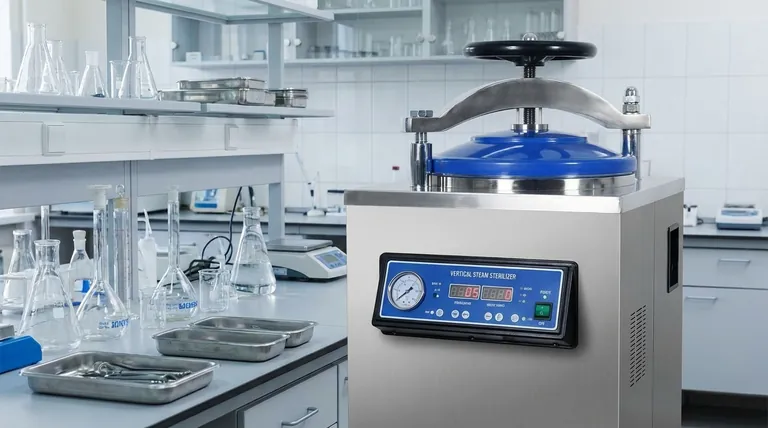
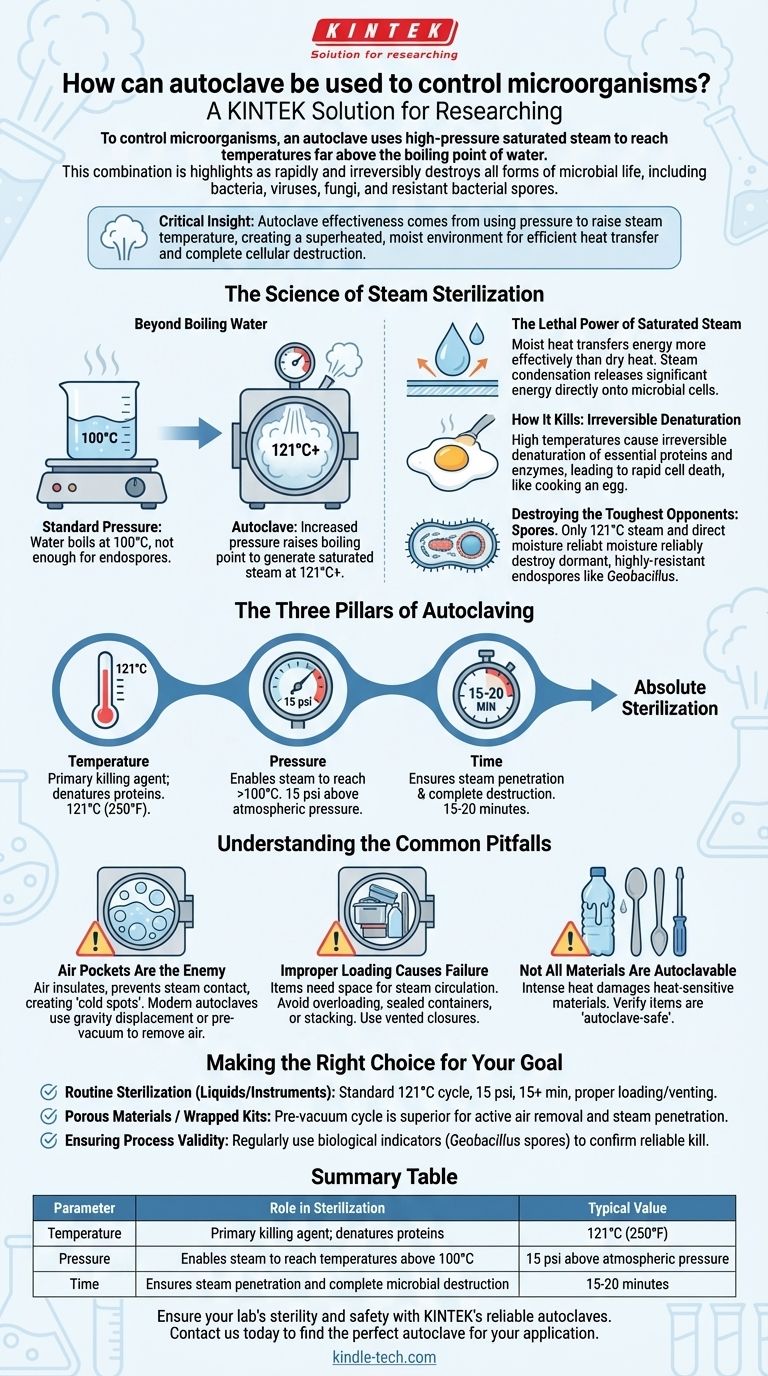
To control microorganisms, an autoclave uses high-pressure saturated steam to reach temperatures far above the boiling point of water. This combination of intense heat and moisture rapidly and irreversibly destroys all forms of microbial life, including bacteria, viruses, fungi, and even highly resistant bacterial spores, making it the gold standard for sterilization.
The critical insight is that an autoclave's effectiveness comes not from pressure itself, but from using pressure to raise the temperature of steam. This superheated, moist environment transfers heat far more efficiently than dry air, ensuring the complete destruction of essential cellular components in all microorganisms.

The Science of Steam Sterilization
To understand the power of an autoclave, we must first understand the limitations of simple boiling. The core principle lies in the physics of water and the biology of microorganisms.
Beyond Boiling Water
At standard atmospheric pressure, water boils at 100°C (212°F). While this temperature can kill many active bacteria, it is not sufficient to eliminate highly resistant bacterial endospores.
An autoclave is a sealed chamber that increases the pressure, which in turn raises the boiling point of water. This allows it to generate saturated steam at much higher temperatures, typically 121°C (250°F) or higher.
The Lethal Power of Saturated Steam
The key to an autoclave's success is saturated steam, not just hot air. Moist heat is significantly more effective at transferring thermal energy than dry heat.
When this high-temperature steam makes contact with cooler items in the chamber, it condenses into water, releasing a large amount of energy directly onto the microbial cells. This process is much faster and more penetrating than heating with dry air alone.
How It Kills: Irreversible Denaturation
The high temperatures achieved inside an autoclave cause the denaturation of essential proteins and enzymes within microbial cells.
Think of it like cooking an egg: the liquid egg white (protein) turns solid and opaque. This change is irreversible. In the same way, the autoclave's heat permanently damages the structural proteins and enzymes that microbes need to live and reproduce, leading to rapid cell death.
Destroying the Toughest Opponents: Spores
Certain bacteria, such as Geobacillus and Clostridium species, can form dormant, highly-resistant structures called endospores. These spores can survive boiling, radiation, and many chemical disinfectants.
The combination of 121°C steam and direct moisture contact is one of the few methods that reliably destroys these endospores, ensuring a true state of sterility where no viable organisms remain.
The Three Pillars of Autoclaving
Successful sterilization depends on a precise balance of three critical parameters: temperature, pressure, and time.
Temperature
This is the primary killing agent. The most common standard for general sterilization is 121°C (250°F). For specific applications, such as destroying prions, temperatures may be raised to 134°C (273°F).
Pressure
Pressure is the enabling factor. It does not kill microbes directly but allows water to exist as steam at temperatures above 100°C. A pressure of approximately 15 psi (pounds per square inch) above atmospheric pressure is required to achieve 121°C.
Time
The load must be exposed to the target temperature for a sufficient duration to ensure the steam penetrates all items and kills all microorganisms. A standard cycle for laboratory media or medical instruments at 121°C is typically 15 to 20 minutes, though this can vary based on the size and density of the load.
Understanding the Common Pitfalls
While highly effective, autoclaving is a precise process. Failure to follow correct procedures can lead to incomplete sterilization.
Air Pockets Are the Enemy
Air trapped within the autoclave chamber or inside packaging acts as an insulator, preventing steam from reaching surfaces. This creates "cold spots" where microorganisms can survive. Modern autoclaves use gravity displacement or pre-vacuum cycles to actively remove air before sterilization begins.
Improper Loading Causes Failure
Items must be loaded to allow for free circulation of steam. Overloading the chamber, using tightly sealed containers, or stacking flat trays prevents steam penetration. Always leave space between items and use vented closures for any bottles.
Not All Materials Are Autoclavable
The intense heat and pressure will damage or destroy heat-sensitive materials. Many plastics will melt, sharp instruments can become dulled, and certain chemicals may degrade or become hazardous. Always verify that an item is rated as "autoclave-safe."
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
Applying these principles correctly ensures the complete elimination of microorganisms for your specific application.
- If your primary focus is routine sterilization of liquids or durable instruments: Use a standard cycle of 121°C at 15 psi for at least 15 minutes, ensuring proper loading and venting.
- If your primary focus is sterilizing porous materials or wrapped kits: A pre-vacuum autoclave cycle is superior, as it actively removes air to guarantee complete steam penetration.
- If your primary focus is ensuring process validity: Regularly use biological indicators (vials containing tough Geobacillus spores) to confirm your autoclave is achieving a reliable kill every time.
By mastering the interplay of steam, pressure, and time, you can confidently achieve absolute sterilization and safeguard the integrity of your work.
Summary Table:
| Parameter | Role in Sterilization | Typical Value |
|---|---|---|
| Temperature | Primary killing agent; denatures proteins | 121°C (250°F) |
| Pressure | Enables steam to reach temperatures above 100°C | 15 psi above atmospheric pressure |
| Time | Ensures steam penetration and complete microbial destruction | 15-20 minutes |
Ensure your lab's sterility and safety with KINTEK's reliable autoclaves. Our equipment is designed to deliver precise temperature and pressure control, eliminating all microorganisms—even the toughest bacterial spores. Whether you're sterilizing lab instruments, media, or porous materials, KINTEK provides solutions tailored to your laboratory needs. Contact us today to find the perfect autoclave for your application and achieve uncompromising sterilization results.
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Laboratory High Pressure Steam Sterilizer Vertical Autoclave for Lab Department
- Desktop Fast Laboratory Autoclave Sterilizer 35L 50L 90L for Lab Use
- Laboratory Sterilizer Lab Autoclave Herbal Powder Sterilization Machine for Plant
- Portable Digital Display Automatic Laboratory Sterilizer Lab Autoclave for Sterilization Pressure
- Portable High Pressure Laboratory Autoclave Steam Sterilizer for Lab Use
People Also Ask
- What is the function of an Autoclave in paper pretreatment? Boost Saccharification Yield with Precision Heating
- Why is a 24-hour hydrothermal treatment in an autoclave necessary for BMO nanosheets? Unlock Superior Photocatalysis
- What is a "standard load" in the context of autoclave load validation? Define Your Sterilization Ceiling
- What should be autoclaved in a lab? A Guide to Safe and Effective Sterilization
- What environment does a PTFE-lined autoclave provide for TiO2-GQD synthesis? Achieve Superior Nanocomposite Results
- What is the function of high-pressure autoclaves in LH synthesis of zeolite membranes? Key Roles & Benefits
- How does the autoclave sterilize materials? Unlock the Power of Pressurized Steam for Absolute Sterility
- How does a high-pressure autoclave assist in acid etching TiO2 nanobelts? Enhance Surface Area and Reactivity



















