At its core, high temperature is the most reliable and widely used method for sterilization because it inflicts catastrophic and irreversible damage on the essential machinery of microbial life. The intense thermal energy physically breaks down the proteins, enzymes, and membranes that microorganisms need to function and reproduce, ensuring their complete destruction.
The importance of high temperature is not just that it kills microbes, but how it kills them. It is a brute-force physical process that causes a complete and irreversible collapse of the cell's structure and metabolic functions, a level of destruction that more subtle methods cannot guarantee.
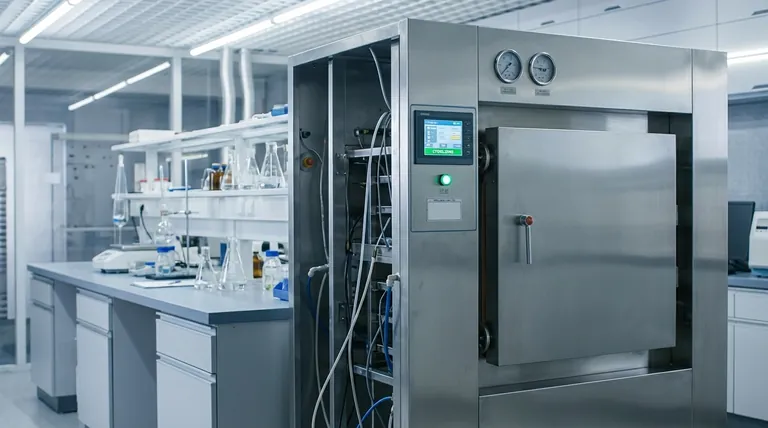

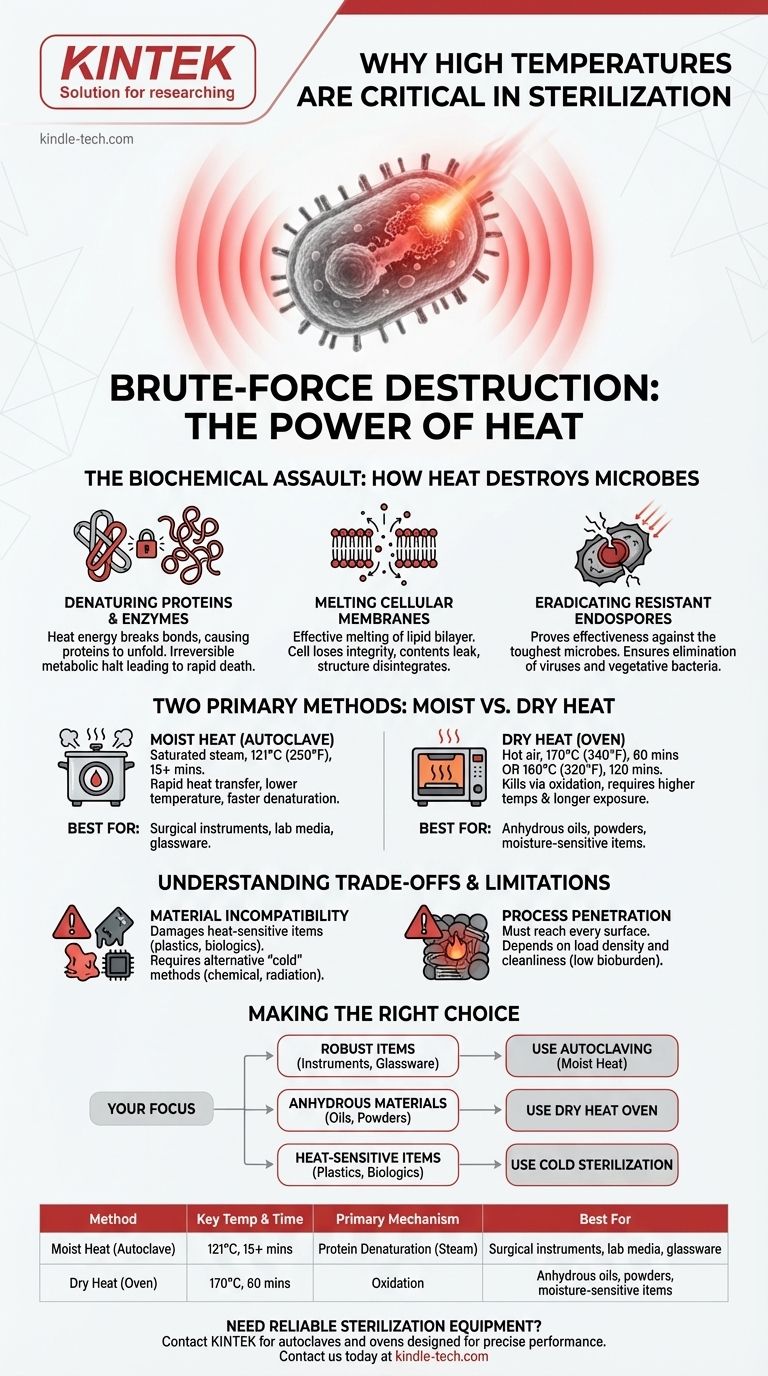
The Biochemical Assault: How Heat Destroys Microbes
To understand why heat is so effective, we must look at what it does to a microbial cell at the molecular level. It is not a gentle process; it is a multi-pronged attack on the very components of life.
Denaturing Essential Proteins and Enzymes
A cell's functions are carried out by proteins and enzymes, which must maintain a specific, complex three-dimensional shape to work. High heat provides enough energy to break the delicate bonds holding these shapes together, causing the proteins to unfold and tangle.
This process, called denaturation, is irreversible—much like you cannot unscramble an egg. When a microbe's enzymes are denatured, its metabolism grinds to a complete halt, leading to rapid cell death.
Melting Cellular Membranes
Microorganisms are encased in a cell membrane, a critical barrier made of a lipid bilayer. Heat effectively melts this structure, destroying its integrity.
The compromised membrane can no longer regulate what enters or leaves the cell. Essential contents leak out, the cell loses its physical structure, and it rapidly disintegrates.
Eradicating the Most Resistant Organisms
The true test of any sterilization process is its ability to kill bacterial endospores. These are dormant, highly protected structures produced by bacteria like Bacillus and Clostridium that are extremely resistant to heat, chemicals, and radiation.
Sterilization protocols, particularly the high temperatures used, are specifically designed to be powerful enough to destroy these resilient endospores. By proving effectiveness against the toughest possible target, we can be confident that all other less-resistant microbes (like viruses and vegetative bacteria) have also been eliminated.
Two Primary Methods: Moist Heat vs. Dry Heat
The way thermal energy is delivered is as important as the temperature itself. The two primary methods, moist heat and dry heat, work on different principles and are used for different applications.
Moist Heat (Autoclaving): The Gold Standard
Moist heat, in the form of saturated steam under pressure, is the most efficient method of thermal sterilization. The standard cycle for an autoclave is 121°C (250°F) for at least 15 minutes.
Water is a much more effective conductor of thermal energy than air. The moisture in the steam rapidly transfers heat to microorganisms and plays a key role in accelerating the denaturation of proteins, allowing sterilization to occur at lower temperatures and in less time compared to dry heat.
Dry Heat (Ovens): For Specific Applications
Dry heat sterilization is performed in a hot air oven and requires higher temperatures and significantly longer exposure times, such as 170°C (340°F) for 60 minutes or 160°C (320°F) for 120 minutes.
Instead of denaturation via steam, dry heat kills microbes primarily through oxidation, essentially slow-baking them until their cellular components are destroyed. This method is reserved for materials that are sensitive to moisture or impenetrable to steam, such as anhydrous oils, powders, and certain glassware.
Understanding the Trade-offs of Thermal Sterilization
While highly effective, using high temperatures is not a universal solution. Understanding its limitations is critical for making correct procedural choices.
Material Incompatibility
The primary drawback is that high heat damages or destroys heat-sensitive (thermolabile) materials. Many plastics, complex electronics, and biological products like certain pharmaceuticals or vaccines cannot withstand the temperatures required for thermal sterilization.
Need for Alternative Methods
Because of these material limitations, other sterilization methods are essential. These "cold" sterilization techniques include chemical sterilization (using gases like ethylene oxide), radiation (gamma or e-beam), and sterile filtration for liquids.
Process Penetration and Bioburden
The effectiveness of heat depends on its ability to reach every surface. Sterilization cycles must be validated to ensure steam or hot air penetrates the entire load, especially for complex instruments or densely packed items. Furthermore, items must be thoroughly cleaned first, as high bioburden (the initial number of microbes) or organic debris can insulate microorganisms from the heat.
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
Selecting the correct sterilization method is a critical decision based on material compatibility and the nature of the item being processed.
- If your primary focus is sterilizing robust surgical instruments, lab media, or glassware: Autoclaving with moist heat is the fastest, most reliable, and most economical method.
- If your primary focus is sterilizing anhydrous materials like oils, powders, or heat-stable instruments you must keep dry: A dry heat oven is the correct choice, but you must account for the required higher temperatures and longer cycle times.
- If your primary focus is sterilizing heat-sensitive items like plastics, electronics, or biologics: Thermal sterilization is inappropriate, and you must use an alternative such as chemical gas, radiation, or filtration.
Ultimately, understanding the destructive power of heat at the molecular level allows you to apply sterilization principles safely and effectively across any discipline.
Summary Table:
| Sterilization Method | Key Temperature & Time | Primary Mechanism | Best For |
|---|---|---|---|
| Moist Heat (Autoclave) | 121°C for 15+ minutes | Protein denaturation via steam | Surgical instruments, lab media, glassware |
| Dry Heat (Oven) | 170°C for 60 minutes | Oxidation | Anhydrous oils, powders, moisture-sensitive items |
Need Reliable Sterilization Equipment for Your Lab?
High-temperature sterilization is non-negotiable for lab safety and integrity. KINTEK specializes in durable autoclaves and ovens designed for precise, consistent performance. Whether you're processing instruments, media, or sensitive materials, our solutions ensure complete microbial eradication.
Contact us today to find the perfect sterilization system for your laboratory's unique needs.
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Laboratory Sterilizer Lab Autoclave Herbal Powder Sterilization Machine for Plant
- Laboratory High Pressure Steam Sterilizer Vertical Autoclave for Lab Department
- Laboratory Sterilizer Lab Autoclave Pulsating Vacuum Desktop Steam Sterilizer
- Desktop Fast Laboratory Autoclave Sterilizer 35L 50L 90L for Lab Use
- Portable Digital Display Automatic Laboratory Sterilizer Lab Autoclave for Sterilization Pressure
People Also Ask
- Why use Zirconia rods for sample mounting in high-pressure autoclaves? Ensure Data Purity and Chemical Stability.
- How should solid materials in bags be prepared for decontamination? Master Steam Penetration for Safe Sterilization
- What are the limitations of autoclave? Understanding Material and Operational Constraints
- Can an autoclave reach temps as high as 121 degrees Celsius? The Definitive Guide to Steam Sterilization
- What is the equivalent of an autoclave? Find the Right Sterilization Method for Your Needs
- Why are stainless steel autoclaves essential for LDH synthesis? Optimize 2D Nanomaterial Crystallinity
- What function does a PTFE-lined autoclave serve for ZnS nanopowder? Achieve Pure, High-Performance Synthesis
- What temperature should incubator be for sterilization? The Critical Mistake You Must Avoid



















