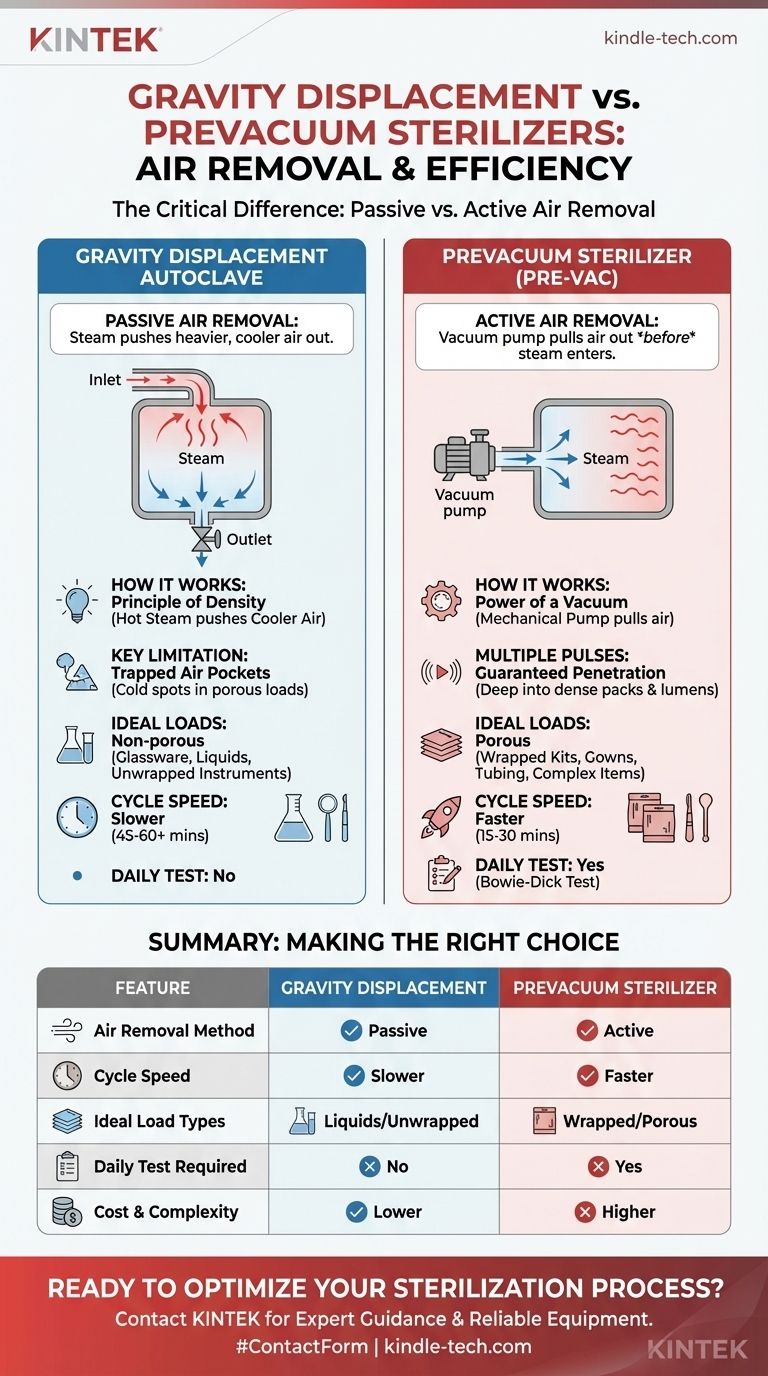
At their core, all steam autoclaves perform the same function: they use high-temperature, high-pressure steam to sterilize items. The critical difference between a gravity displacement autoclave and a prevacuum sterilizer lies entirely in how they remove ambient air from the chamber, a crucial step that directly impacts their speed, efficiency, and the types of materials they can reliably sterilize.
The fundamental distinction is passive versus active air removal. Gravity sterilizers passively use incoming steam to push heavier, cooler air out. Prevacuum sterilizers actively use a vacuum pump to pull air out before steam is ever introduced, resulting in faster and more thorough steam penetration.

The Gravity Displacement Method: A Simple, Passive Approach
The gravity displacement autoclave is the original and mechanically simplest form of steam sterilizer. Its operation is based on the basic principle of density.
How It Works: The Principle of Density
Hot steam is less dense than cooler, ambient air. As steam is piped into the sterilization chamber, it fills the upper areas first. This incoming steam pushes the heavier, cooler air downwards.
The Critical Role of the Drain
A temperature-sensitive valve on a drain port at the bottom of the chamber remains open as long as cooler air is present. The displaced air exits through this drain. Once the chamber is filled with steam and reaches the target temperature, the valve closes, and the pressurization and sterilization phase begins.
Key Limitation: Trapped Air Pockets
This passive method is effective for simple, non-porous items like lab glassware or unwrapped metal instruments. However, it struggles with complex loads. Air can easily become trapped inside tubing, wrapped instrument packs, or porous materials like textiles and gowns, creating "cold spots" that steam cannot reach, leading to sterilization failure.
The Prevacuum (Pre-vac) Method: An Active, Engineered Solution
Prevacuum sterilizers, often called dynamic air removal systems, were engineered to overcome the limitations of the gravity method. They don't rely on density but on mechanical force.
How It Works: The Power of a Vacuum
The key component is a vacuum pump. Before the steam cycle begins, the pump actively removes a very high percentage of the air from the sealed chamber. This creates a near-vacuum environment.
Multiple Pulses for Guaranteed Penetration
Most modern prevacuum systems use a series of alternating vacuum and steam-injection pulses. This process forcibly removes air from the most challenging places—deep within dense textile packs or the long, narrow lumens of surgical instruments—and ensures that when the final steam charge is introduced, it can instantly penetrate the entire load.
Faster, More Efficient Cycles
By actively removing air before sterilization, the entire process is significantly accelerated. Steam penetrates the load almost instantaneously without the slow process of displacing air, dramatically reducing overall cycle times.
Understanding the Trade-offs
Choosing between these two technologies is a matter of balancing speed, load type, and cost. There is no single "best" option, only the right tool for a specific application.
Speed and Throughput
A prevacuum autoclave is significantly faster. A wrapped instrument cycle might take 15-30 minutes in a prevacuum unit, compared to 45-60 minutes or more in a gravity unit. This makes prevacuum systems ideal for high-volume environments like surgical centers.
Load Versatility
This is the most critical difference. Prevacuum sterilizers are essential for porous loads (gowns, drapes, dressings), items with lumens (tubing, cannulas), and complex, wrapped instrument kits. Gravity autoclaves should be limited to non-porous items like media, liquids, and simple, unwrapped instruments.
Cost and Complexity
Gravity autoclaves have a simpler design, making them less expensive to purchase and maintain. Prevacuum systems include a vacuum pump and more complex controls, which increases their initial cost and potential for maintenance.
Required Quality Assurance
Prevacuum sterilizers require a daily Bowie-Dick test. This specific test validates the efficacy of the air removal system, ensuring the vacuum pump is functioning correctly and no air leaks are present. This is a critical quality control step for clinical and healthcare settings.
Making the Right Choice for Your Application
Your sterilization needs should dictate your equipment choice.
- If your primary focus is sterilizing lab media, glassware, or unwrapped solid instruments: A gravity displacement autoclave is a reliable and cost-effective solution.
- If your primary focus is sterilizing wrapped instrument kits, surgical textiles, or items with hollow channels: A prevacuum sterilizer is the necessary choice to ensure effective and rapid steam penetration.
- If your primary focus is high-throughput sterile processing in a clinical setting: The speed, efficiency, and validated air removal of a prevacuum sterilizer are indispensable.
Understanding that effective sterilization depends on total steam contact is the key to selecting the right process for your specific needs.
Summary Table:
| Feature | Gravity Displacement Autoclave | Prevacuum Sterilizer |
|---|---|---|
| Air Removal Method | Passive (steam pushes air out) | Active (vacuum pump pulls air out) |
| Cycle Speed | Slower (45-60+ minutes) | Faster (15-30 minutes) |
| Ideal Load Types | Liquids, unwrapped instruments, glassware | Wrapped kits, porous materials (gowns), items with lumens |
| Daily Test Required | No | Yes (Bowie-Dick Test) |
| Cost & Complexity | Lower | Higher |
Ready to Optimize Your Sterilization Process?
Choosing the right autoclave is critical for ensuring sterility and maximizing lab efficiency. Whether you need the simplicity of a gravity displacement model for liquids and glassware or the advanced capabilities of a prevacuum sterilizer for complex surgical packs, KINTEK has the solution.
As your trusted lab equipment partner, we provide:
- Expert Guidance: We'll help you select the perfect autoclave for your specific materials and throughput needs.
- Reliable Equipment: From basic gravity units to high-performance prevacuum sterilizers, we offer durable, dependable solutions.
- Ongoing Support: We ensure your equipment operates at peak performance with comprehensive service and consumables.
Don't leave sterilization to chance. Contact our experts today to find the ideal autoclave for your laboratory!
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Portable High Pressure Laboratory Autoclave Steam Sterilizer for Lab Use
- Portable Digital Display Automatic Laboratory Sterilizer Lab Autoclave for Sterilization Pressure
- Laboratory Horizontal Autoclave Steam Sterilizer Lab Microcomputer Sterilizer
- Laboratory High Pressure Steam Sterilizer Vertical Autoclave for Lab Department
- Desktop Fast Laboratory Autoclave Sterilizer 20L 24L for Lab Use
People Also Ask
- Should glassware be autoclaved? A Guide to Safe and Effective Sterilization
- What is the time required for autoclaving at 121 C? A Guide to Sterilization Cycles
- What role does an autoclave play in the synthesis of MnO2 nanofibers? Mastering Hydrothermal Growth
- What role does a PTFE-lined stainless steel autoclave play in the synthesis of BiOBr precursor nanosheets?
- What is the principle of autoclave in microbiology? The Key to Complete Sterilization
- Why is a PTFE-lined stainless steel autoclave required for Ag@N-TiO2? Ensure Purity and Performance in Synthesis
- How often should a dental autoclave be cleaned? A Daily, Weekly, and Monthly Guide
- What is the role of a high-pressure autoclave in hydrothermal synthesis? Unlock Precision Metal Oxide Nanomaterials



















