Yes, you can rotovap ethanol. Rotary evaporation (rotovap) is a common technique used to remove solvents like ethanol from a solution under reduced pressure and controlled temperature. The process is efficient, preserves the integrity of the solution, and avoids oxidation. Below is a detailed explanation of how and why ethanol can be effectively rotovapped, along with key considerations for the process.
Key Points Explained:
-
Compatibility of Ethanol with Rotary Evaporation
- Ethanol is a volatile solvent with a relatively low boiling point (78.37°C at atmospheric pressure). Rotary evaporation is particularly effective for solvents like ethanol because the process reduces the boiling point by lowering the pressure, allowing for gentle and efficient evaporation.
- The process avoids overheating, which is critical for preserving heat-sensitive compounds in the solution.
-
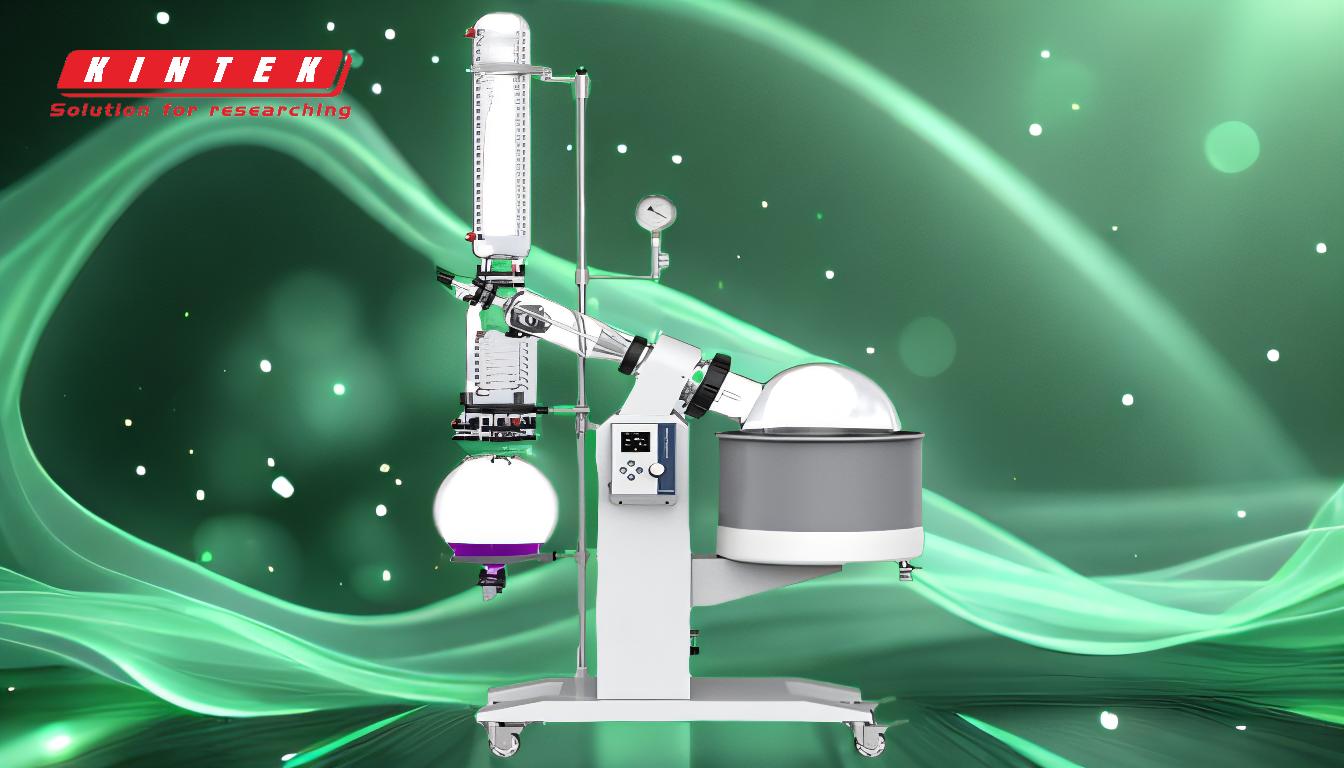
Steps to Rotovap Ethanol
-
Set Up the Rotary Evaporator:
- Fill the water bath to the appropriate level and set the temperature slightly below ethanol’s boiling point (e.g., 40-50°C). This ensures gentle heating and prevents violent boiling.
- Attach the round-bottom flask containing the ethanol solution to the rotovap. Ensure all connections are secure to maintain a proper vacuum.
-
Create a Vacuum:
- Activate the vacuum pump to reduce the pressure in the system. Lowering the pressure significantly reduces ethanol’s boiling point, allowing it to evaporate at a lower temperature.
-
Rotate the Flask:
- Start rotating the flask slowly to increase the surface area of the solution. This promotes faster and more uniform evaporation.
-
Condense the Ethanol Vapor:
- The evaporated ethanol travels to the condenser, where it is chilled (using a coolant like water or glycol) and condensed back into liquid form. The condensed ethanol is collected in a receiving flask.
-
Monitor and Adjust:
- Adjust the vacuum pressure and heating bath temperature as needed to maintain a steady evaporation rate without causing bumping or foaming.
-
Complete the Process:
- Once the desired amount of ethanol has been collected, stop the rotation, turn off the heating bath, and release the vacuum before disassembling the setup.
-
Set Up the Rotary Evaporator:
-
Advantages of Rotovapping Ethanol
- Efficiency: Rotary evaporation is faster than traditional evaporation methods due to the increased surface area and reduced boiling point.
- Gentle Process: The controlled temperature and vacuum prevent overheating, making it suitable for heat-sensitive compounds.
- Solvent Recovery: Ethanol can be collected and reused, reducing waste and costs.
- Oxidation Prevention: The closed system minimizes exposure to air, preserving the solution’s integrity.
-
Key Considerations
- Safety: Ethanol is flammable, so ensure proper ventilation and avoid open flames or sparks.
- Vacuum Strength: Use a vacuum pump capable of achieving the necessary pressure reduction for efficient evaporation.
- Temperature Control: Avoid excessive heat, as it can cause bumping or degradation of heat-sensitive materials.
- Condenser Efficiency: Ensure the condenser is adequately cooled to prevent ethanol vapor from escaping into the vacuum pump.
-
Applications of Rotovapping Ethanol
- Laboratory Research: Removing ethanol from reaction mixtures or extracts.
- Pharmaceuticals: Concentrating or purifying ethanol-based solutions.
- Food and Beverage: Extracting or concentrating flavors and essences.
- Cannabis Industry: Separating ethanol from cannabis extracts for product refinement.
By following these steps and considerations, ethanol can be effectively and safely removed using a rotary evaporator. The process is widely used in various industries due to its efficiency, precision, and ability to preserve the quality of the solution.
Summary Table:
| Key Aspect | Details |
|---|---|
| Ethanol Compatibility | Low boiling point (78.37°C) makes it ideal for rotary evaporation. |
| Steps | Set up, create vacuum, rotate flask, condense vapor, monitor, and complete. |
| Advantages | Efficiency, gentle process, solvent recovery, oxidation prevention. |
| Key Considerations | Safety, vacuum strength, temperature control, condenser efficiency. |
| Applications | Lab research, pharmaceuticals, food & beverage, cannabis industry. |
Need help with rotary evaporation? Contact our experts today for personalized guidance!











