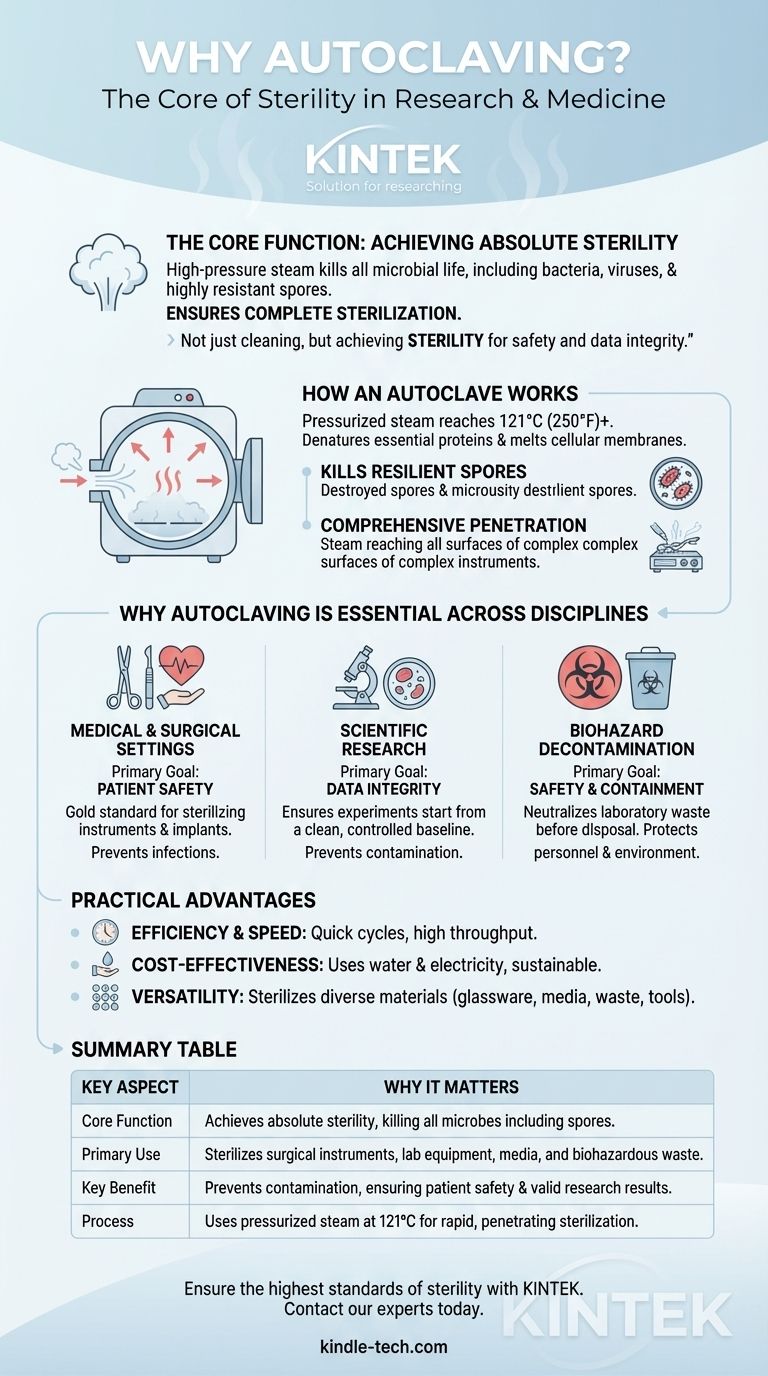
At its core, autoclaving is used because it is one of the most effective and reliable methods for complete sterilization. By using high-pressure steam to kill all forms of microbial life—including bacteria, viruses, and highly resistant spores—it ensures that instruments, media, and waste are rendered completely sterile for critical applications in research and medicine.
The fundamental reason for its widespread use is not just cleaning, but achieving sterility. Autoclaving provides the absolute certainty required to prevent contamination in sensitive experiments and to guarantee patient safety during medical procedures.
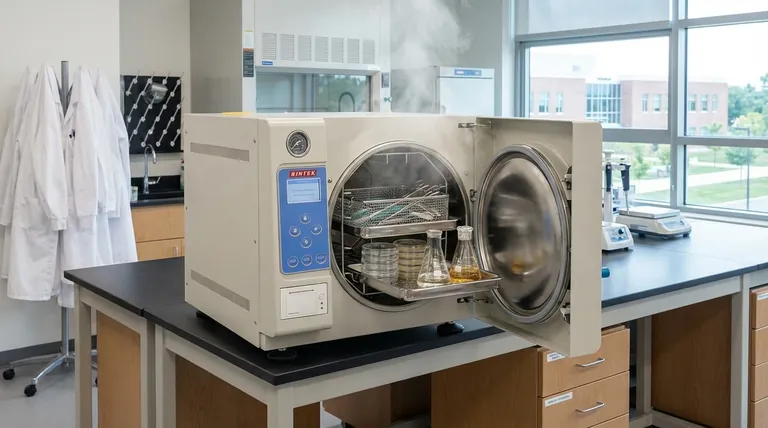

The Core Function: Achieving Absolute Sterility
An autoclave's effectiveness stems from its ability to harness the power of pressurized steam. This creates an environment far more lethal to microorganisms than boiling water or chemical disinfectants alone.
How an Autoclave Works
An autoclave is essentially a highly specialized pressure chamber. It works by replacing the air inside with saturated steam and then increasing the pressure.
This pressure allows the steam to reach temperatures far above the normal boiling point of water, typically 121°C (250°F) or higher.
Killing the Most Resilient Microbes
This combination of intense heat and moisture is exceptionally destructive to all microorganisms. It rapidly denatures essential proteins and melts cellular membranes, ensuring destruction.
Crucially, this process is lethal to bacterial spores, which are dormant, tough structures that can survive boiling and many chemical treatments. This makes autoclaving a true sterilization method, not just a disinfection process.
Penetration for Comprehensive Sterilization
Pressurized steam has excellent penetration properties. It can reach every surface of complex surgical instruments, seep into porous materials, and sterilize liquids in sealed containers.
This ensures that even hidden or hard-to-reach areas are fully sterilized, leaving no safe harbor for microbial life.
Why Autoclaving is Essential Across Disciplines
The need for absolute sterility makes autoclaving a non-negotiable tool in any field where microbial contamination can have severe consequences.
In Medical and Surgical Settings
The primary goal here is patient safety. Autoclaving is the gold standard for sterilizing surgical instruments, implantable medical devices, and other equipment that comes into contact with a patient's body.
This practice is fundamental to preventing surgical site infections and ensuring successful medical outcomes.
In Scientific Research
In labs, the goal is data integrity. An unsterilized petri dish, contaminated culture medium, or dirty piece of glassware can introduce foreign microbes into an experiment.
This contamination can completely invalidate research results. Autoclaving ensures that experiments start from a clean, controlled baseline.
In Biohazard Decontamination
Autoclaves play a critical role in safety and containment. Laboratory and medical waste, such as used culture plates or contaminated disposables, must be neutralized before disposal.
By sterilizing this biohazardous waste, autoclaves prevent the accidental release of potentially dangerous microorganisms into the environment, protecting both facility personnel and the public.
The Practical Advantages of Autoclaving
Beyond its effectiveness, the autoclave is a cornerstone of sterile processing due to its efficiency and versatility.
Efficiency and Speed
Compared to other sterilization methods like ethylene oxide gas or dry heat, autoclaving cycles are relatively short, often completing in under an hour. This allows for a high throughput of sterile goods.
Cost-Effectiveness
The process is economical, relying primarily on water and electricity. It does not require expensive chemical agents or disposables for its basic operation, making it a sustainable choice for most facilities.
Versatility of Materials
Autoclaves can sterilize a vast range of materials. This includes surgical equipment, laboratory glassware, pipette tips, various autoclavable plastics, culture media, solutions, and of course, biohazardous waste.
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
The application of autoclaving is always tied to a critical need for sterility. Understanding your specific goal clarifies its importance.
- If your primary focus is patient safety in a clinical setting: Autoclaving is the definitive method for sterilizing reusable surgical instruments to eliminate the risk of infection.
- If your primary focus is data integrity in a research lab: It is the essential first step for preparing media and equipment to ensure your experimental results are repeatable and valid.
- If your primary focus is workplace and environmental safety: Autoclaving provides a reliable and effective final step for neutralizing biohazardous waste before it leaves your facility.
Ultimately, autoclaving is the trusted foundation for safety and reliability in any environment where microbial contamination is not an option.
Summary Table:
| Key Aspect | Why It Matters |
|---|---|
| Core Function | Achieves absolute sterility by killing all microbes, including resistant spores. |
| Primary Use | Sterilizes surgical instruments, lab equipment, media, and biohazardous waste. |
| Key Benefit | Prevents contamination, ensuring patient safety and valid research results. |
| Process | Uses pressurized steam at 121°C (250°F) for rapid, penetrating sterilization. |
Ensure the highest standards of sterility and safety in your facility. KINTEK specializes in providing reliable, high-performance autoclaves and lab equipment tailored to the rigorous demands of medical and research environments. Our solutions help you guarantee patient safety, maintain data integrity, and manage biohazardous waste effectively. Contact our sterilization experts today to find the perfect autoclave for your critical needs!
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Desktop Fast Laboratory Autoclave Sterilizer 35L 50L 90L for Lab Use
- Desktop Fast Laboratory Autoclave Sterilizer 20L 24L for Lab Use
- Laboratory Sterilizer Lab Autoclave Pulsating Vacuum Desktop Steam Sterilizer
- Laboratory High Pressure Steam Sterilizer Vertical Autoclave for Lab Department
- Portable High Pressure Laboratory Autoclave Steam Sterilizer for Lab Use
People Also Ask
- What is the guideline for autoclave? A Step-by-Step Protocol for Safe Sterilization
- How often should a dental autoclave be cleaned? A Daily, Weekly, and Monthly Guide
- How is high pressure generated in an autoclave? Unlock the Science of Sterilization & Synthesis
- Can all materials be sterilized in the autoclave? A Guide to Safe & Effective Sterilization
- Do you need to autoclave glassware? A Guide to Sterilization vs. Cleaning
- What types of items and materials can be processed in a laboratory autoclave? Essential Guide for Lab Safety
- What is the specific function of a high-pressure autoclave in the hydrothermal synthesis? Master Crystal Growth
- Do autoclaves use a lot of electricity? Managing Energy Costs in Your Sterilization Process



















