Working Principles and influencing factors of Ball Mills
Ball mills are widely used in various industries for grinding materials into fine powder. The working principles of ball mills involve feeding materials into the cylinder, introducing a fixed number of balls, adjusting the speed, and achieving the desired particle size. The impact of ball mill speed on size reduction is crucial, with low speed, high speed, and normal speed each affecting the milling process differently.
When operating a ball mill, the material to be ground is fed into the mill through the feed port. The grinding medium inside the mill rotates, causing the balls to impact and grind the material. The ground material is then discharged through the discharge port. To effectively grind materials, the ball mill must operate above its critical speed. This ensures continuous tumbling and impacting of the grinding medium on the material.
Several factors influence the grinding performance of a ball mill, including the speed of rotation, size and type of grinding medium, material properties, and the filling ratio of the mill. Ball mills are versatile machines capable of grinding various materials into a fine powder.
In high-energy milling processes, such as those used for synthesizing materials, ball mills play a crucial role. These mills offer efficient grinding solutions for a wide range of materials, from iron ore to ceramics. Various types of ball mills exist, differing in their operating principles and maximum capacity. These include planetary ball mills, mixer mills, vibration mills, and horizontal rolling ball mills.
The degree of milling in a ball mill can be influenced by factors such as the residence time of material in the mill chamber, the size and density of the grinding medium, the hardness of the grinding material, feed rate, level in the vessel, and the rotation speed of the cylinder. Different types of ball mills operate based on these varying parameters.
Ball Mill Speed Impact on Size Reduction
-
Low speed: At low speeds, the mass of balls slides or rolls over each other, resulting in minimal size reduction.
-
High speed: High speeds cause balls to be thrown to the cylinder wall by centrifugal force, leading to limited grinding.
-
Normal speed: Operating at normal speed, balls are carried almost to the top of the mill before cascading across the diameter, allowing for maximum size reduction.
Advantages of ball mills include suitability for both wet and dry grinding processes and the ability to maintain sterility due to a closed container system, making them useful in producing parenteral and ophthalmic products. Additionally, reducing particle size in ball mills is a straightforward process.
Advantages of Ball Milling
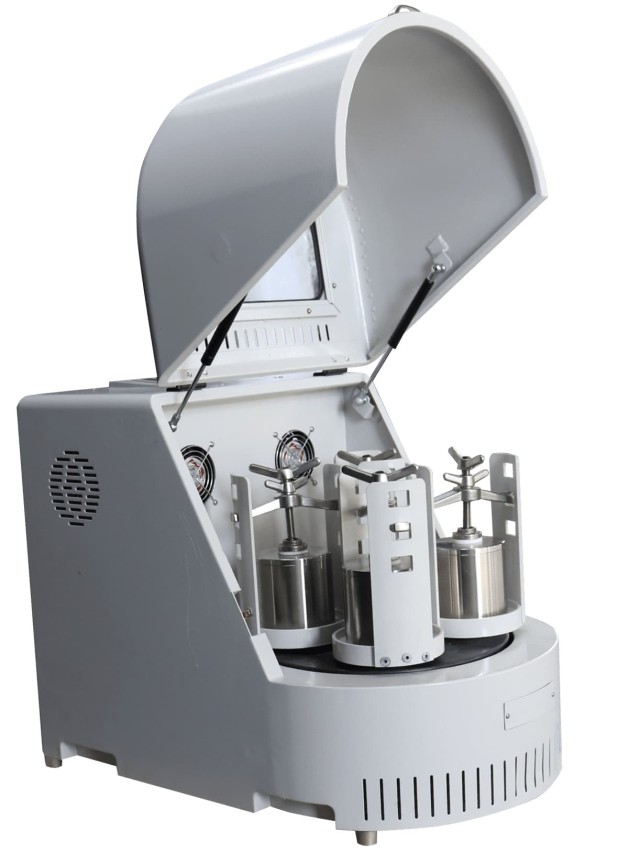

Ball milling has several advantages that make it a popular choice in the laboratory and industrial settings. Some of the key advantages include the following:
1. Universality and High Capacity
Ball mills offer universality and high capacity, making them suitable for a wide range of applications. They can efficiently grind various materials, including those with high hardness and viscosity, producing fine powders with a particle size less than or equal to 10 microns.
2. Permanence of Milling Fineness
Ball mills can maintain a prescribed milling fineness over long periods of time, with periodic addition of balls for compensation of wear. This ensures consistent and reliable performance in achieving the desired fineness of the milled materials.
3. Reliability, Safety, and Simplicity of Servicing
The structure of ball mills is simple, and they are easy to use and maintain. With proper attention to material addition and regular equipment maintenance, ball mills can operate reliably and safely. Additionally, they offer the simplicity of servicing, contributing to their widespread utility.
4. Ability to Mill Abrasive Materials
The ability of ball mills to mill abrasive materials further expands their utility in handling challenging materials, contributing to their versatility and practicality.
The distinct advantages of ball milling make it an invaluable tool for a variety of applications, providing high grinding efficiency, simple maintenance, high precision, and a wide range of applications. These features position ball milling as a versatile and reliable technique in materials processing and research.
Applications of Ball Mills
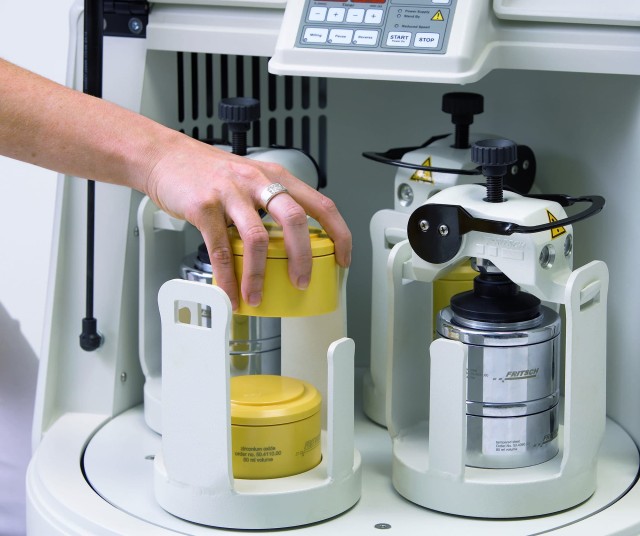

Ball mills have diverse applications in various industries for grinding materials such as mining ores, coal, pigments, and feldspar for pottery. They are used for both wet and dry grinding processes and have scientific applications for reducing particle size, eliminating agglomeration, and changing the shape of particles. The following key scientific and industrial applications highlight the versatility of ball mills:
Mechanical Alloying
Ball mills are widely utilized for mechanical alloying, a process that involves blending various materials to create new alloys. This application is crucial in the development of advanced materials with enhanced properties and functionalities.
Mixing and Blending
In laboratories and industrial settings, ball mills are employed to effectively mix and blend a wide range of materials to achieve homogeneity and desired properties. These materials include chemicals, ceramics, minerals, and more.
Production of Powders
The production of powders using ball mills is a common practice in industries requiring finely powdered materials. This process is essential in the manufacturing of products such as pigments, ceramics, and various types of coatings.
Changing Material Properties
Ball mills play a vital role in altering the properties of materials through processes such as grinding, blending, and refining. The ability to modify material properties makes them indispensable in industries requiring tailored material characteristics.
Nanomaterial Preparation
Ball mills are extensively utilized for the preparation of nanomaterials, allowing for the production of nanoparticles ranging from 1 nanometer to 100 nanometers. These nanomaterials possess unique physical and chemical properties, making them valuable in electronics, medicine, and environmental protection applications.
Preparation of Magnetic Materials
The preparation of magnetic materials is another significant application of ball mills. These mills enable the efficient and cost-effective production of magnetic particles and magnetic nanomaterials, which find use in various technological and industrial applications.
Biomedical Field
In the biomedical field, ball mills are employed to prepare specialized biomaterials used in applications such as bone grafts, artificial joints, and repair materials. The control over particle size and surface morphology achieved through ball milling contributes to the development of biomaterials with tailored biological properties.
Electronic Materials Preparation
Ball mills play a critical role in the preparation of electronic materials, enabling the production of materials with specific electrical and mechanical properties. For instance, they are used to prepare conductive adhesives with controlled resistance characteristics to meet diverse application requirements.
The applications of ball mills extend beyond traditional grinding processes, encompassing a wide range of scientific and industrial endeavors. These diverse applications underscore the significance of ball mills in materials research, development, and manufacturing processes.
Related Products
- Laboratory Ball Mill Jar Mill with Metal Alloy Grinding Jar and Balls
- High Energy Vibratory Laboratory Ball Mill Grinding Mill Single Tank Type
- High Energy Vibratory Ball Mill for Lab Use
- High Energy Vibratory Laboratory Ball Mill Double Tank Type
- High Energy Planetary Ball Mill Milling Machine for Laboratory
Related Articles
- Disc / Cup Vibratory Mill: A Comprehensive Guide for Laboratory Experts
- Features of Different Laboratory Mills: An Overview
- Understanding the Tablet Press Machine R&D Lab Model and its Features(2)
- PTFE Shovel: A Comprehensive Guide to Its Uses, Advantages, and Applications
- Additive Manufacturing for Isostatic Pressing: Bridging New Technology with Traditional Manufacturing








