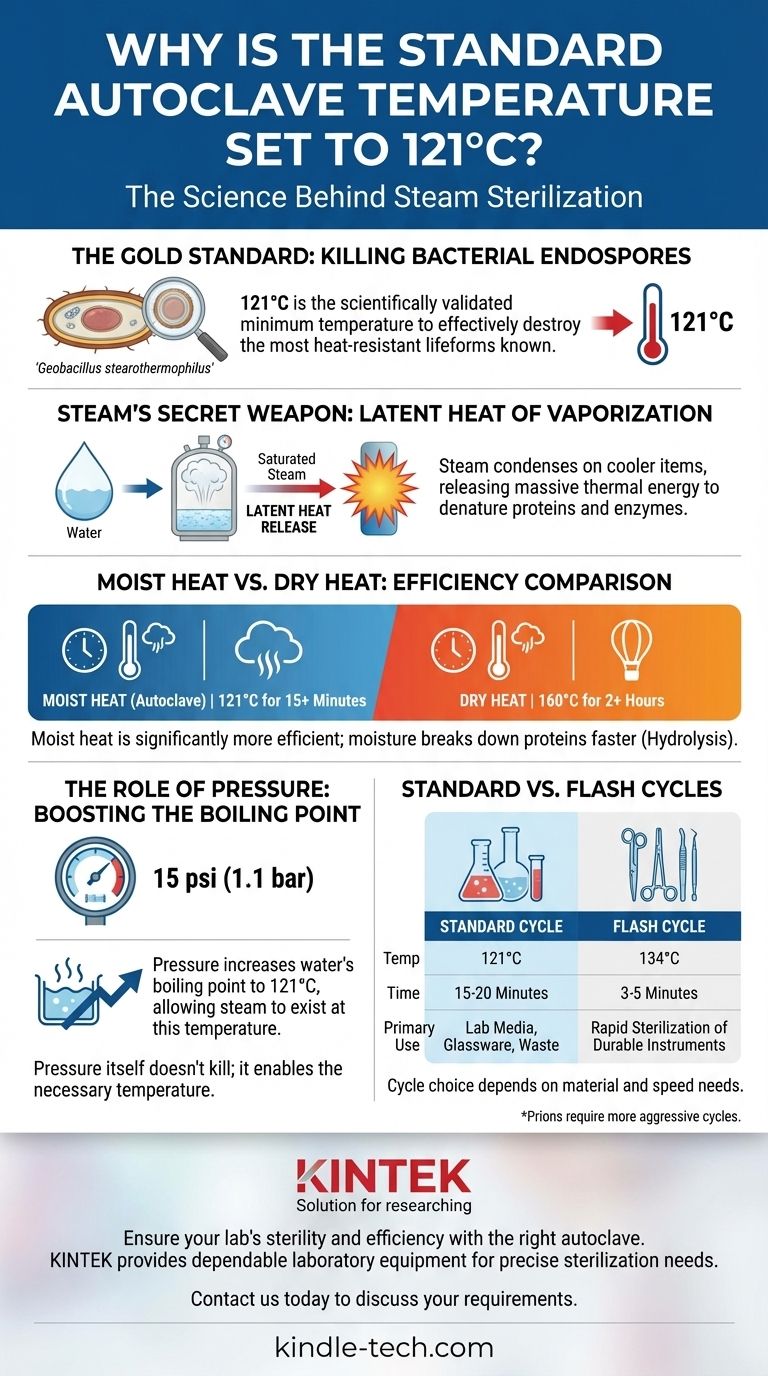
The standard autoclave temperature is 121°C because this is the precise temperature required to effectively kill the most heat-resistant lifeforms known: bacterial endospores. This temperature is achieved by using pressurized steam, which is a far more efficient method of heat transfer for sterilization than dry heat alone.
The selection of 121°C isn't arbitrary; it is the scientifically validated minimum temperature that, when combined with the immense energy of saturated steam, ensures the complete destruction of highly resistant bacterial spores within a practical timeframe.

The Science Behind Steam Sterilization
To understand why 121°C is the benchmark, we must look beyond the temperature itself and examine the core principles of how an autoclave works. The true sterilizing agent is not just heat, but saturated steam under pressure.
The True Killer: Saturated Steam and Latent Heat
Saturated steam is water vapor at the exact temperature at which it boils for its given pressure. It holds a tremendous amount of thermal energy.
When this 121°C steam makes contact with a cooler item inside the autoclave, it immediately condenses back into liquid water.
This phase change releases a massive amount of energy known as latent heat of vaporization directly onto the surface of the item. This rapid and efficient energy transfer is what fatally denatures the essential proteins and enzymes of microorganisms.
Why Moist Heat is Superior to Dry Heat
Moist heat sterilization is significantly more effective than dry heat. For comparison, achieving the same level of sterility with dry heat would require a temperature of 160°C for at least two hours.
The moisture in the steam helps break down microbial proteins more easily, a process called hydrolysis, which accelerates their destruction.
The Role of Pressure: A Means to an End
A common misconception is that the pressure inside an autoclave kills microorganisms. This is incorrect.
The sole purpose of the pressure (typically 15 psi or 1.1 bar above atmospheric pressure) is to increase the boiling point of water. At standard atmospheric pressure, water boils at 100°C.
By increasing the pressure inside the sealed chamber, the autoclave allows water to exist as steam at 121°C, unlocking its potent sterilizing properties.
The Target: Defeating the Toughest Opponent
Sterilization standards are not designed to kill common, fragile bacteria. They are established to ensure the destruction of the most resilient challenge possible.
The Benchmark: Bacterial Endospores
The gold standard for validating sterilization is the ability to kill bacterial endospores. These are dormant, highly protected structures produced by certain bacteria, such as Geobacillus stearothermophilus.
Endospores have tough outer coats and dehydrated cores, making them incredibly resistant to heat, radiation, and chemicals.
Establishing the Standard Cycle
Through extensive research, it was determined that exposing these endospores to saturated steam at 121°C for a minimum of 15 minutes provides a sufficient kill rate to ensure sterility. This forms the basis of the most common and universally recognized autoclave cycle.
Understanding the Trade-offs and Variations
While 121°C is the most common standard, it is not the only temperature used in autoclaving. The choice of cycle depends on the material being sterilized and the need for speed.
Heat-Sensitive Materials
Some materials, particularly certain types of plastics or complex biological media, can be damaged by the heat and pressure of a standard 121°C cycle.
In these cases, alternative sterilization methods like chemical sterilization or filtration may be required.
Higher Temperature, Shorter Time
In many medical and dental settings, a higher temperature of 134°C is used for a much shorter duration, often just 3 to 5 minutes. This is known as a "flash" cycle.
This approach is effective for sterilizing robust metal instruments quickly between uses but is unsuitable for liquids or materials that can be damaged by the higher temperature.
The Challenge of Prions
Prions, the infectious proteins responsible for diseases like Creutzfeldt-Jakob disease, are even more resistant to denaturation than bacterial spores.
Sterilizing instruments potentially contaminated with prions requires much more aggressive cycles, often involving both chemical soaks and extended autoclave cycles at temperatures of 134°C for an hour or more.
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
Selecting the correct autoclave cycle is critical for ensuring both sterility and the integrity of your materials.
- If your primary focus is standard sterilization of lab media, glass, or waste: The 121°C for 15 minutes cycle is the proven, reliable standard.
- If your primary focus is rapid turnaround of durable surgical instruments: A 134°C cycle for a shorter time is often the most efficient and appropriate choice.
- If your primary focus is sterilizing heat-sensitive liquids or plastics: You must verify the material's tolerance or consider non-autoclave methods entirely.
Ultimately, the 121°C standard represents a precisely engineered balance of microbial lethality, efficiency, and material compatibility.
Summary Table:
| Cycle Type | Temperature | Time | Primary Use Case |
|---|---|---|---|
| Standard Cycle | 121°C | 15-20 minutes | Sterilizing lab media, glassware, waste |
| Flash Cycle | 134°C | 3-5 minutes | Rapid sterilization of durable instruments |
Ensure your lab's sterility and efficiency with the right autoclave.
At KINTEK, we specialize in providing reliable laboratory equipment, including autoclaves, to meet your precise sterilization needs. Whether you require a standard cycle for general labware or a high-temperature flash cycle for rapid instrument turnaround, our experts can help you select the perfect solution.
Contact us today to discuss your laboratory's requirements and discover how KINTEK can support your research with high-quality, dependable equipment.
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Laboratory High Pressure Steam Sterilizer Vertical Autoclave for Lab Department
- Portable High Pressure Laboratory Autoclave Steam Sterilizer for Lab Use
- Laboratory Sterilizer Lab Autoclave Herbal Powder Sterilization Machine for Plant
- Desktop Fast Laboratory Autoclave Sterilizer 35L 50L 90L for Lab Use
- Portable Digital Display Automatic Laboratory Sterilizer Lab Autoclave for Sterilization Pressure
People Also Ask
- What are the requirements for routine process monitoring of a validated autoclave? Ensure Full Sterilization Safety
- Why is a High-Pressure Autoclave Needed for Nuclear Fuel Cladding Wear Tests? Ensure Safety in Reactor Simulations
- Why must a Teflon-lined high-pressure autoclave be used for TiO2 bamboo deposition? Ensure Purity and Safety.
- What is gravity displacement autoclave? A Guide to Simple, Reliable Sterilization
- Is autoclave the same as sterilization? Unlocking the Key Differences for Lab Safety
- Why is a high-pressure autoclave essential for HMF conversion? Achieve Efficient Lignocellulose Synthesis
- Why is a high-pressure steam sterilizer or autoclave required during the biomass pretreatment process? Optimize Yields
- What is the alternative method of sterilization for culture media if autoclaving is not suitable? Protect Heat-Sensitive Components



















